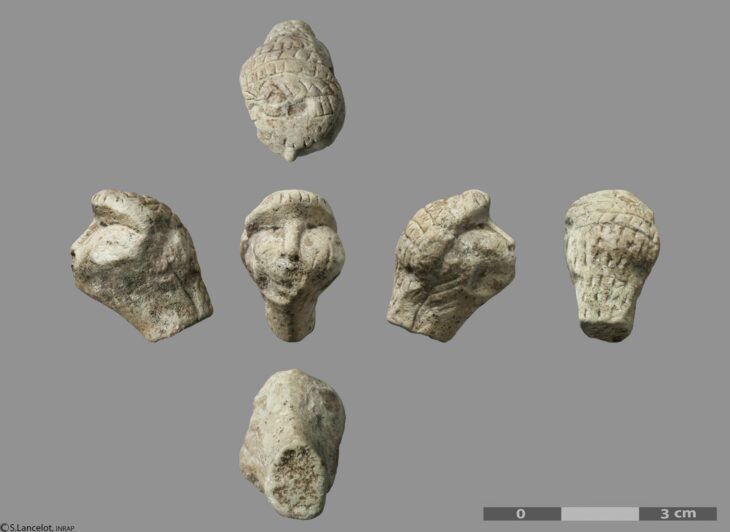
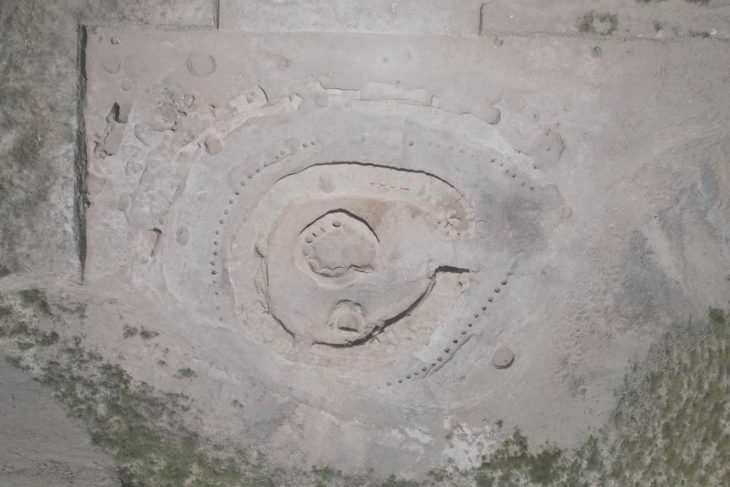
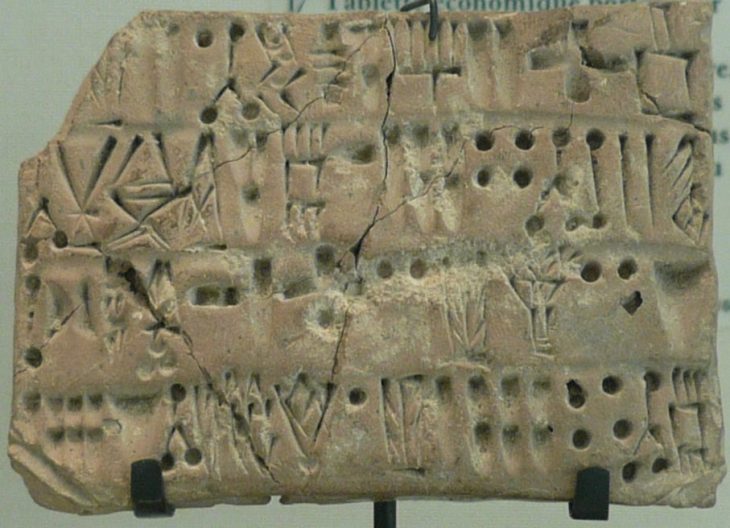
During the Paleolithic period, hominins lived in tiny groups and subsisted by collecting plants, fishing, and killing or scavenging wild animals.
So how far did these small groups go when they lived in caves? Seems like quite a lot!
