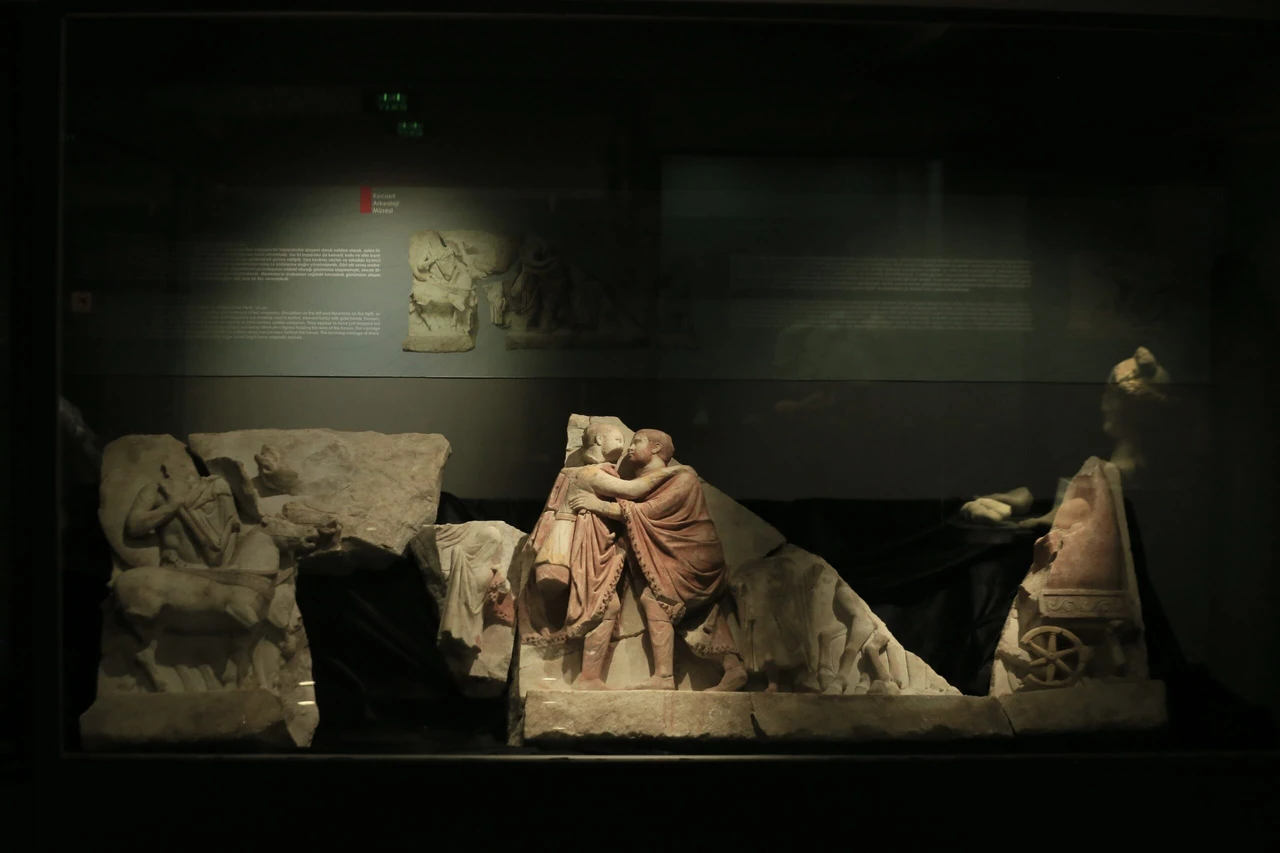
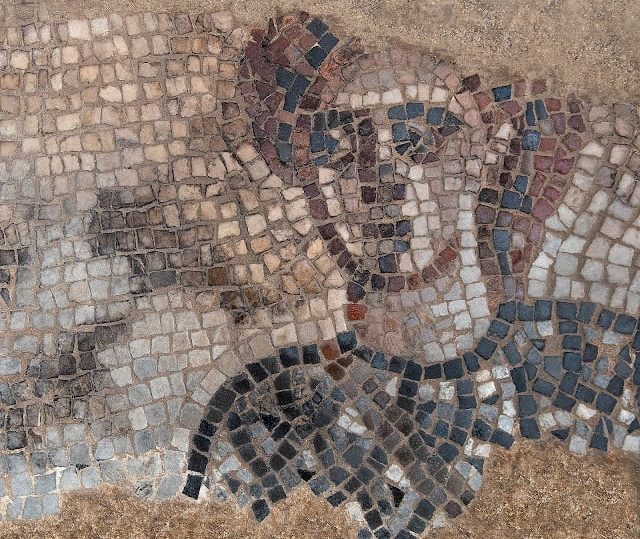
A relief depicting two Roman emperors’ embrace of Diocletian and Maximian during a ceremonial event, each other welcomes visitors for the first time after 23 years in the Kocaeli Archaeology Museum.
