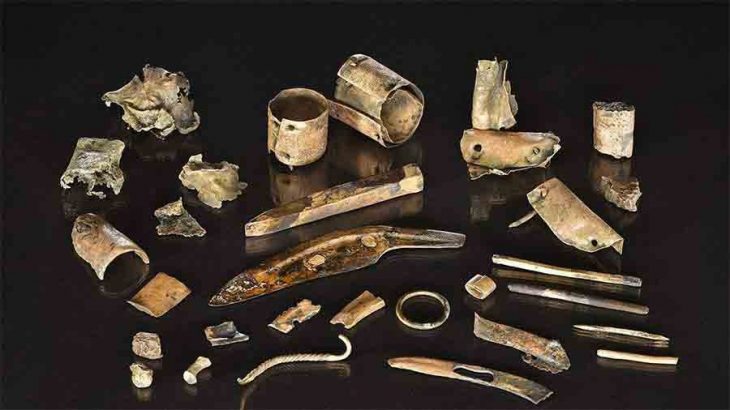
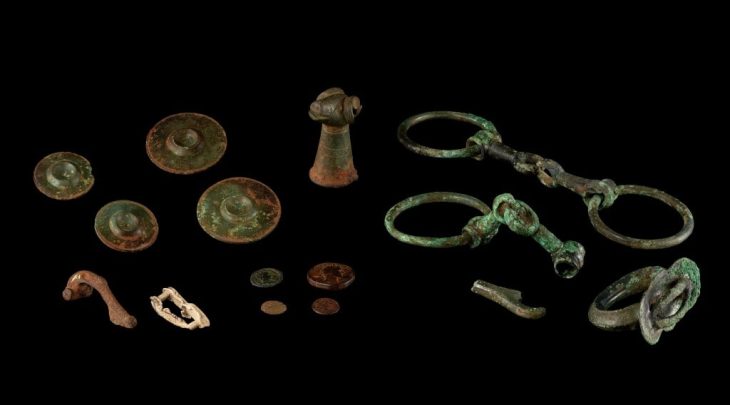
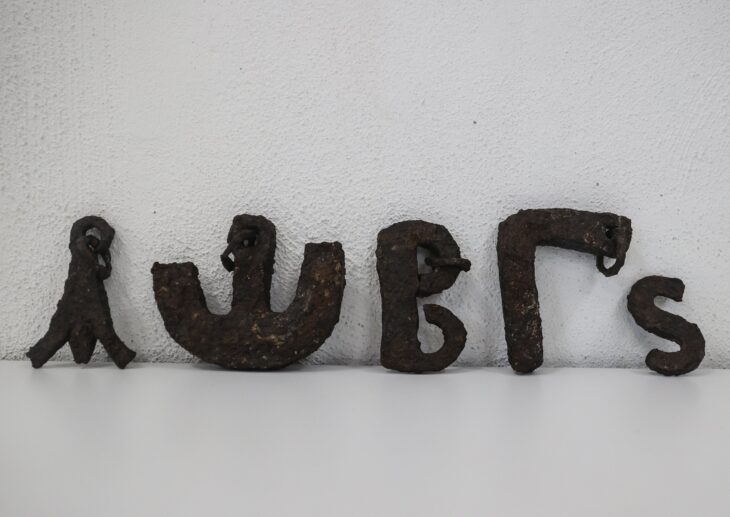In a remarkable new chapter for Cypriot archaeology, researchers from the Pyla-Koutsopetria Archaeological Project (PKAP) have unveiled groundbreaking findings from their 19th excavation season at Pyla-Vigla, a fortified Hellenistic settlement overlooking the Gulf of Larnaca. The results, announced by the Department of Antiquities of Cyprus, shed light on how inhabitants of this strategic site skillfully balanced domestic life, craft production, and military defense nearly 2,300 years ago.