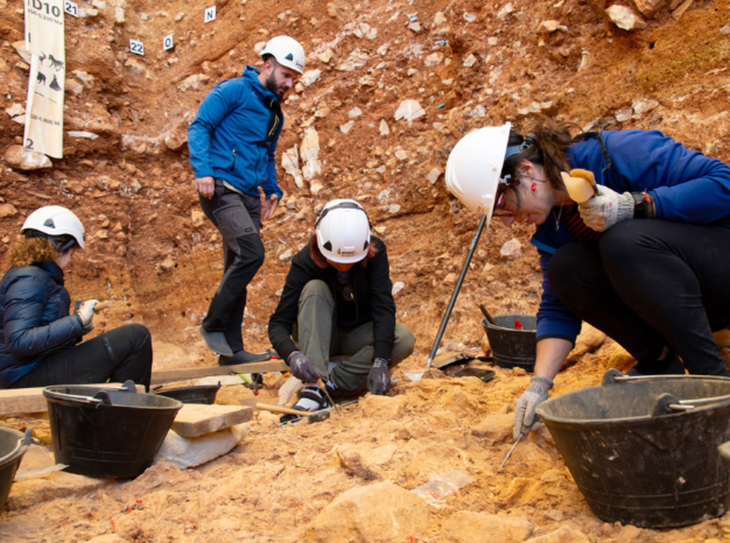
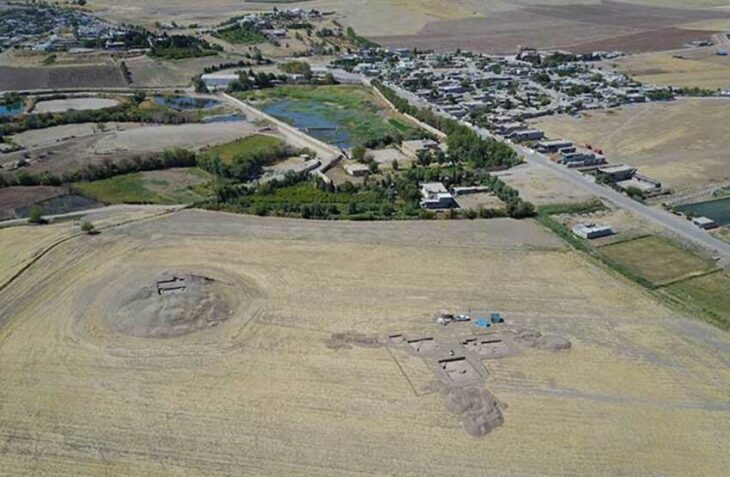
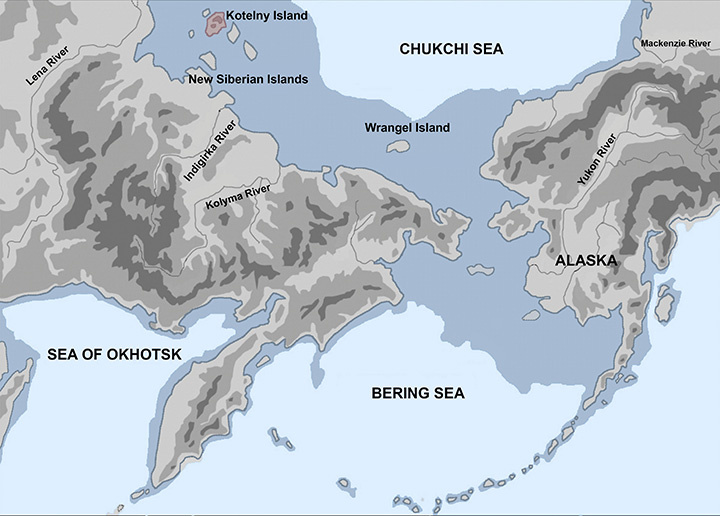
Experts confirmed that ancient hunters lived in Koterny near the coast of Yakutia, at 75°20’N 141°00’E north latitude, 990 kilometers (615 miles) north of the Arctic Circle.
