Archaeologists in Western Siberia have unearthed unique Bronze Age ceramics that could belong either to the little-known Ust-Tartas culture or to a completely new archaeological culture previously unknown to science. The discovery, made in the Vengerovo district of the Novosibirsk region, may significantly expand our understanding of early human settlements in the Baraba forest-steppe — a key crossroads of ancient cultures in northern Eurasia.
The research team from the Institute of Archaeology and Ethnography of the Siberian Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences, led by Academician Vyacheslav Molodin, discovered the ceramics while excavating a large dwelling dated to the late fourth to early third millennium BCE — the early Bronze Age. According to Molodin, the site revealed “very unusual and fascinating pottery that does not resemble any known Siberian ceramic traditions.”
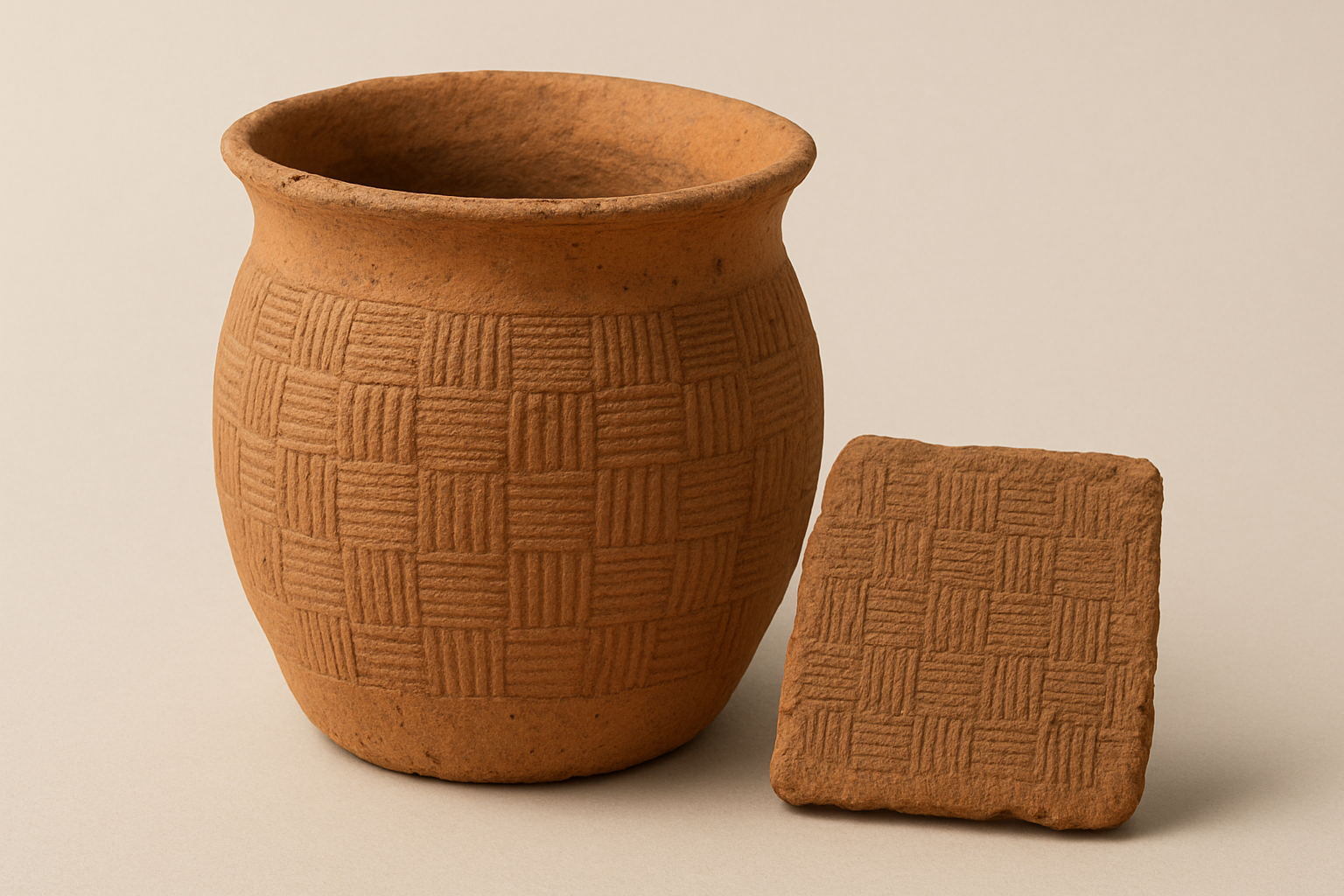
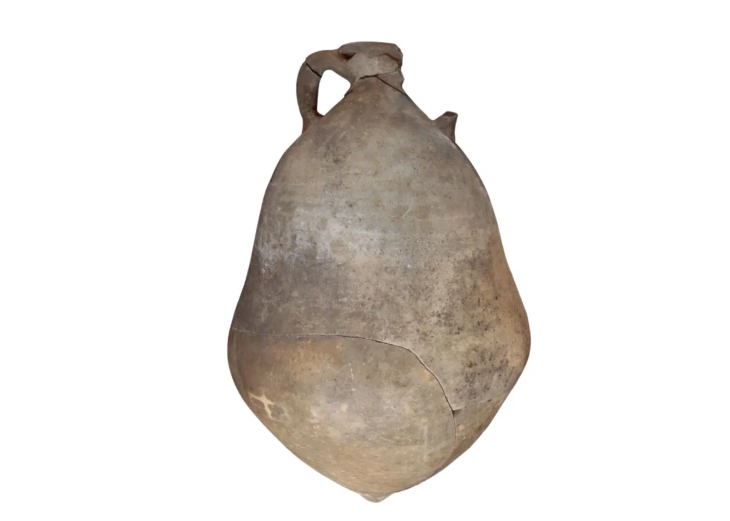
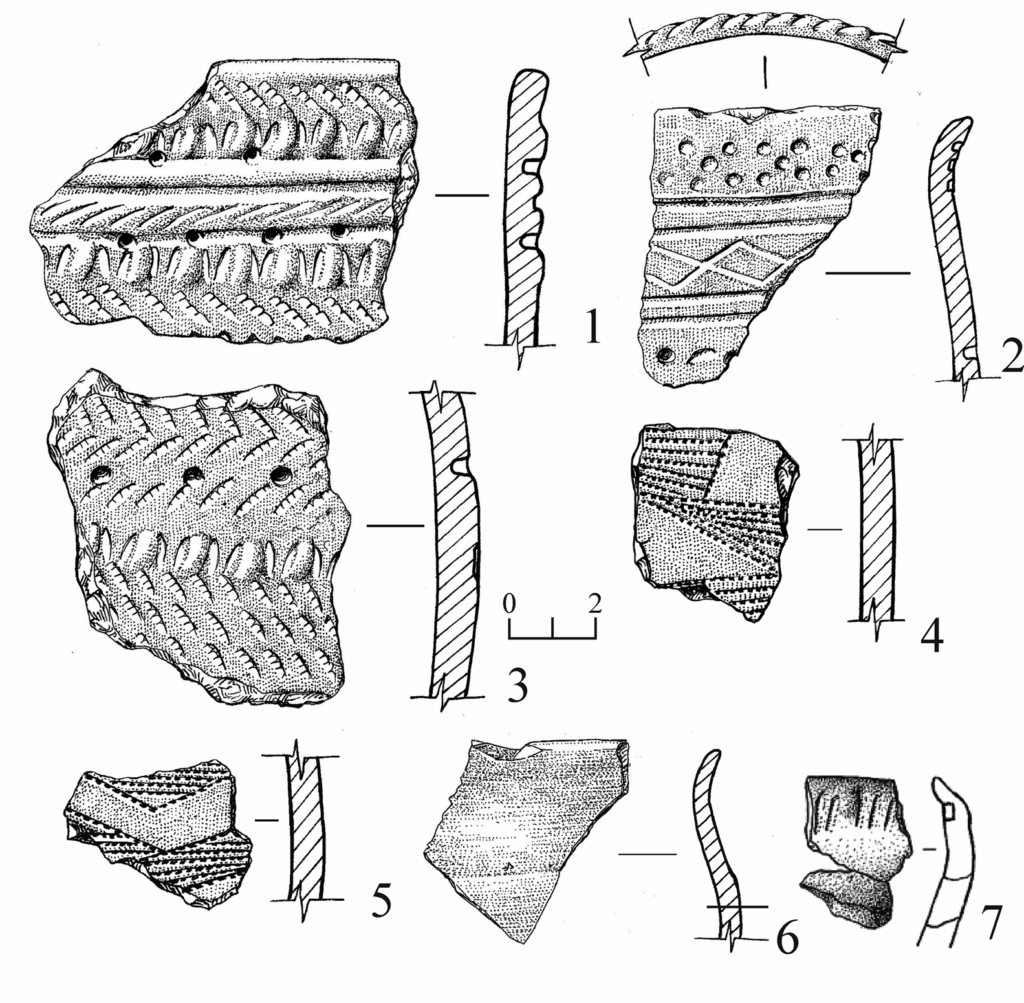
The vessels are flat-bottomed and decorated with patterns that imitate the texture of woven fabric. Archaeologists believe the decoration was made by pressing cloth against the wet clay before firing. “One of the vessels even shows a checkerboard pattern,” Molodin told the TASS news agency. “I have never seen ceramics like this before. Despite knowing the chronological age of the site, culturally it remains a mystery.”
