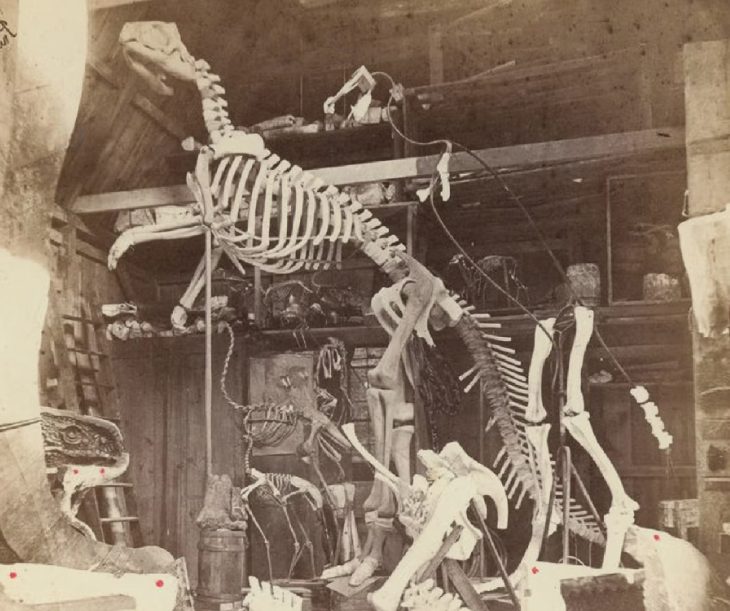
A team of underwater archaeologists from the University of Zadar has discovered the sunken ruins of a 7,000-year-old road that once linked an ancient artificial landmass to the Croatian island of Korčula.
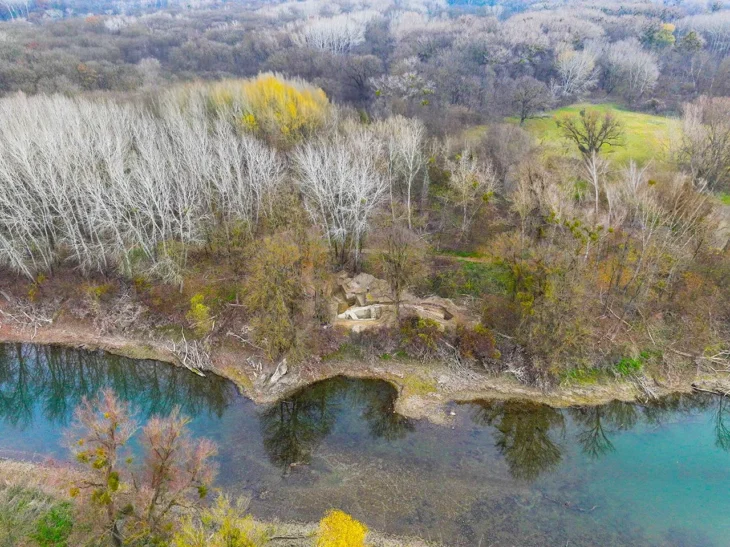
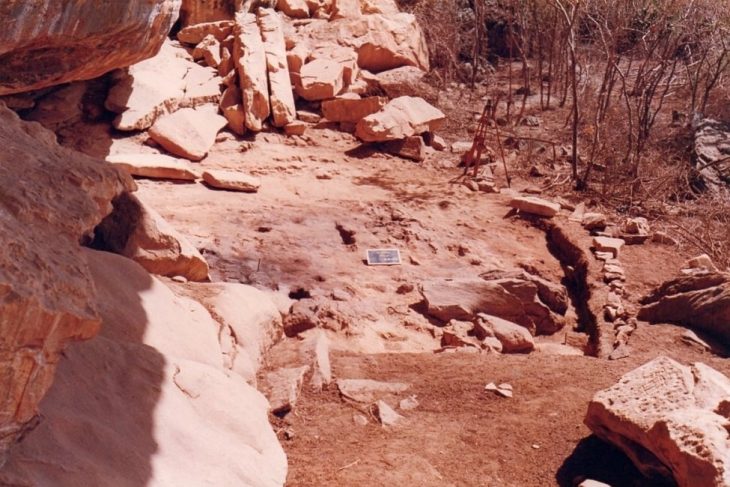
The road is located at a depth of 5 meters in sediment deposits at the submerged archaeological site of Soline, an artificial landmass and Neolithic settlement of the island Korčula and along with several other artifacts, belonged to a lost maritime culture known as the Hvar, who occupied this area during the Neolithic Era.
By radiocarbon analysis of preserved wood found in the last campaign, the entire settlement was dated around 4,900 years before Christ.
A four-meter-wide linear road made of stone slabs was discovered during a recent underwater survey of the site. People walked on this road almost 7,000 years ago.
