Archaeologists have made a groundbreaking discovery in the ancient capital of the Silla Kingdom (57 BC-AD 935) in the ancient tombs site at Jjoksaem in Gyeongju that challenges long-held assumptions about early Korean burial practices.
Gyeongju, also known as Seorabeol, is a coastal city in the far southeastern corner of North Gyeongsang Province, South Korea. The ancient tombs site at Jjoksaem in Gyeongju serves as a collective burial ground for Silla royalty and nobility located to the east of the Daereungwon Ancient Tomb Complex, which houses the Cheonmachong Tomb and Hwangnamdaechong Tomb—tombs of Silla’s prominent rulers.
The Silla kingdom ruled south-eastern Korea during the Three Kingdoms period from the 1st century BCE to the 7th century CE. The capital was Geumseong (Gyeongju) with a centralized government and hierarchical system of social ranks. In the ancient world, the Korean kingdom of Silla was renowned as a country of gold.
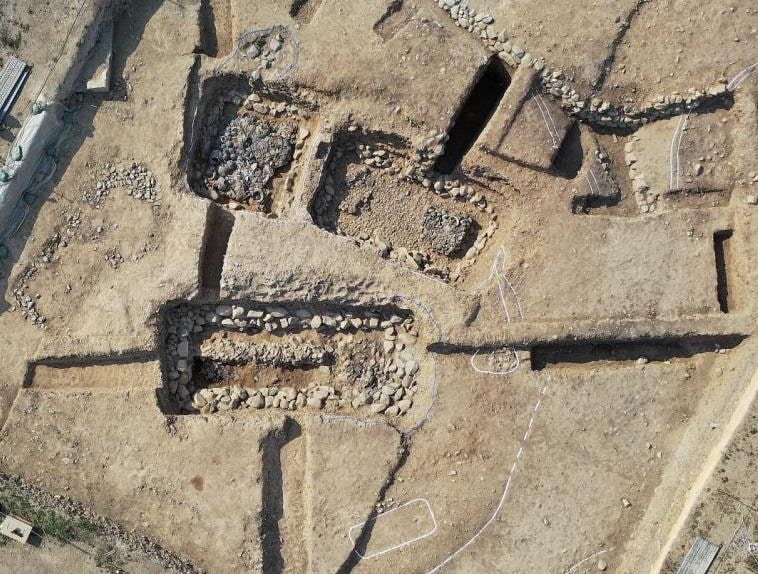
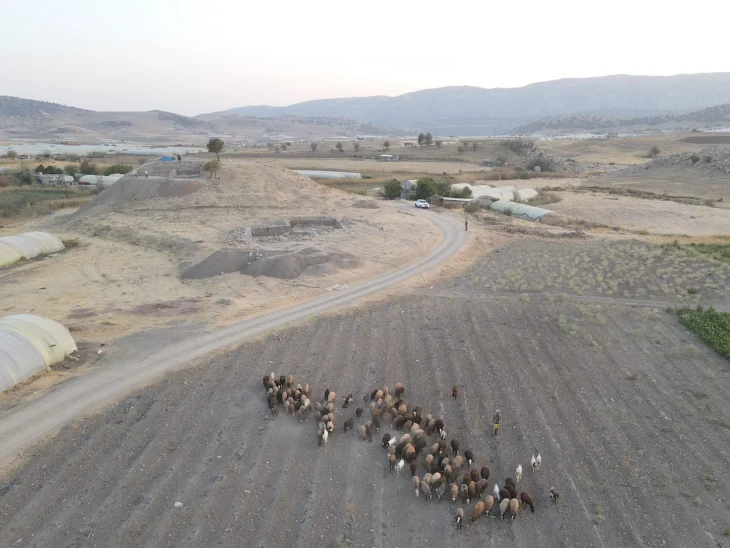
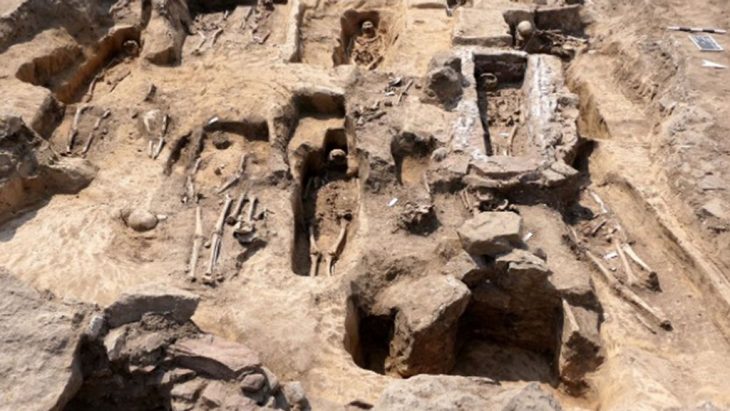
Two recently excavated tombs in Gyeongju’s Jjoksaem district have revealed a previously unknown burial type for the period, according to a statement made on Wednesday by the Gyeongju National Research Institute of Cultural Heritage.