A Fortress Above the Sea
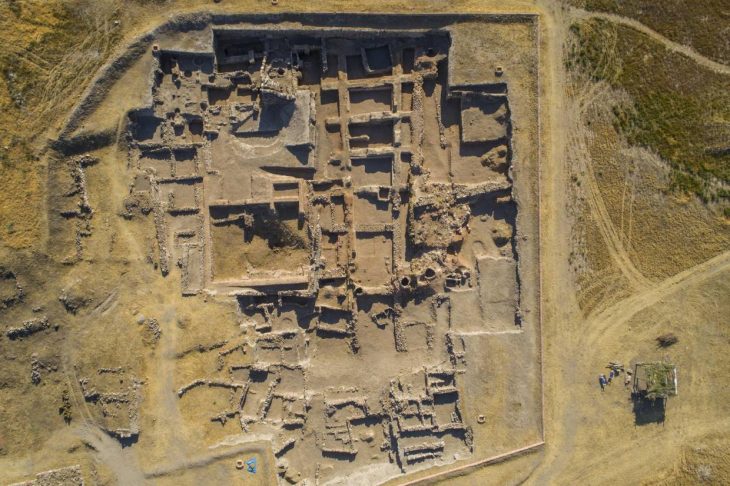
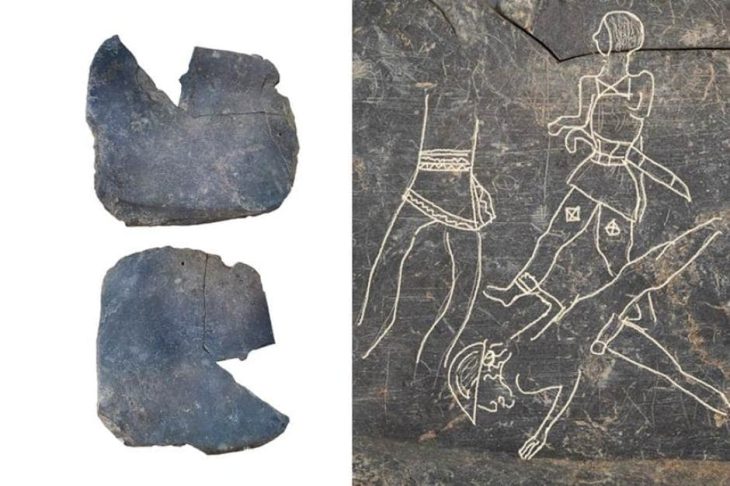
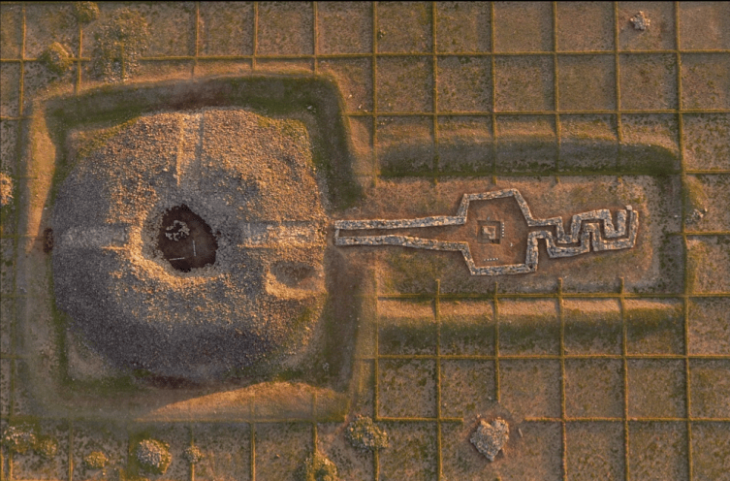
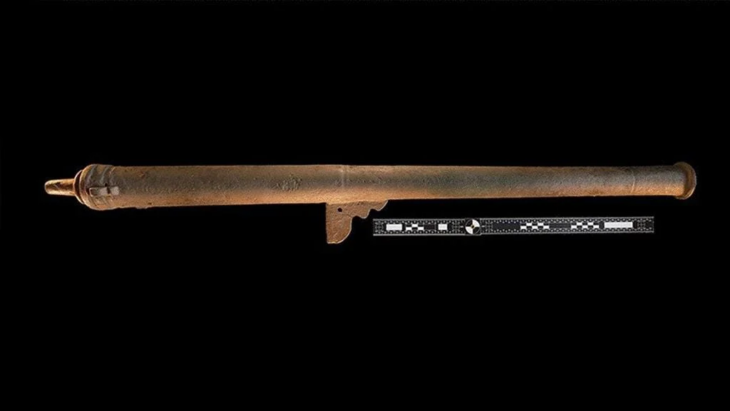
Perched on a steep plateau on Cyprus’s southeastern coast, Pyla-Vigla has long been recognized for its strategic military role. The location offered commanding views of both land and sea routes, making it an ideal post for monitoring movements across the region. Previous campaigns had revealed massive fortification walls, lead sling bullets, arrowheads, and evidence of weapon production, firmly situating the site within the late 4th to early 3rd century BCE, the dawn of the Hellenistic era following Alexander the Great’s conquests.
