Around 60,000 years ago, modern humans left Africa and quickly spread across six continents. Researchers can trace this epic migration through the DNA of living and long-dead people, but they were missing genetic data from America, the final major stop on this human journey.
The Americas were the last continent to be inhabited by humans. An increasing body of archaeological and genomic evidence has hinted at a complex settlement process. This is especially true for South America, where unexpected ancestral signals have raised perplexing scenarios for the early migrations into different regions of the continent.
Many unanswered questions still persist, such as whether the first humans migrated south along the Pacific coast or by some other route. While there is archaeological evidence for a north-to-south migration during the initial peopling of the Americas by ancient Indigenous peoples, where these ancient humans went after they arrived has remained elusive.
Using DNA from two ancient human individuals unearthed in two different archaeological sites in northeast Brazil – Pedra do Tubarão and Alcobaça – and powerful algorithms and genomic analyses, Florida Atlantic University researchers in collaboration with Emory University have unraveled the deep demographic history of South America at the regional level with some unexpected and surprising results.
Not only do researchers provide new genetic evidence supporting existing archaeological data of the north-to-south migration toward South America, but they also have discovered migrations in the opposite direction along the Atlantic coast – for the first time. The work provides the most complete genetic evidence to date for complex ancient Central and South American migration routes.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
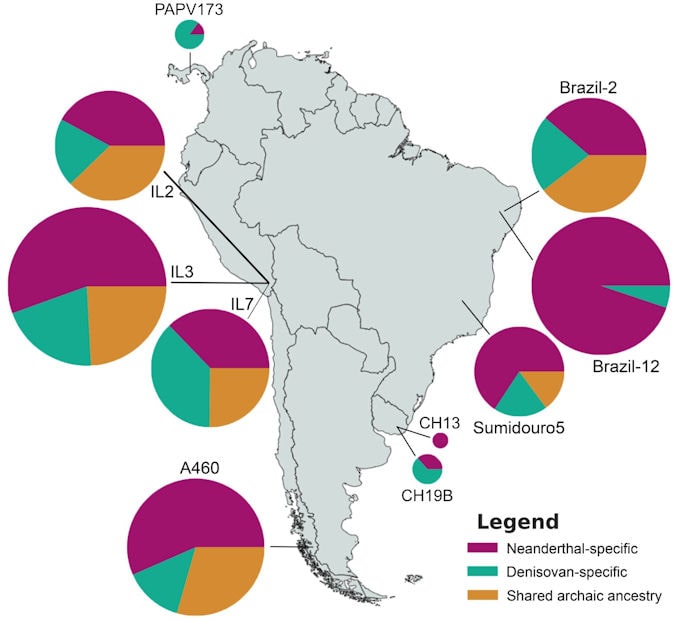
Among the key findings, researchers also have discovered evidence of Neanderthal ancestry within the genomes of ancient individuals from South America. Neanderthals are an extinct population of archaic humans that ranged across Eurasia during the Lower and Middle Paleolithic.
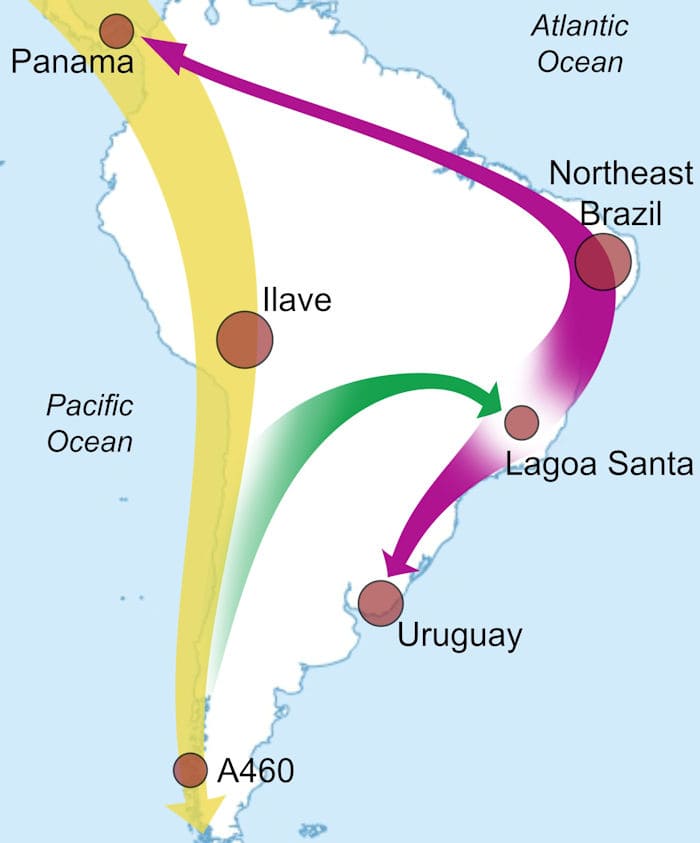
Results of the study, published in the journal Proceedings of the Royal Society B. (Biological Sciences), suggest that human movements closer to the Atlantic coast eventually linked ancient Uruguay and Panama in a south-to-north migration route – 5,277 kilometers (3,270 miles) apart. This novel migration pattern is estimated to have occurred approximately 1,000 years ago based on the ages of the ancient individuals.