A Mysterious Discovery in the Baraba Steppe
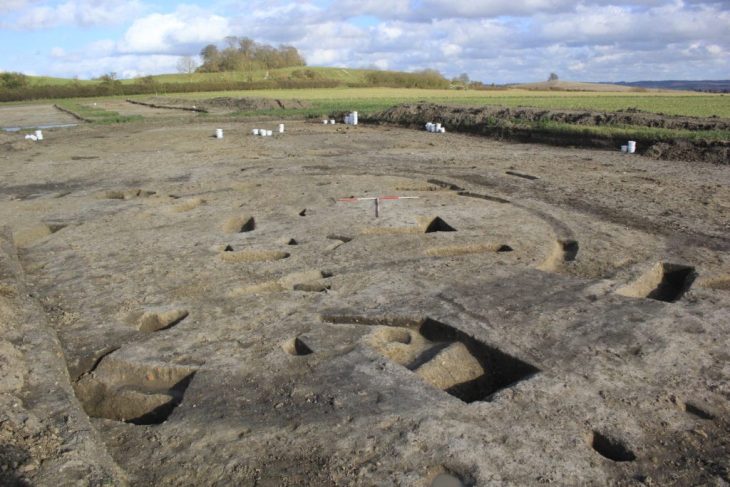
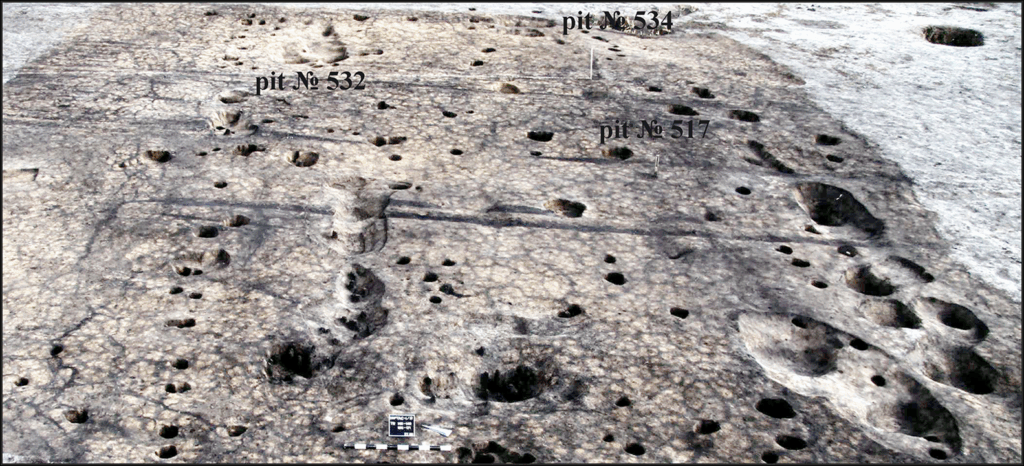
The find was made at the vast archaeological complex known as Tartas-1, one of the largest prehistoric sites in Western Siberia. The Tartas-1 complex includes both ancient settlements and a huge necropolis containing over 800 burials. It was first discovered in 2003 during a survey for a fiber-optic cable project, when geophysical data revealed a massive burial field hidden beneath the flat steppe landscape. Since then, systematic excavations have continued for more than two decades, gradually uncovering layers of human activity spanning from the Neolithic to the Iron Age.
