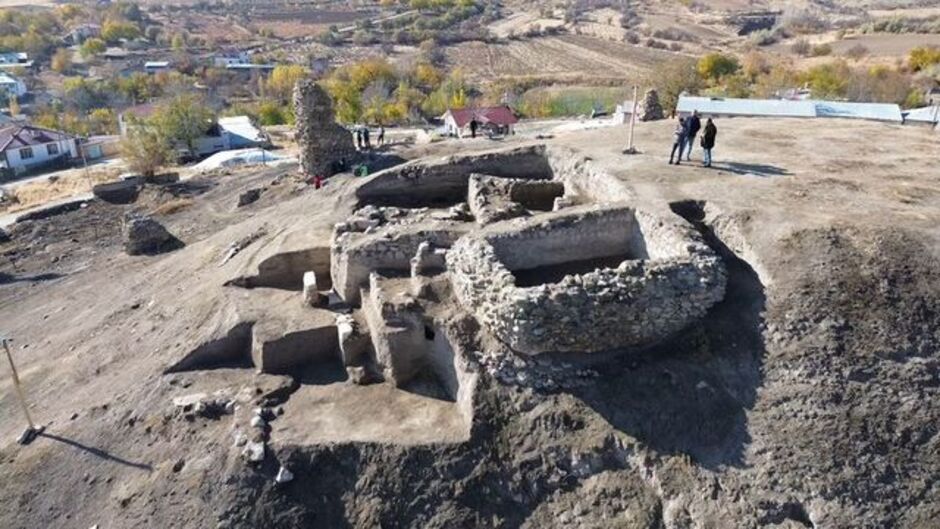
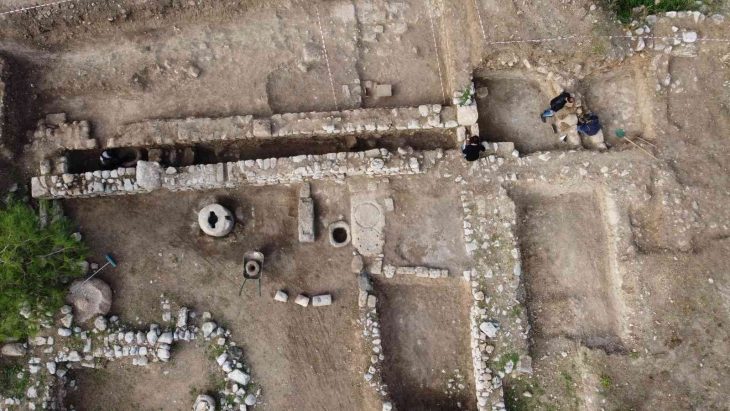
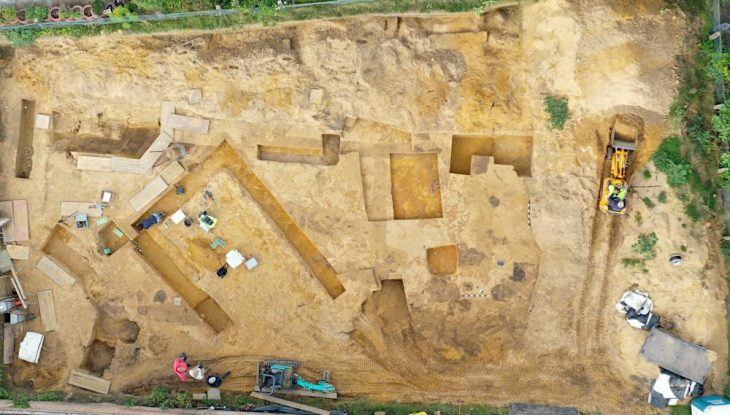
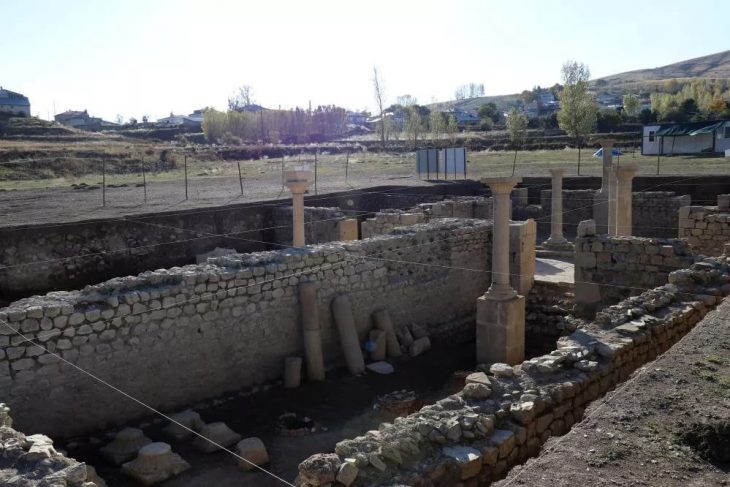
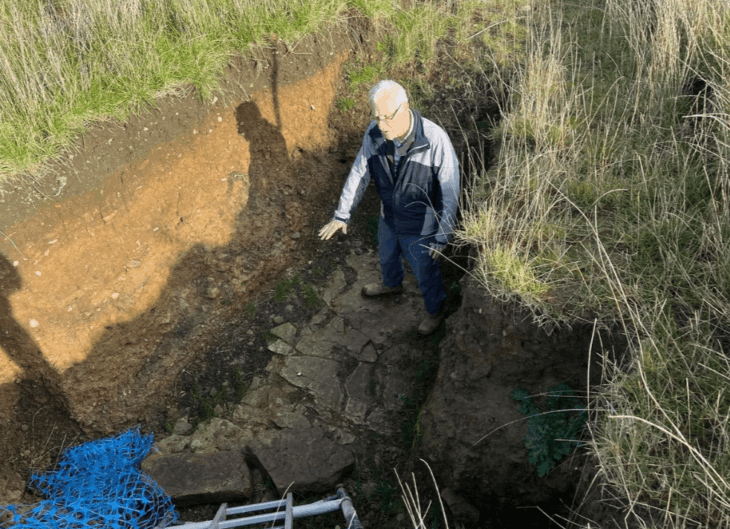
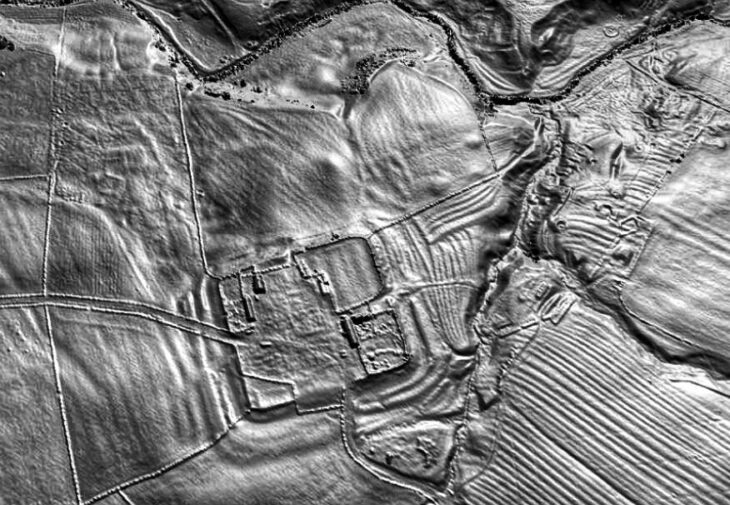
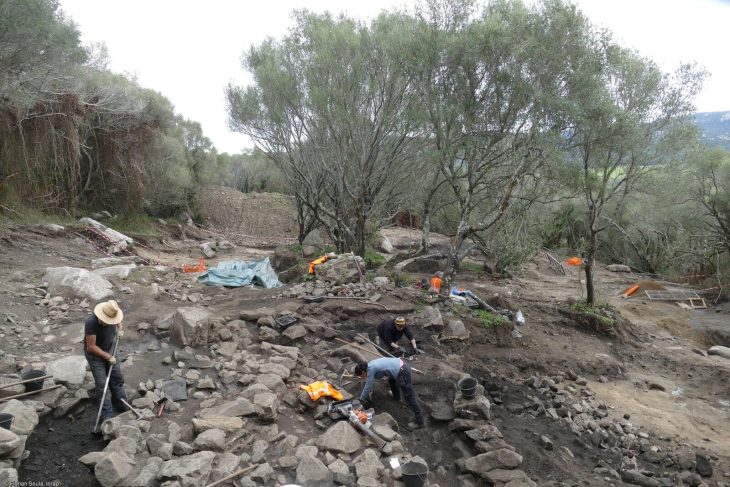
Archaeological excavations at Tadım Castle and Tadım Mound (Tadım Höyük), located within the borders of Tadım Village in Elazığ, continue to uncover significant findings that illuminate the region’s history. The excavations conducted by the Elazığ Archaeology and Ethnography Museum have revealed numerous artifacts dating back to the Late Chalcolithic and Early Bronze Ages.