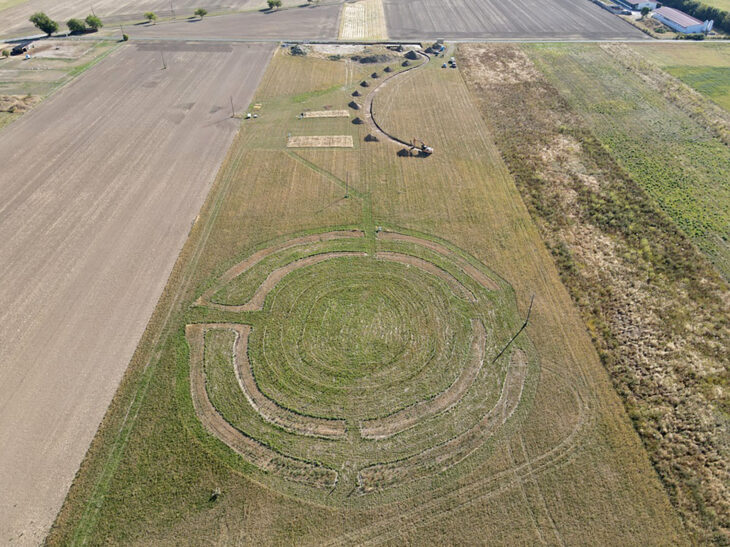
The 2025 excavation season, directed by Dr. Brandon R. Olson (Metropolitan State University of Denver), Dr. Melanie Godsey (Trinity University), and Dr. Tom Landvatter (Reed College), focused on the heart of the plateau. Here, archaeologists uncovered a complex of domestic buildings that reveal the daily rhythms of a community living under constant military readiness.
Life Within the Walls
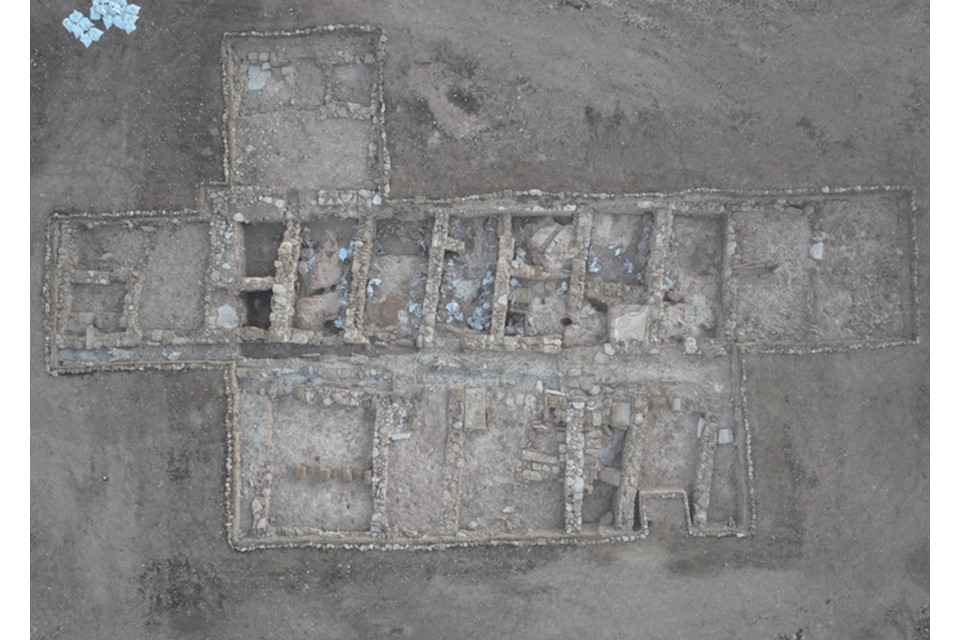
Excavations revealed at least four interconnected structures, including a long rectangular building divided into repetitive rooms. Over time, these rooms had been modified with cross walls and paved corridors, reflecting evolving architectural needs. South of this building, another large hall supported by stone bases came to light, suggesting a communal or administrative function. To the east, foundations of yet another structure aligned differently—perhaps built in a later phase—add to the narrative of a settlement that evolved dynamically over generations.