For the first time, this rare artifact offers visitors an exceptional glimpse into the grandeur and political intricacies of the Roman Empire.
The relief was unearthed during rescue excavations in Kocaeli’s Cukurbag neighborhood, following the devastating 1999 Marmara Earthquake. Eight relief panels, two statues, and 12 pieces of statues were found during the rescue excavations initiated in 2001 by the Kocaeli Museum Directorate. They were put on display for the first time in 2022.
The relief, which was found in the same period and restored using 10 separate broken pieces, depicts the scene where Roman emperors Diocletian and Maximian embrace each other after getting off the chariot during the “adventus” ceremony at the entrance to the city.
The Adventus ceremony is an ancient Roman tradition celebrating the rulers’ entrance into a city.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Serkan Gedük, branch manager of the Culture and Tourism Ministry’s General Directorate of Cultural Heritage and Museums, explained that the restored work depicts an imperial procession approaching from both sides.
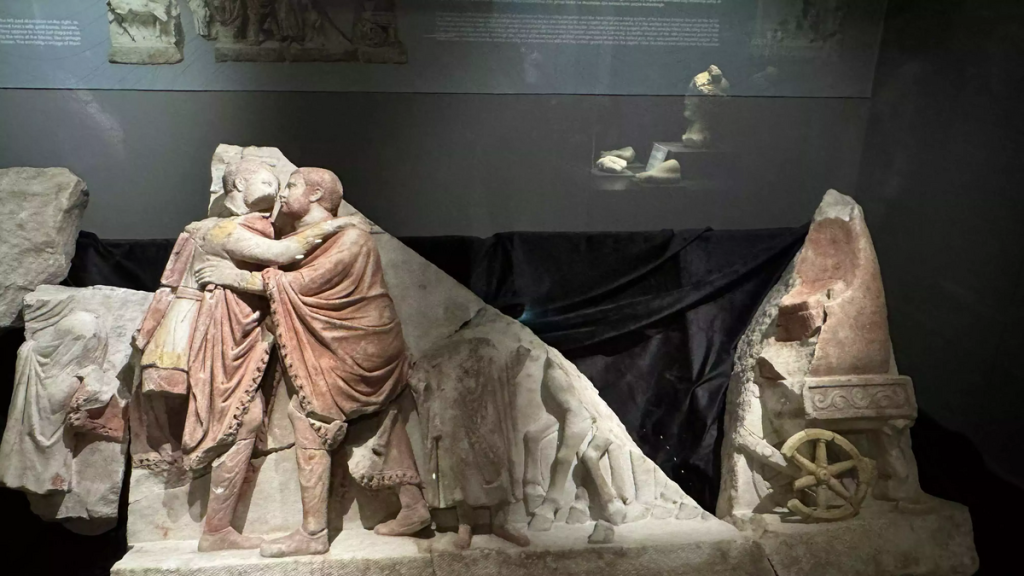

“One of the scenes depicts adventures, or parade, held at the entrance to the city, with Emperor Diocletian on the left and Emperor Maximian on the right embracing each other. We see that both emperors are depicted in magnificent attire, wearing a belted, sleeved tunic decorated with gold bands, trousers and a tasseled imperial cloak. Their short-cropped hair and beards are one of the most important scenes in terms of representing a typical example of the third-century Roman soldier emperors,” he said.
