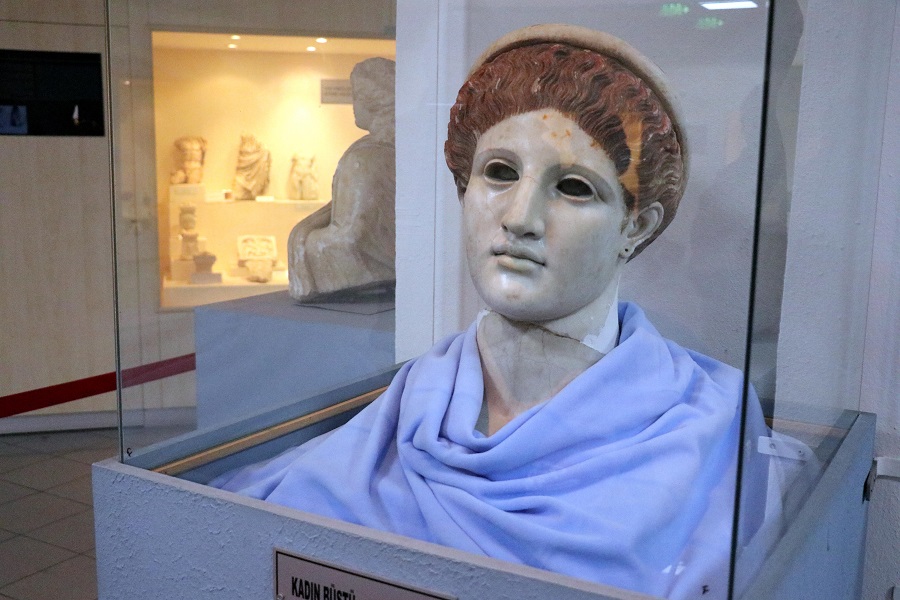
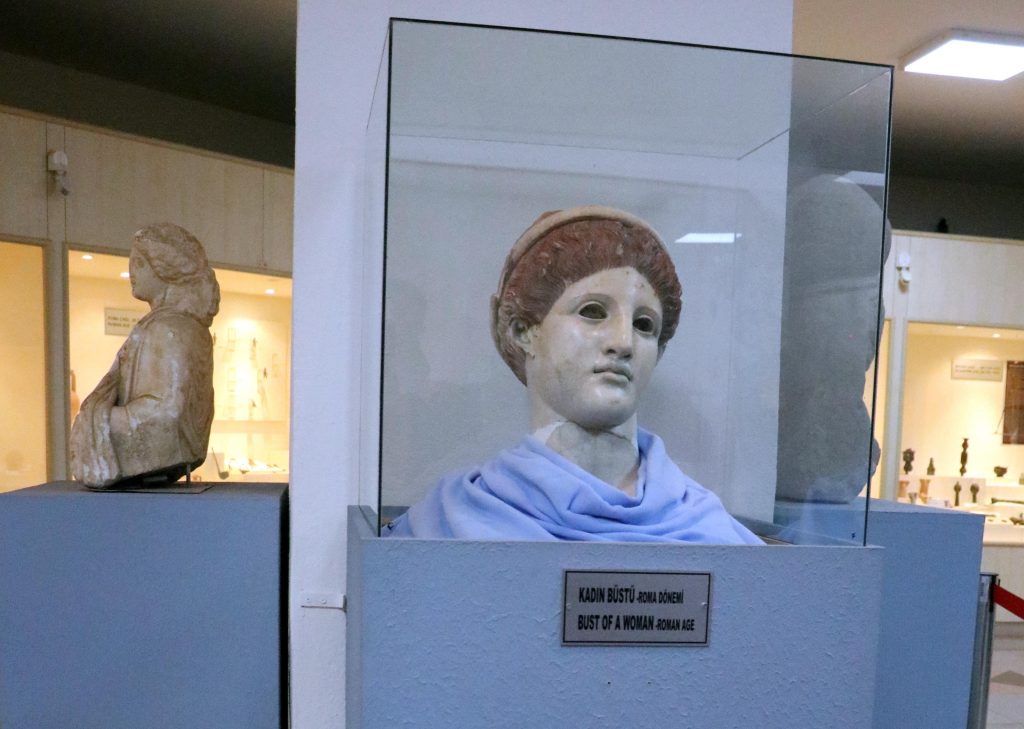
50 years ago, foundation excavation work was started for the construction of Girls’ Institute in Akpınar Neighborhood of Bolu city (in Turkey) center. During the foundation excavation, workers found a marble female bust and handed it over to the Bolu Museum authorities. Museum officials determined that the bust of women they examined belongs to the Roman period and has continued to be exhibited in the museum as a Roman-era female bust ever since. However, recent studies have revealed a surprising fact about the female bust of the Roman period.
According to the news on the Cumhuriyet Newspaper website; The Bolu Chamber of Commerce and Industry formed a delegation of archaeologists in order to promote historical tourism in the city. The delegation examined the sculptures in the Bolu City Museum. The work was started on the thought that the statue, which has been exhibited for 50 years as the “Female Bust of Roman Period” in the museum, may belong to Artemis. As a result of the study, it was determined by the experts that the statue belonged to the Greek mythology goddess Artemis.
“IT IS A HIGHLY HIGH-LEVEL ARTWORK”
Providing information about the statue, Düzce Konuralp Antique Theater Excavation Team Member Archaeologist Dr. Güzin Bilir, “The” painted woman’s head “in front of you is Artemis, which is the symbolized form of wild nature, abundance, hunting, and archery. The head of Artemis, which is a kind of personification of the natural resources of Bolu, is a very high-level work of art, probably made of island marble or Athens marble. The work, which attracts attention with its quality and craftsmanship, was probably imported, and its workshop may have originated in the southern Italy region. As for its stylistic features, the striking point of the work is that there are traces of intense dye, especially the presence of dark red dye on her hair. The red dye was preferred for women’s hair, as red hair is seen as a symbol of beauty, ”she said.

Produced for propaganda during Augustus
Güzin Bilir stated that the statue might have been sent to important cities for propaganda during the period of the first Roman Emperor Augustus, “It is an ‘eclectic’, that is, a mixed work, showing the sculpting features of both the Classical and Hellenistic periods. Such works were produced for propaganda purposes, especially during the period of the first Roman emperor Augustus, and were erected in important places in the Roman provinces. The artifact, which we can date to 27 BC and 14 AD, was found during the construction of a girls’ institute in the most central part of the city of Bolu, Akpınar district, and since it was very well preserved, it must have been in a closed area within an important public building in the city center. The presence of such a quality work of art in Bolu proves to us that there are historical and cultural beauties as well as natural and natural beauties. In fact, this work is a kind of combination of Bolu’s natural riches and cultural heritage, ”she said.
Explaining that the statue found in the city shows the importance of Bolu in the Roman Empire, Bilir said, “Foreign tourists want to see this head of Artemis in a beautiful area when they come. Other examples in the world are exhibited in very important museums. A small number of them are the subject of printing a continuous model in their era. However, this is such a statute; it is being printed and its repetition is not printed. That is why it is very important and very valuable in terms of the marble used. This means that it is an indication of how important Bolu’s place and value were in the Roman Empire. “It is made in Naples and sent here.”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Source: DHA Cumhuriyet Newspaper