The discoveries were announced by Elazığ Governor Numan Hatipoğlu through his social media account, highlighting the significance of these findings in shedding light on the region’s rich historical and cultural heritage.
Tadım Mound, located in Elazığ, Türkiye, is an important archaeological site that dates back to the Neolithic period and has been continuously inhabited for thousands of years. The mound is part of a larger cultural landscape that reflects the region’s rich history and diverse civilizations, including the Late Chalcolithic and Early Bronze Ages.
The village, known as Dadíma in the records of Georgios Kiprios from 610 and as Tadem in Armenian sources from 1628, served as the administrative center of the 4th Armenian Province of the Byzantine Empire. Located in the Elazığ Province and lying within the ancient province of Sophene, Tadım is believed to have functioned as the capital of the Roman province of Fourth Armenia.
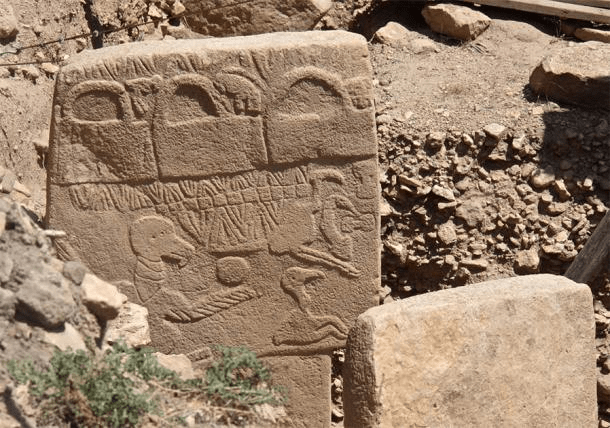
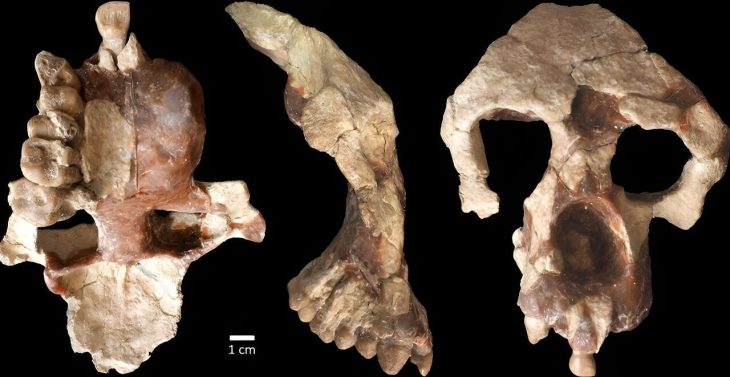
Among the discoveries are twelve Karaz pottery pieces dating to 4000-3000 BC, a painted pot adorned with mountain goat motifs from 3200 BC, and two unique sacred hearths featuring bull decorations, also dating back to 4000-3000 BC. These sacred hearths, estimated to be 6,000 years old, provide crucial insights into the region’s religious beliefs and social life. It is believed that in ancient times, when fire was considered sacred, these hearths were used in religious rituals and represented the family.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
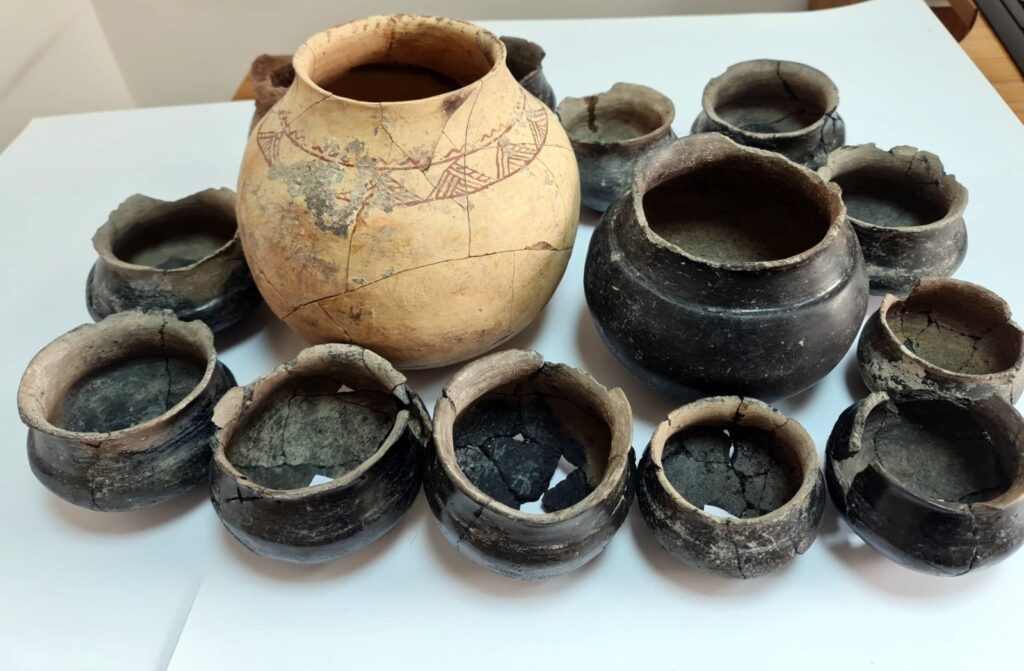