The newly excavated dwelling is large and carefully constructed, suggesting a settled lifestyle rather than a temporary seasonal camp. Its discovery adds a new dimension to the long-term occupation of the Baraba steppe, an area that served as a cultural bridge between the ancient populations of the Ural Mountains, the Altai region, and Central Asia.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

The Enigmatic Ust-Tartas Culture
Archaeologists suspect the newly found pottery may be connected to the Ust-Tartas culture, a poorly studied archaeological culture that existed in Western Siberia between roughly the late fifth and early third millennium BCE. This culture is named after the Ust-Tartas River area, where its characteristic settlements and burials were first discovered.
Typical Ust-Tartas artifacts include simple flat-bottomed ceramic vessels decorated with comb-stamped or cord-impressed patterns, as well as stone and bone tools. The people of this culture appear to have lived in small, semi-sedentary communities, hunting, fishing, and possibly engaging in early forms of animal herding. Burials associated with the culture often contain multiple individuals in a single grave, arranged in rows, and oriented along a north-south axis — an unusual pattern that distinguishes them from neighboring groups.
However, the newly discovered ceramics differ markedly from the usual Ust-Tartas pottery. The textile-imprint technique and geometric checkerboard motifs have no direct parallels in known Siberian collections. This raises the possibility that the pottery may belong to a separate, as-yet-unidentified culture that coexisted with or evolved from the Ust-Tartas tradition.
Implications for Siberian Prehistory
If the ceramics do indeed represent a new archaeological culture, the implications could be profound. The early Bronze Age in Siberia remains one of the least understood periods in Eurasian prehistory. While steppe cultures such as Afanasievo and Okunevo are well documented farther south, the forest-steppe zone of the Baraba region still hides many unanswered questions about cultural development and interaction.
The textile-patterned vessels could provide clues about social identity, technological innovation, and trade. The use of fabric in pottery decoration may even suggest that weaving and textile production were more advanced in the region than previously believed. Combined with the evidence of a large, well-built dwelling, the finds point toward a community with stable habitation, craft specialization, and perhaps complex ritual practices.
Continuing Excavations and Future Research
Excavations at Tartas-1 will continue in the coming field seasons, supported by interdisciplinary analyses including radiocarbon dating, residue studies, and ancient DNA tests. These methods could help determine whether the newly uncovered culture had genetic or cultural ties to neighboring Bronze Age populations.
“The Baraba steppe still holds many secrets,” Molodin said. “Every year we uncover something that challenges our understanding of how early societies developed in Siberia. These new ceramics remind us that even in well-studied regions, the past can still surprise us.”
As researchers continue to sift through layers of soil and time, the story of the Baraba steppe — and of the mysterious people who once shaped clay with the imprint of woven cloth — is only beginning to emerge.
Representational image: a clay vessel featuring a textile-imprint checkerboard pattern, created with artificial intelligence to illustrate the type of pottery described by archaeologists from the Novosibirsk region.
Molodin, V. I., Selin, D. V., Mylnikova, L. N., Durakov, I. A., & Efremova, N. S. (2021). A unique cultic complex of the transitional period from the Bronze Age to Early Iron Age in Western Siberia. Antiquity, 95(379), e3. doi:10.15184/aqy.2020.243
