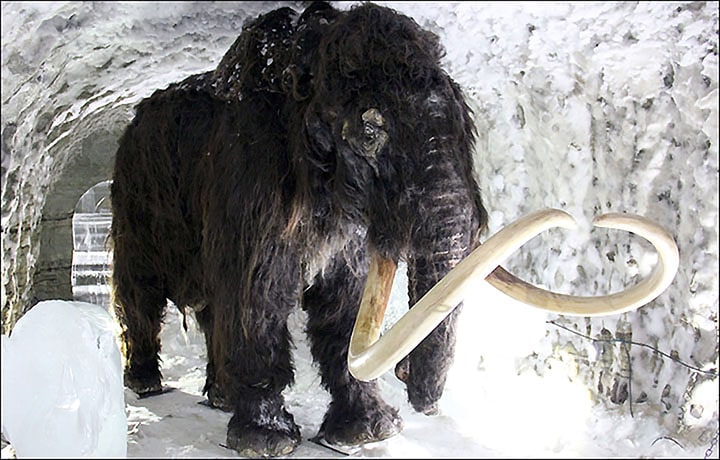
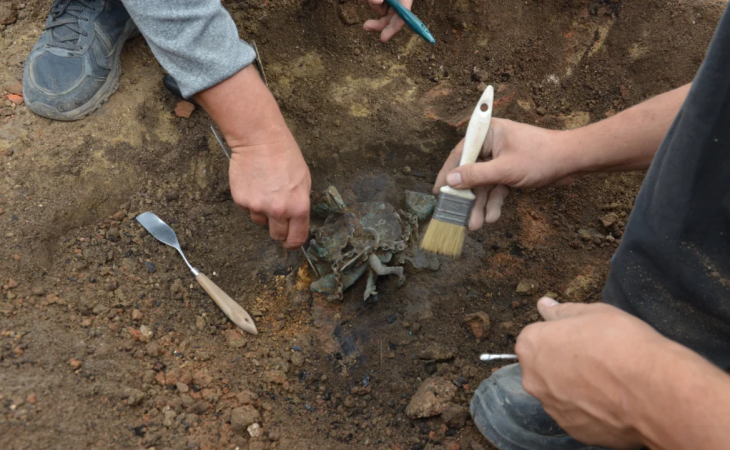
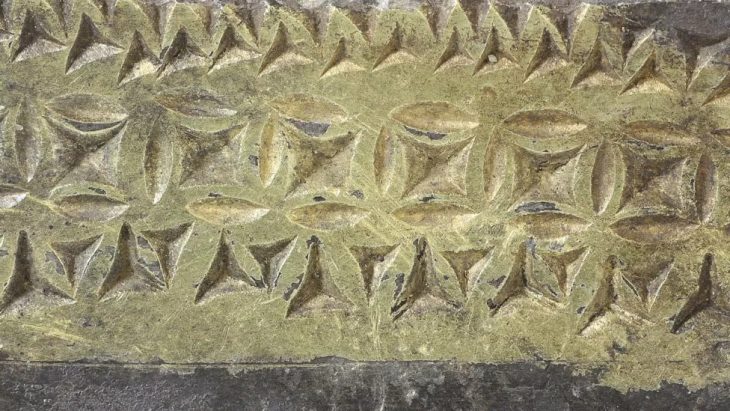
Their butchering tools were discovered with the bones of extinct woolly mammoths. Scientists have reconstructed 70% of the bones of a Palaeolithic mammoth that these hardy humans dined on.