Typical early Silla burials feature a wooden frame (dutneol) for the body, covered by an earthen mound and surrounded by a distinctive stone boundary. The newly discovered tombs, provisionally named J171 and J172, lack this characteristic stone perimeter.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
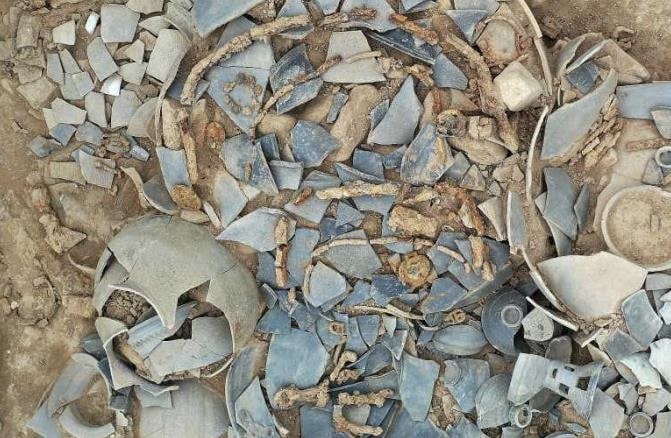

“This is the first time we’ve encountered Silla-era tombs without the stone boundary,” said an institute official.
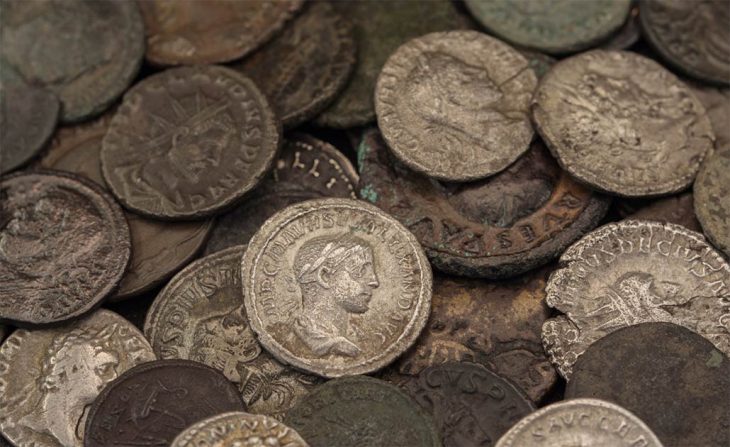
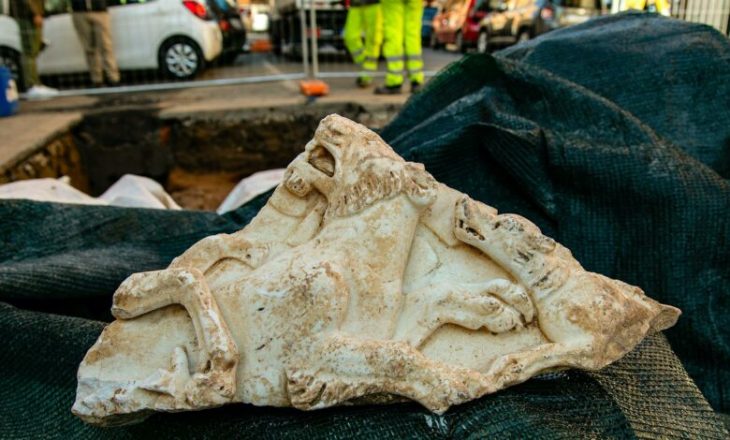
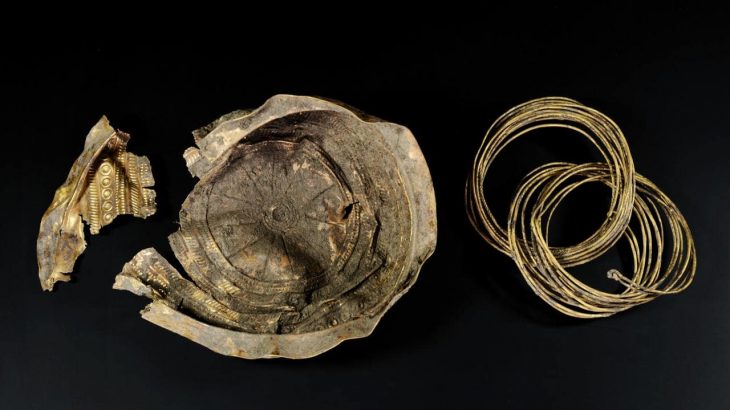
In addition, archaeologists also uncovered a trove of artifacts within the mounds, including decorated pottery lids, legged bowls, and an array of silver-laden equipment for horses – a rarity in previous excavations. The rare silver horse ornaments have sparked particular interest, as they are considered to have been important status symbols in ancient Silla society.
Since 2021, the Gyeongju National Research Institute of Cultural Heritage has conducted annual surveys and research to uncover the nature of these tombs. As a result of this effort, important tomb data was obtained and approximately 40 previously undiscovered Silla tombs were identified. Building on these successes, the Institute intends to elucidate the central tombs of Gyeongju and investigate the features of the tombs in more detail.
Gyeongju National Research Institute of Cultural Heritage
Cover Photo: The newly discovered tombs, provisionally named J171 and J172, in Gyeongju’s Jjoksaem district. Gyeongju National Research Institute of Cultural Heritage