Findings show a distinct relationship among ancient genomes from northeast Brazil, Lagoa Santa (southeast Brazil), Uruguay and Panama. This new model reveals that the settlement of the Atlantic coast occurred only after the peopling of most of the Pacific coast and Andes.
“Our study provides key genomic evidence for ancient migration events at the regional scale along South America’s Atlantic coast,” said Michael DeGiorgio, Ph.D., co-corresponding author who specializes in human, evolutionary, and computational genomics and is an associate professor in the Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science within FAU’s College of Engineering and Computer Science. “These regional events likely derived from migratory waves involving the initial Indigenous peoples of South America near the Pacific coast.”
Researchers also found strong Australasian (Australia and Papua New Guinea) genetic signals in an ancient genome from Panama.
“There is an entire Pacific Ocean between Australasia and the Americas, and we still don’t know how these ancestral genomic signals appeared in Central and South America without leaving traces in North America,” said Andre Luiz Campelo dos Santos, Ph.D., first author, an archaeologist and a postdoctoral fellow in FAU’s Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science.
To further add to the existing complexity, researchers also detected greater Denisovan than Neanderthal ancestry in ancient Uruguay and Panama individuals. Denisovans are a group of extinct humans first identified from DNA sequences from the tip of finger bone discovered around 2008.
“It’s phenomenal that Denisovan ancestry made it all the way to South America,” says John Lindo, Ph.D., a co-corresponding author of the article who specializes in ancient DNA analysis and is an assistant professor in the Department of Anthropology at Emory University. “The admixture must have occurred a long time before, perhaps 40,000 years ago. The fact that the Denisovan lineage persisted and its genetic signal made it into an ancient individual from Uruguay that is only 1,500 years old suggests that it was a large admixture event between a population of humans and Denisovans.”
Previously at the Federal University of Pernambuco in Recife, Brazil, dos Santos and colleagues uncovered the remains of the two ancient humans from northeast Brazil, which date back to at least 1,000 years before present, and sent them to Lindo for DNA extraction and subsequent genomic sequencing and analyses. Raw data were then sent to FAU for computational analysis of the whole genome sequences from northeast Brazil.
Researchers compared the two newly sequenced ancient whole genomes from northeast Brazil with present-day worldwide genomes and other ancient whole genomes from the Americas. As of the publication date of the article, Lindo says that only a dozen or so ancient whole genomes from South America have been sequenced and published, in contrast to hundreds from Europe.
