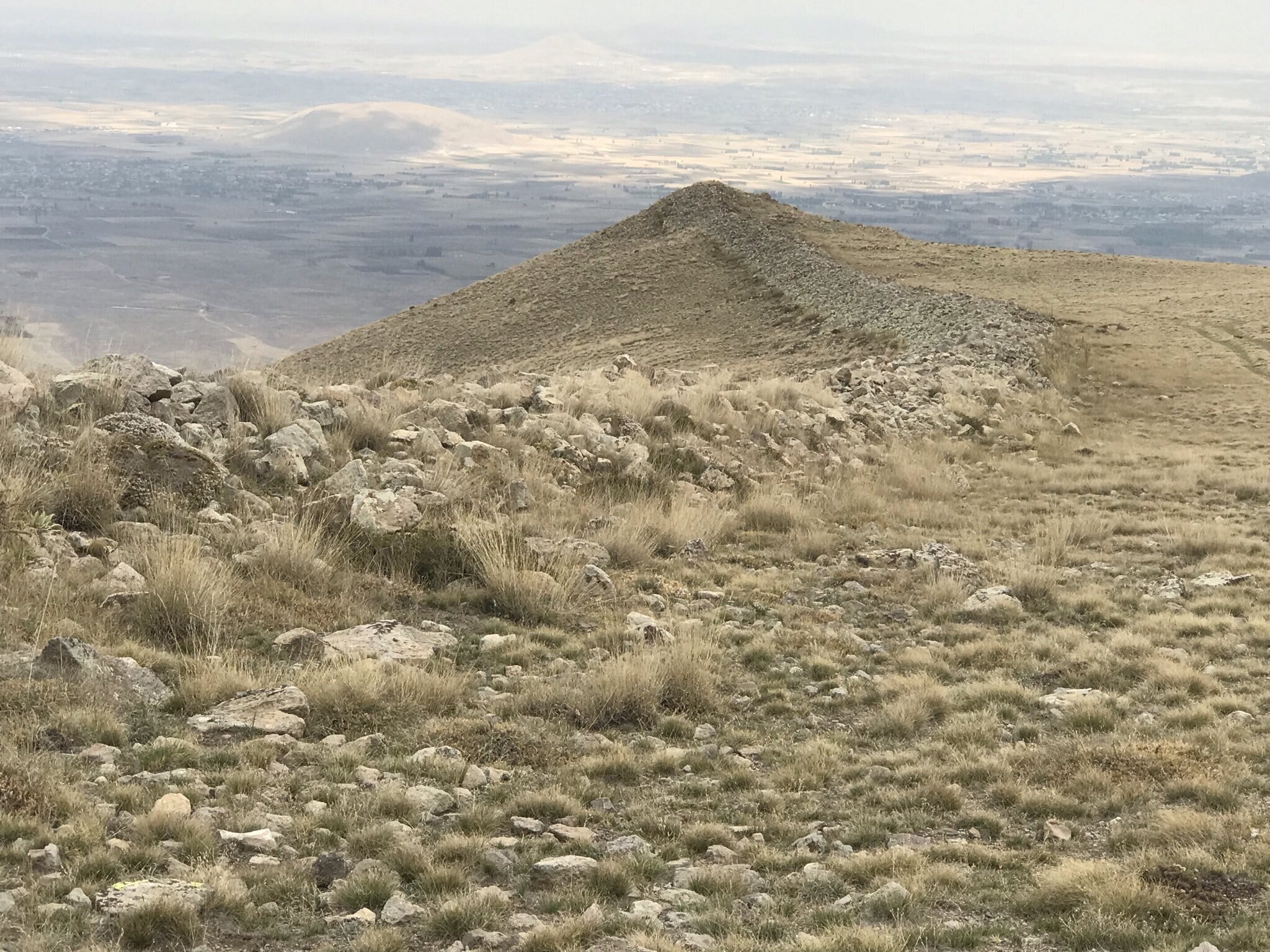
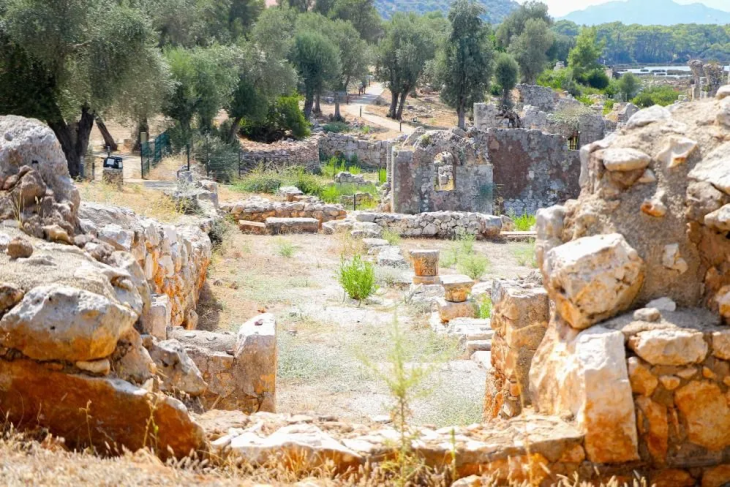
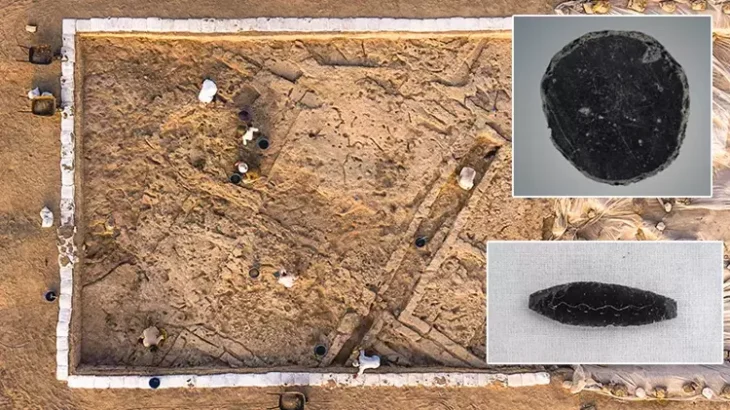
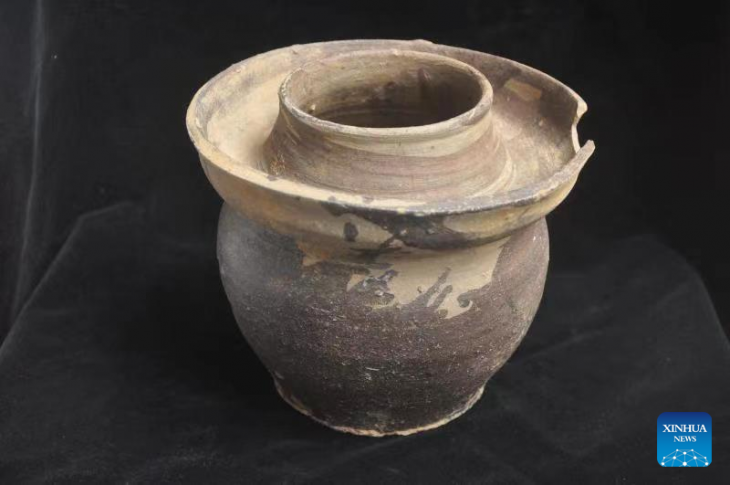
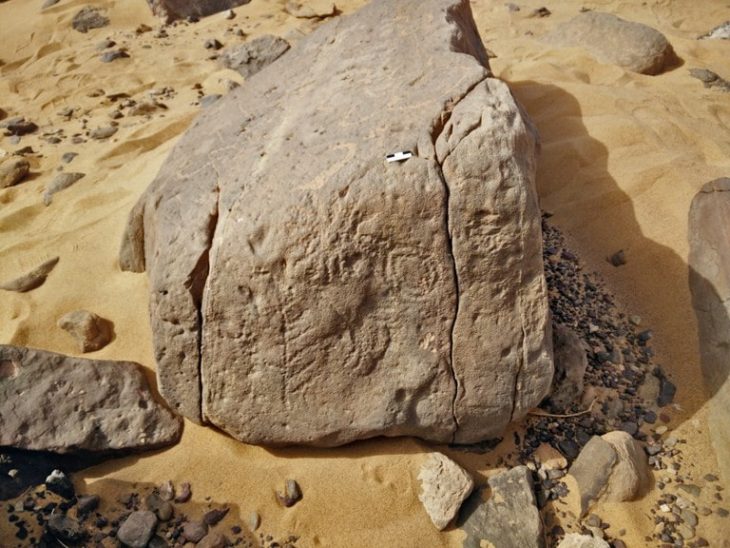
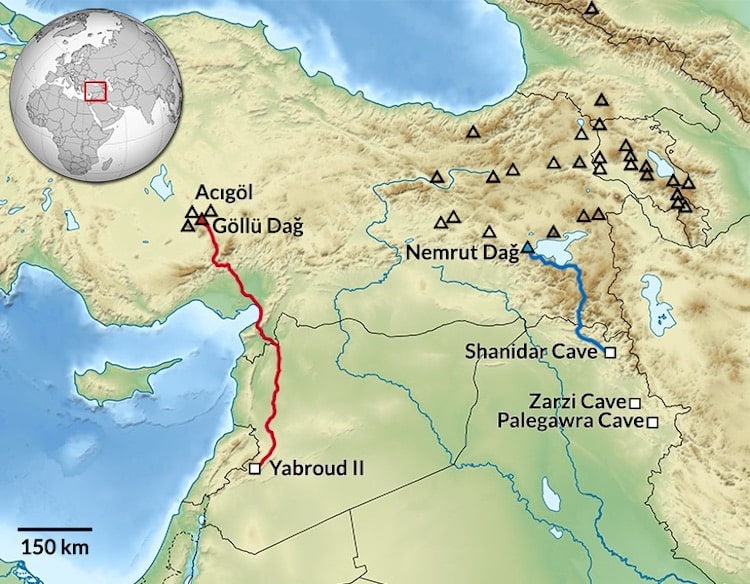
The researches conducted in Göllü Dağ and its surroundings, located within the borders of Niğde province in Central Anatolia, and the Obsidian resources and workshops discovered in the region in the 1960s may change the route of the migration routes where the first humans spread from Africa to the world.