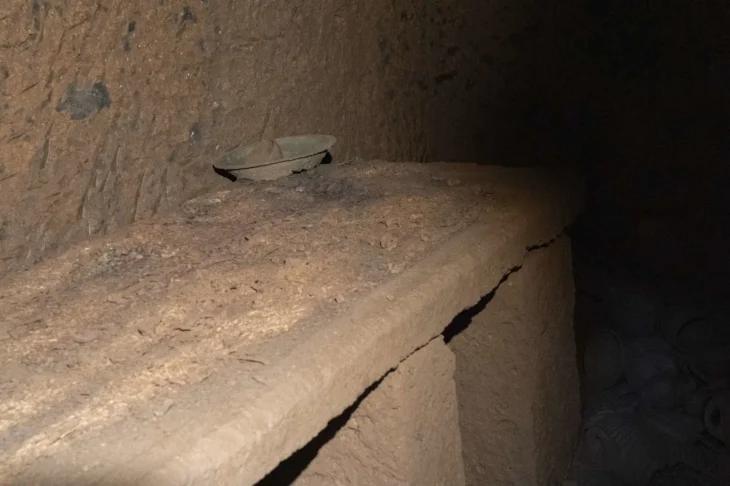
Inside these buildings, archaeologists found kitchenware, tableware, metal tools, and personal grooming items, indicating a range of household activities from cooking to self-care. Yet, not all rooms were purely domestic. The discovery of plastered basins, drainage channels, and transport amphorae points to storage and small-scale craft production, revealing how this settlement operated as a self-sufficient military outpost.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
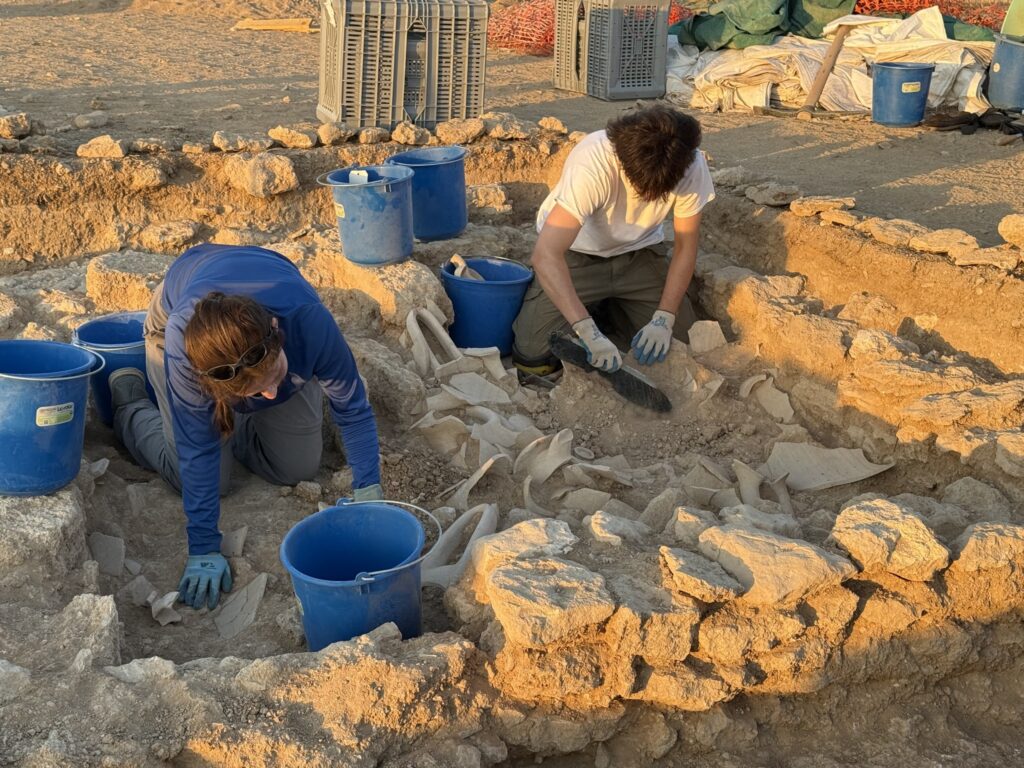

A Blend of Warfare and Daily Routine
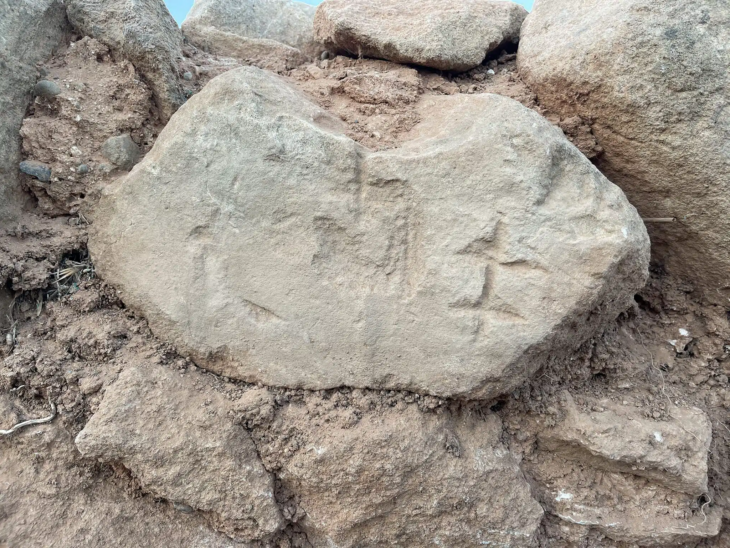
The presence of bronze, lead, and iron weapon fragments reinforces the site’s defensive nature. However, what makes Pyla-Vigla truly fascinating is the way ordinary domestic routines—food preparation, pottery use, and storage—were intertwined with the demands of military life. The community appears to have embodied a hybrid existence, where soldiers and civilians shared spaces, tools, and responsibilities.
This duality—between everyday domestic life and the ever-present shadow of warfare—provides rare insight into the human side of Hellenistic military settlements. Rather than existing solely as garrisons, these fortified communities were also centers of local production, family life, and regional control.
Mapping the Social Fabric of Hellenistic Cyprus
