Archaeologists excavated a 2000-year-old fast food and drink counter “termopolium” on the streets of the ancient Roman city of Pompeii last year, which will be open to the public this summer.
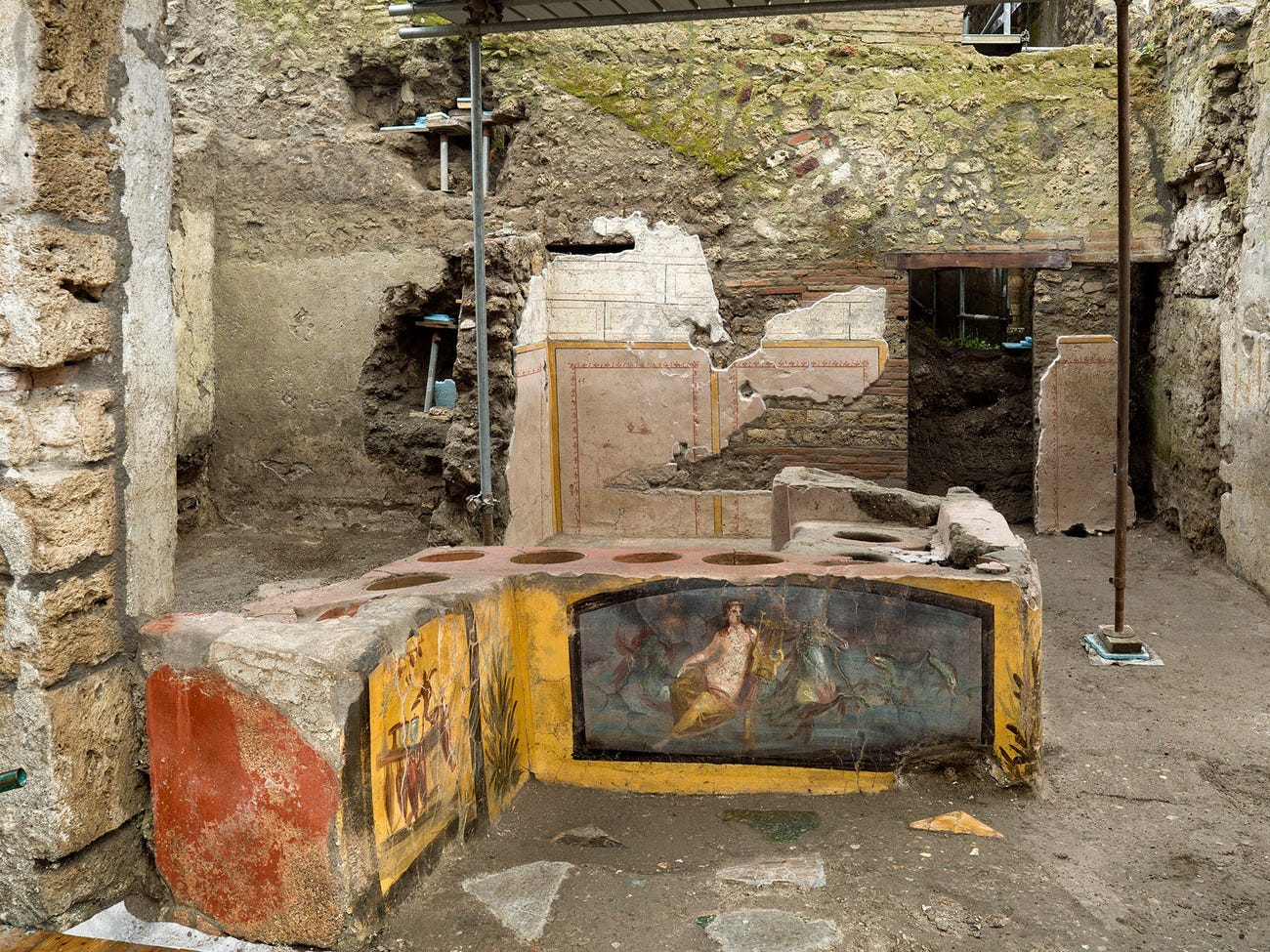
The thermopolium – from the Greek “thermos” meaning hot and “poleo” for sale – was the Roman era version of a fast-food snack stand, located at a bustling junction of Silver Wedding Street and Alley of Balconies.
In earthenware pots, the researchers discovered duck bone pieces as well as the bones of pigs, goats, fish, and snails. Some of the components had been cooked together in the style of a Roman paella. Crushed fava beans, which are used to alter the flavor of wine, were discovered in the bottom of one jar.
In Roman times, the Thermopolium was highly popular. Around 80 were found in Pompeii alone. The counter, which is adorned with vividly colored frescos and deep circular slots that would have held jars, is the first of 80 food bars discovered in perfect condition.
When the volcano on neighboring Mount Vesuvius erupted in 79 AD, it buried Pompeii in a sea of boiling lava, killing between 2,000 and 15,000 people. Archaeologists continue to make discoveries there.
The massive site, which spans 44 hectares (110 acres), is all that remains of one of the Roman empire’s wealthiest towns. Many structures and items, including curled-up bodies of victims, were buried under layers of ash in an almost pristine form.
The “thermopolium,” is slated to open on August 12.
Cover Photo: An ancient counter depicting a nymph riding a horse. Luigi Spina/Parco Archeologico di Pompei via AP