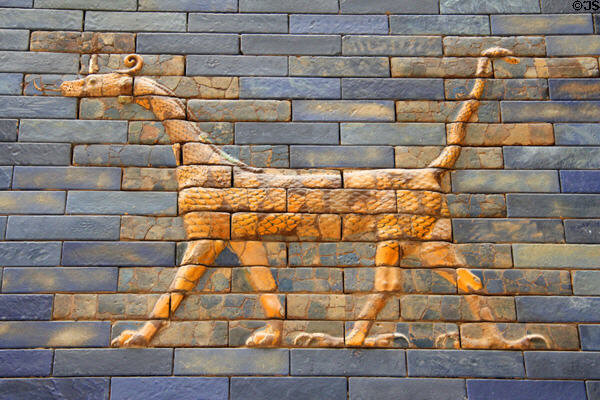
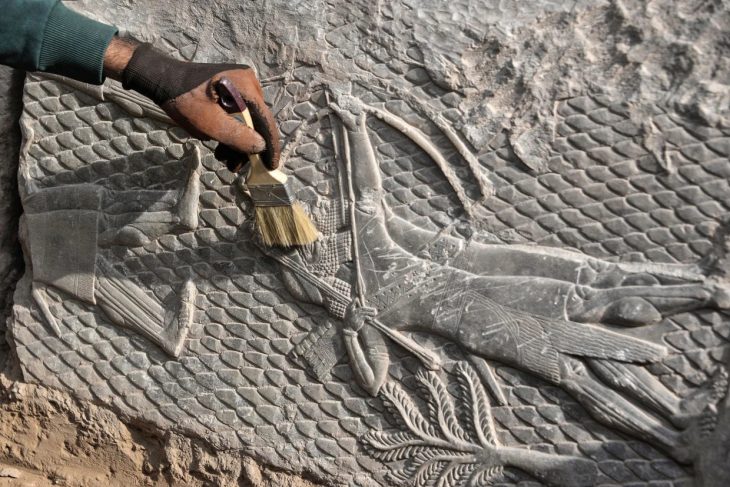
“Temple of the Eye”, one of the pilgrimage centers of humanity in the chalcolithic age, is an important faith epicenter like Göbeklitepe.
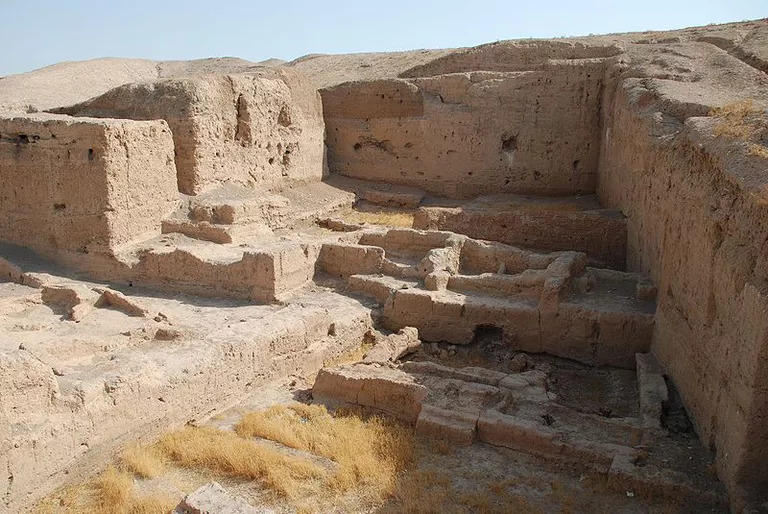
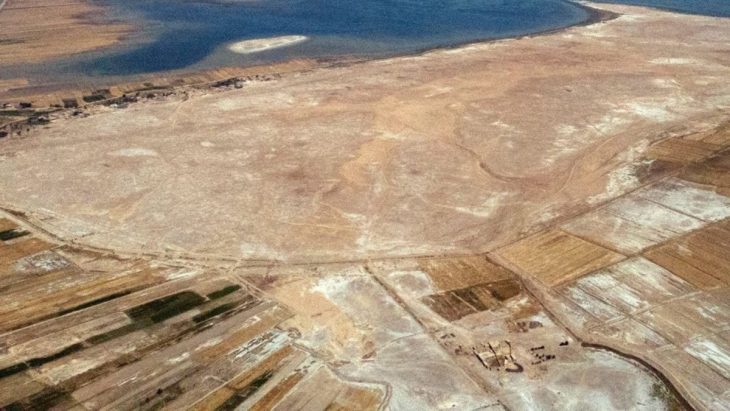
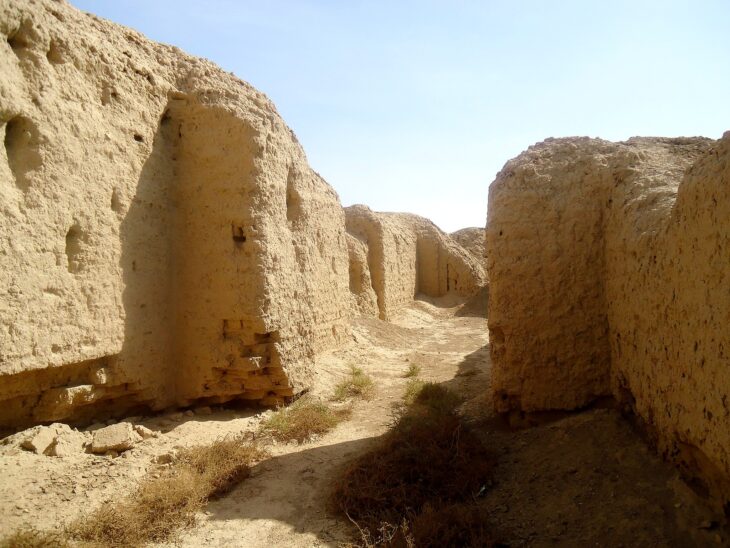
Tell Brak is an important place in the upper Habur plain and, unlike other Uruk colonies, has a much older settlement.Approximately BC. It has a history dating back 4000 years. Max Mallowan, who excavated in the region in the 1930s, is the person who unearthed the Eye temple, one of the most important structures of the Uruk Period.
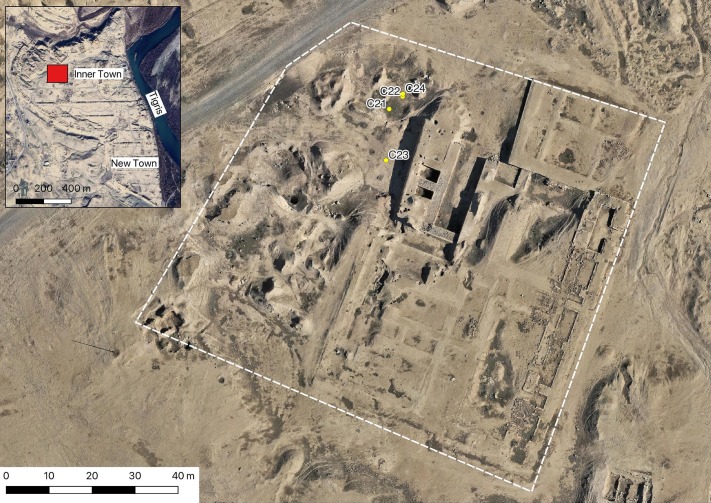
The temple has a 3-part structure like a typical Uruk structure. A central room is a structure in which there are two small rooms around it (one of which is used for storage purposes), niches and buttresses are widely used in this space, and the decorations are made of clay and eye-shaped idols made of limestone.
Found by Max Mallowan, 3 more phases were unearthed under this temple. Before each renovation, the Temple was completely destroyed and leveled. This flattened area constitutes a platform for the new temple to be built. The fact that it is a common tradition in Southern Mesopotamia to demolish a Temple and build a new Temple instead of it with the same plan shows us the affected of Tell Brak from this region.
The three phases in this temple are named according to the mudbrick colors.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The first phase is known as the Red Eye Temple and red mudbricks were used in its construction.
The second phase is known as the Gray Eye Temple and as its name suggests, gray adobe was used in its construction.
When it comes to the third phase, the White Eye Temple is named after the floor plastered with white lime.