Over the weekend, the University of Zadar released new footage of the underwater passage, which was made of stacked stones and measured some 12 feet across.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
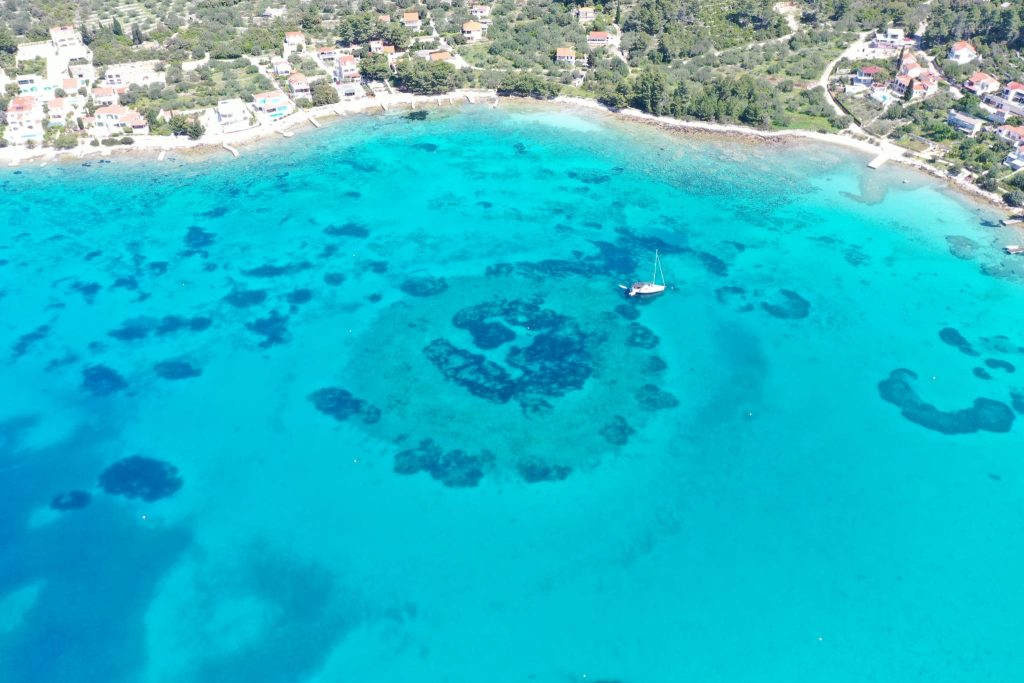

“In underwater archaeological research of the submerged neolithic site of Soline on the island of Korčula, archaeologists found remains that surprised them,” said the University of Zadar in a statement posted to Facebook on Sunday.
“Namely, beneath the layers of sea mud, they discovered a road that connected the sunken prehistoric settlement of the Hvar culture with the coast of the island of Korčula.”
According to the university, several scientists and organizations are working together on underwater research, which is being directed by archaeologist Mate Parica, who has been studying the location for a while.
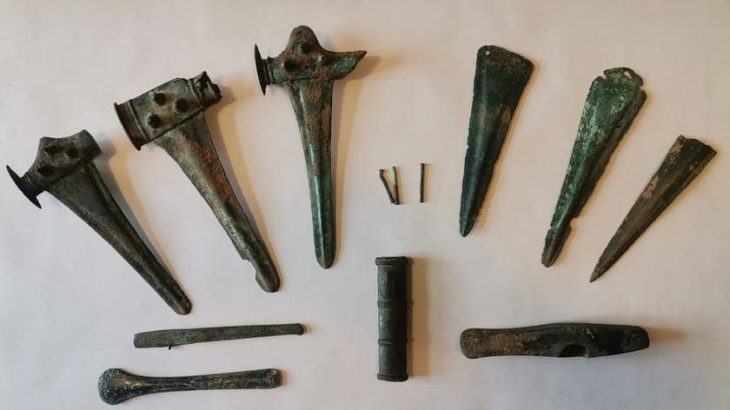
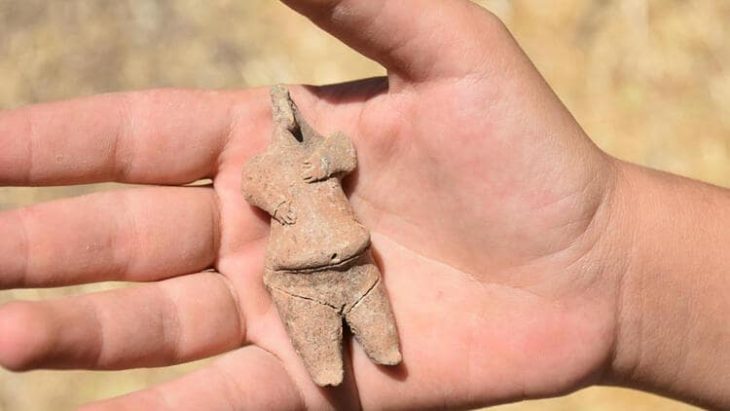
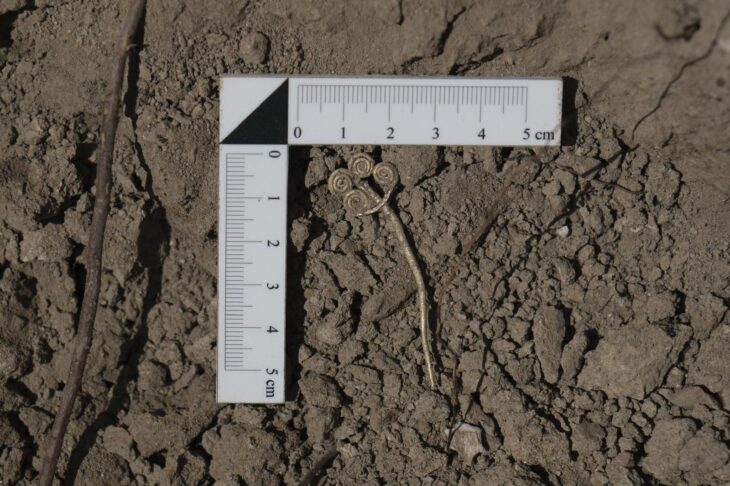
The team also found fragments of millstones, flint blades, and stone axes among the underwater ruins. The artifacts shed light on the enigmatic Hvar peoples, who first appeared on the islands and coasts of the northeast Adriatic Sea around 7,000 years ago.
Korčula is part of an archipelago in the Adriatic that was once a part of the continent. The coastal valleys of the Dinaric Mountains began to flood as a result of the Earth’s ice cap melting after 12,000 BC, and by 6000 BC the archipelago had roughly reached its current configuration.