According to the Department of Antiquities, the findings from Pyla-Vigla significantly expand our understanding of social organization and urban planning during Cyprus’s early Hellenistic period. The coexistence of residential and industrial functions demonstrates how strategic settlements were also socially complex communities, capable of sustaining long-term habitation even amid military demands.
The architectural layout—streets, corridors, and multi-roomed dwellings—reveals a well-organized settlement plan, indicating careful coordination and long-term occupation. Its commanding position over the Gulf of Larnaca not only served defense but also facilitated control over maritime trade routes, linking Cyprus to the broader Hellenistic world.
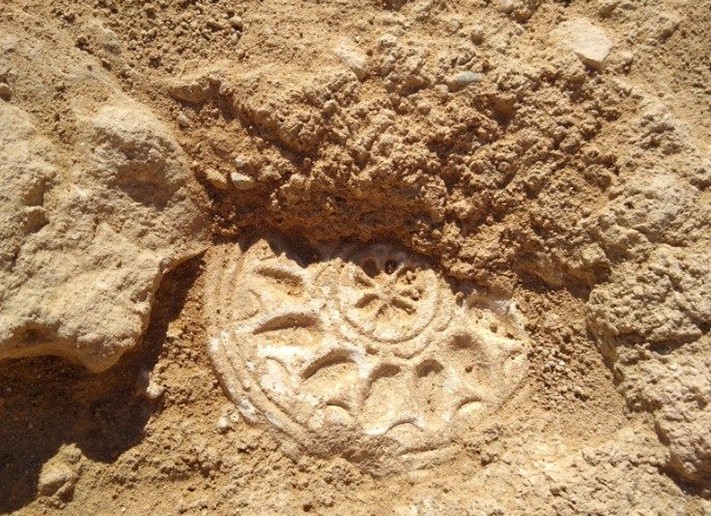

Continuing the Quest for Knowledge
The PKAP team plans to continue studying the artifacts and architecture uncovered in 2025 to refine our understanding of the site’s chronology, function, and regional connections. Through advanced analysis, including residue and material studies, researchers hope to reveal even more about how the people of Pyla-Vigla lived, worked, and defended their community.
As Dr. Olson notes, “Pyla-Vigla offers a unique glimpse into how ordinary life persisted in a militarized environment. It bridges the gap between the archaeological remains of war and the humanity that endured within them.”
For Cyprus, each discovery at Pyla-Vigla adds a new piece to the puzzle of its ancient identity—one that continues to inspire curiosity, scholarship, and a deeper appreciation of how knowledge, discovery, and human resilience shaped the island’s past.
Cover Image Credit: Aerial view of the Pyla-Vigla excavation site. Department of Antiquities of Cyprus