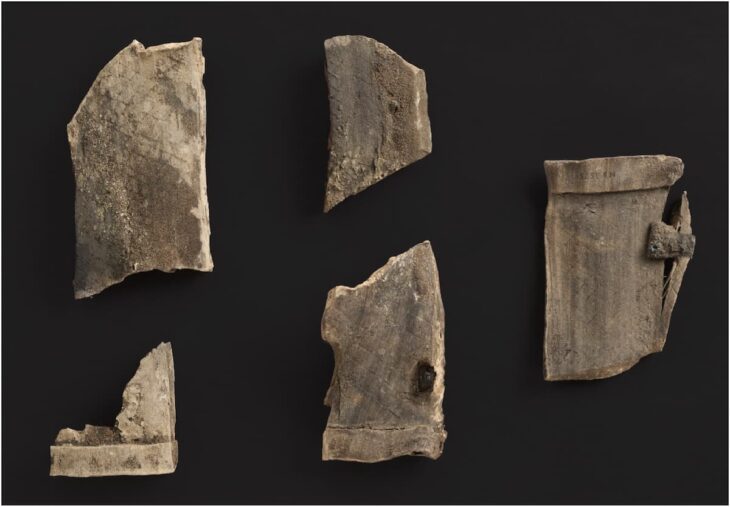
Thousands of eye idols were found in this temple. Undoubtedly, whatever God or Goddess these idols are dedicated to, it is certain that this God or Goddess is the most powerful God / Goddess believed in this region. Although there are many suggested views, these idols relate to the fact that if not the Mother Goddess herself, there may be another identity with similar powers to this Goddess.
The determination of the Eye God cult in places where the Mother Goddess cult was common created the idea of the twin God. It was commented that it is the cult of the Eye God was common in the early periods, and the Eye Idols were the symbols of God who could see everything and observe the future of the city. It is also thought that the Eye Idols may have symbolized the Sun God.
Although it remains a mystery as to which God or Goddess it is, it is certain that it was the head God or head Goddess the strongest this period. The strong acceptance of this belief in Mesopotamia and Anatolia is also important in determining the area of interaction.
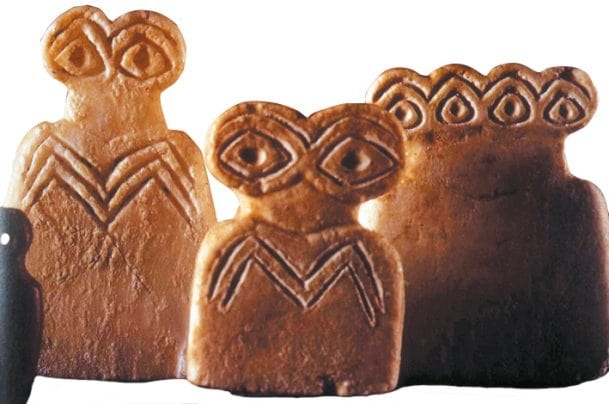

Forms of Eye Idols
When we look at the general structures of the eye idols found in the Tell Brak temple, it is seen that they are simple and abstract looking.
Its legs and arms consist of the upper half and the lower half, which is perceived as an unprocessed head. On some idols, it has been specified on the eyebrows along with the eye. Idols were made by method deep scraping. Looking at the descriptions, it is possible to say that they were made in two different ways.
In the first group examples, the eyes are exaggerated on two adjacent or disjointed almond-shaped surfaces. Edges of the eyes are sometimes single or double line.
In the second group samples, it is similar to the first group in terms of the face frame and the processing of the eyes. The difference is that the neck that separates the head and body is determined by notching on both sides. The lower half is sometimes quadrangular and sometimes bulging dome.
Many similar ones of these idols found in Tell Brak were found in Anatolia. It is understood that this settlement, located in the Habur Plain, was affected by both regions due to its proximity to Mesopotamia and Anatolia.
It is one of the most important temples of the Late Chalcolithic period.
SOURCE: In our article, Information from Prof. Dr. Serap YAYLALI’s article “Eye idols and the example of Pirot Höyük” published in Cedrus magazine was used.