The excavation site has also revealed six different cultural layers from the Ottoman, Seljuk, Eastern Roman, Early-Late Iron Age, Late-Middle-Early Bronze Age, Late Chalcolithic, and Neolithic periods. The wall remnants and ceramic fragments uncovered in these layers indicate that the region has been continuously inhabited for thousands of years.
Protecting the 6,000-Year-Old Sacred Hearths
Thirty-one artifacts unearthed during the excavations have been sent to the Diyarbakır Restoration and Conservation Regional Laboratory Directorate for restoration and conservation processes. Among these artifacts, the two 6,000-year-old sacred hearths stand out. Once restoration is completed, these artifacts will be exhibited at the Elazığ Archaeology and Ethnography Museum for the public to appreciate.
Excavations Set to Resume
The excavation works at Tadım Castle and Mound, conducted by the Provincial Directorate of Culture and Tourism, are planned to resume in the coming days, provided that weather conditions remain within seasonal norms. Archaeologists will continue their efforts to gather more information about the region’s history and uncover new findings.
These discoveries not only provide new insights into the ancient history of Anatolia but also highlight Elazığ’s significance as an archaeological center. Furthermore, it is believed that these efforts will greatly contribute to the region’s tourism potential.
The commitment to preserving and revealing the rich cultural heritage of the province will continue.
Cover Image Credit: Elazığ Governor Numan Hatipoğlu’s social media account.