As a result of the researches, it has been revealed that the use of obsidian in the region has been one of the places preferred by people in terms of raw materials since the Lower Paleolithic period (800.000).
Göllü Dağ, located in the northeast of Niğde province, is a stratovolcano with a diameter of 12 km.
Obsidians extracted from the region were imported to the Levant region and Cyprus. Although the relationships and distribution strategies are still unknown, researches conducted in these regions show that the origin of obsidian belongs to the Göllü Dağ region.
Surveys in many parts of Anatolia, mostly secondary and non-in situ finds, indicate that Anatolia was home to a dense human group during the Middle Pleistocene.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Excavations at Kaletepe in Niğde province are also important in terms of showing the diversity of human groups in the Middle Pleistocene period in this region. The lower layers of the Kaletepe sequence locked between 160/200,000 – 1,000,000 are very important.
Research conducted in Kaletepe shows that after the group that made axes using obsidian, a group that did not know this technique lived in the same region.
Chronologically, the group that knows how to design is older than the group that doesn’t. This situation shows the existence of different evolved groups, at least technically, in the Anatolian sub-paleolithic.
Homo erectus, which emerged from Africa around 1.300.000 – 1.000.000 years, split into two after the Near East and headed towards Asia and Europe. In this period, the place of Anatolia in this migration route was ignored, and the Caucasus and North Black Sea steppes were shown as distribution routes.
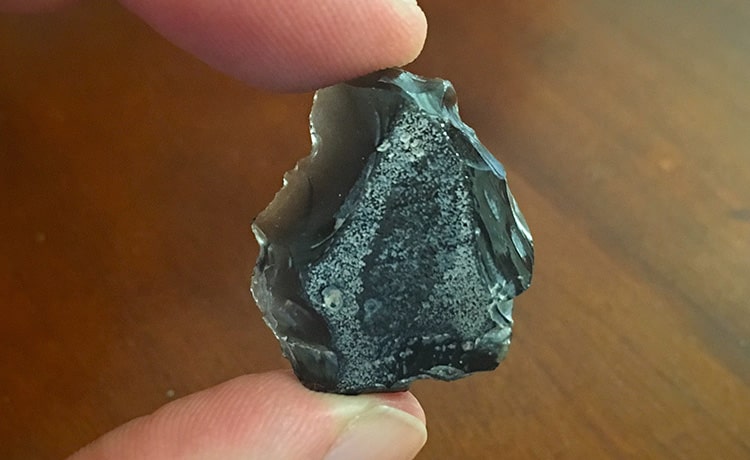

However, as the Göllü Dağ finds show the existence of Homo erectus, the results of the examination of their tools also point to different Homo erectus groups with different technical skills.
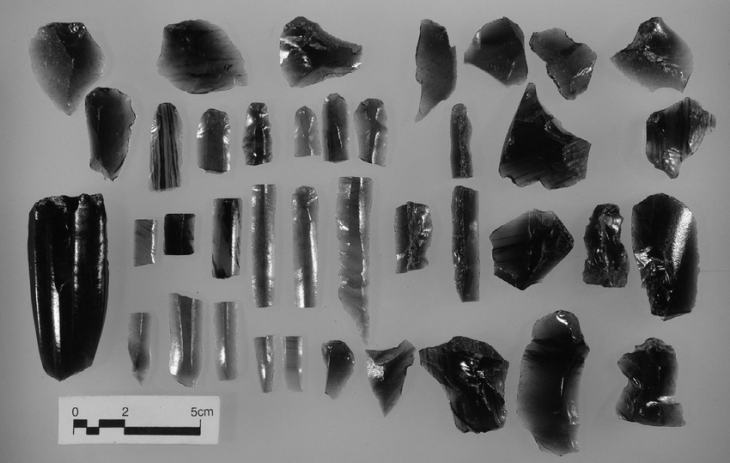
An important part of the Göllü Dağ finds belongs to the Middle Paleolithic. These finds are cores exhibiting the technique used by Neanderthals. These beans have a processing technique called Levallois. In addition, the diversity of nuclei also constitutes evidence for the existence of different human groups.
The researches in the region started with the excavations started by Remzi Oğuz Arık in 1934 and were continued by Burhan Tezcan in 1968-69 and Wulf Schirmer in 1992-98, respectively.
During the excavations carried out in 1996, it was determined that the first people used these areas during their transition from Africa to Europe.
During these research excavations, a settlement belonging to the Late Hittite Kingdoms period was also unearthed.
In this article, excerpts are made from Professor Nur Balkan Atlı’s article titled “Kaletepe Obsidiyen Atölyesi Kazısı ve Göllü Dağ Obsidiyen Projesi”.
Cover Photo: @ekonyar