Gedük explained that the depiction of embracement symbolized the new multiple governance system of the Roman Empire, known as the tetrarchy (rule of four emperors in groups of two), which Diocletian implemented in Nicomedia, and the political harmony between the co-emperors.
Gedük noted that no emperor had ever been depicted so physically close in Roman art before.
“It is derived from the right-hand shaking motif, which is a common iconographic symbol of marriage in Roman art and literature, and we can describe it as a sign of political harmony. This panel belongs to the Tetrarchy Period. It is the oldest and most unique example of the ‘Tetrarchic embracement motif’ from various sculpture groups erected everywhere in the Roman Empire,” he added.
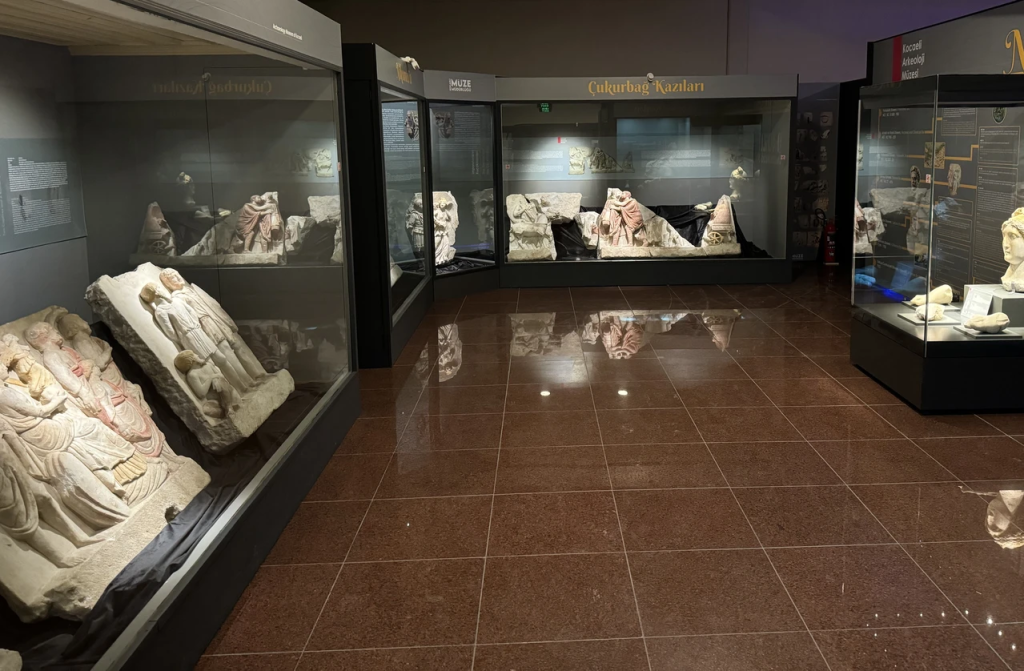

Gedük, who pointed out that they obtained a lot of information about that period from the reliefs, said that they could understand from these reliefs how the horse carriage that Maximianus rode was used at that time and what kind of ceremonial carriage it was.
An exceptional chance to explore the artistic and historical significance of the embrace of the ancient Roman emperors is presented by the unveiling of this ancient masterpiece.
Now, guests at the Kocaeli Archaeology Museum can explore the fascinating realm of Roman ceremonial art and political symbolism while also getting a close-up look at this incredible relic.
Cover Image: Relief of the “Embrace scene of two emperors” depicting the Roman emperors Diocletian and Maximianus together, unearthed in Kocaeli in 2001, Kocaeli Archaeology Museum, Türkiye. Photo: AA