‘This is a unique event for the Arctic and world archeology,’ Alexander Kandyba told Siberiantimes, senior researcher at the Stone Age Archaeology Department of the Institute of Archaeology and Ethnography, part of the Siberian Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
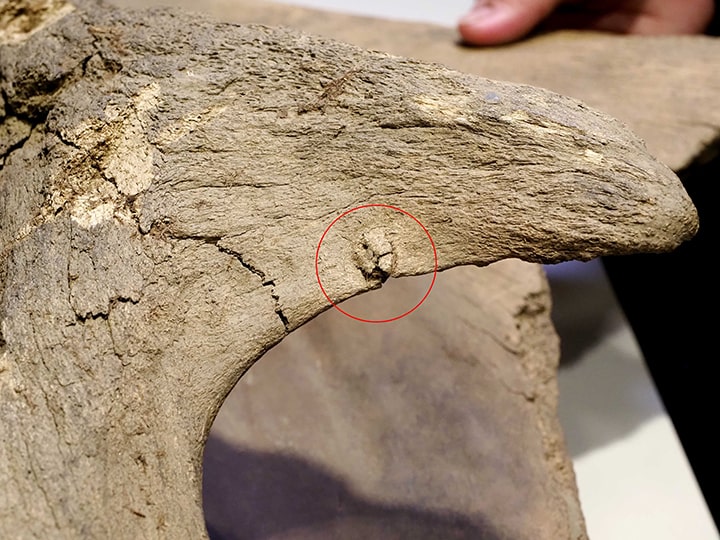

Alexander Kandyba emphasized: ‘We are talking about the northernmost human site in the Palaeolithic era.’
“The mammoth was butchered by people. A large number of processed bones and tusk fragments were found. There are linear cuts, traces of chopping blows on the vertebra. People used a wide range of tools for cutting. There is not a single bone that would be without traces of human impact.’
Scientists can learn not only how man conquered such northern latitudes, but also how he existed. The latest discoveries tend to refute the notion that ancient people were hesitant to hunt the massive hair monsters.
Alexander Kandyba ‘In particular, we now know how they butchered a mammoth,’ said.
Dr. Albert Protopopov, head of the department of mammoth fauna of the Academy of Sciences of Yakutia, confirmed 70% of a newly found mammoth had been collected.
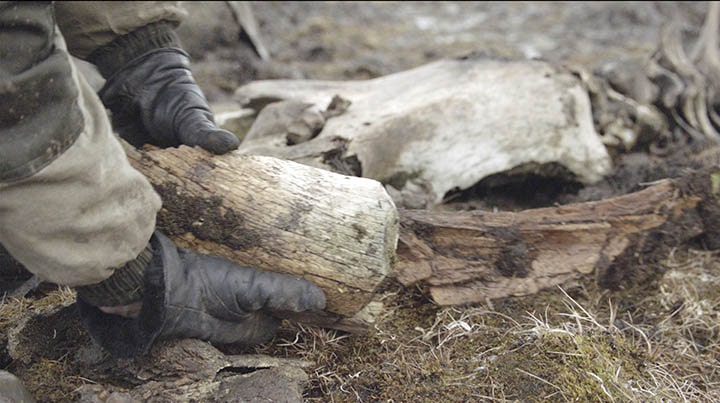

A large number of tusk fragments were found, indicating that animal remains were processed. The Taba-Yuryakh site is the northernmost known place for human existence in the Paleolithic Age. Kotelny is the largest island in the Novosibirsk archipelago, washed by the Laptev Sea and the East Siberian Sea. The remains of woolly mammoths have been found here before.
However, when these ancient humans inhabited this outpost, it was connected to the mainland, and the temperature, albeit northern, was warmer than it is today.
The discoveries were made this summer during a joint expedition led by the Yakutia Academy of Sciences and the Novosibirsk Institute of Archaeology and Ethnography.
The woolly mammoths are roughly the same size as modern African elephants. The male’s shoulder height is between 2.7 to 3.4 m (8.9 to 11.2 feet) and weighs 6 metric tons (6.6 short tons). The female has a shoulder height of 2.6-2.9 m (8.5-9.5 feet) and a weight of 4 metric tons (4.4 short tons). Mammoths adapted well to the cold environment during the last ice age. It was covered in fur, with an outer covering of long guard hairs and a shorter undercoat. The ears and tail are short to minimize frostbite and heat loss. It had long, curved tusks and four molars, which were replaced six times during the lifetime of an individual.
Woolly mammoth information is from Wikipedia.
