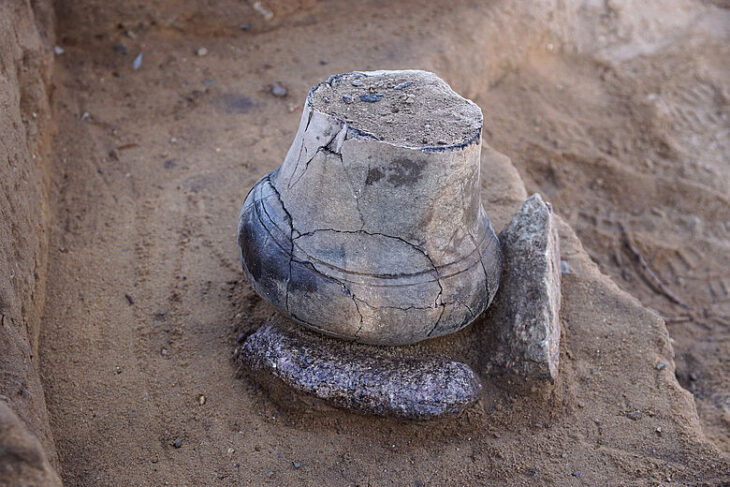
Apart from the occurrence of mass burials in the sites that yielded the samples from northeast Brazil, Uruguay, southeast Brazil and Panama, there is no other evidence in the archaeological record that indicate shared cultural features among them. Importantly, the analyzed ancient individuals from southeast Brazil are about 9,000 years older than those from northeast Brazil, Uruguay, and Panama, enough time for expected and noticeable cultural divergence. Moreover, northeast Brazil, Uruguay, and Panama, though more similar in age, are located thousands of kilometers apart from each other.
“This groundbreaking research involved many different fields from archaeology to biological sciences to genomics and data science,” said Stella Batalama, Ph.D., dean, FAU College of Engineering and Computer Science. “Our scientists at Florida Atlantic University in collaboration with Emory University have helped to shed light on an important piece of the Americas puzzle, which could not have been solved without powerful genomic and computational tools and analysis.”
This research was supported by the National Science Foundation, the National Institutes of Health, and the Fundação de Amparo à Ciência e Tecnologia de Pernambuco.
The study was published in Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences
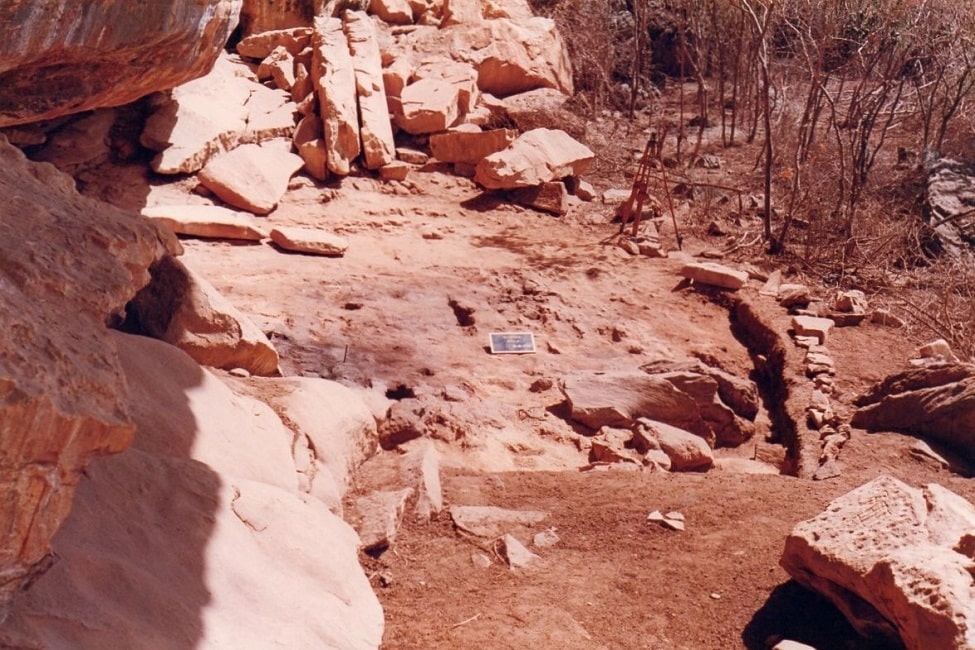
Cover Photo: The Alcobaça archaeological site, in which the skeletal remains of Brazil-12 (northeast Brazil) were unearthed. Photo: Henry Lavalle, Universidade Federal de Pernambuco and Ana Nascimento, Universidade Federal Rural de Pernambuco
















