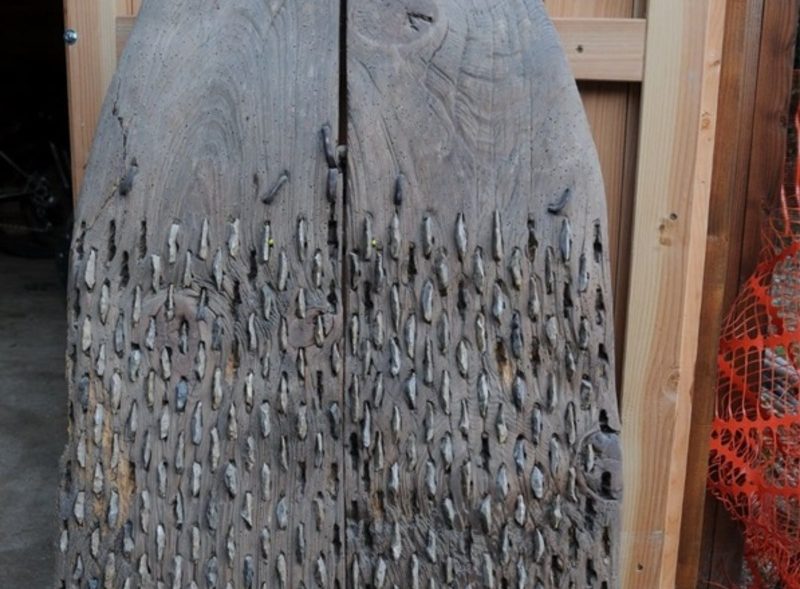
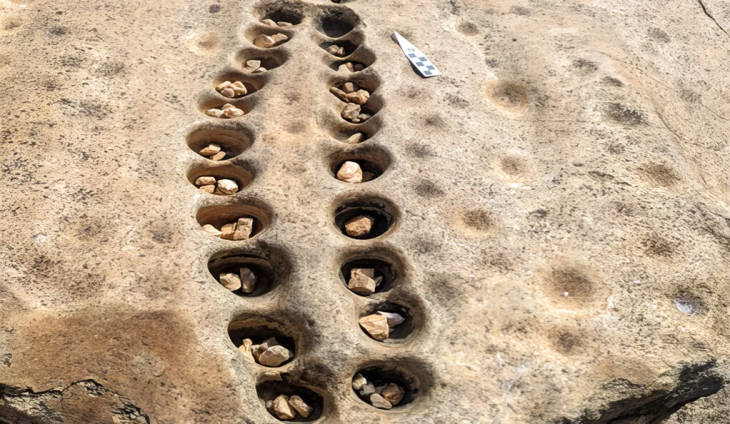
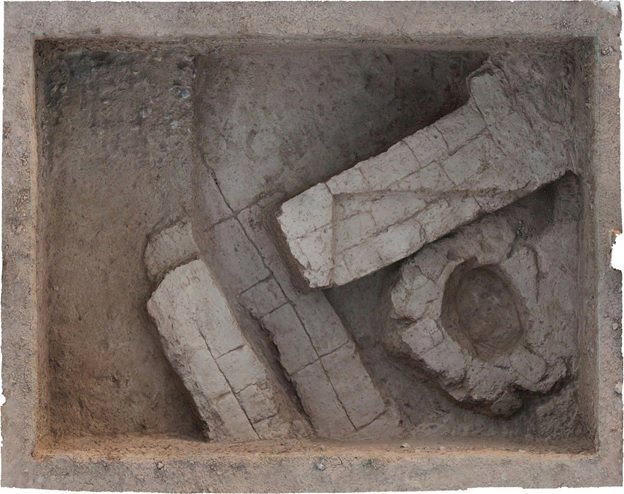
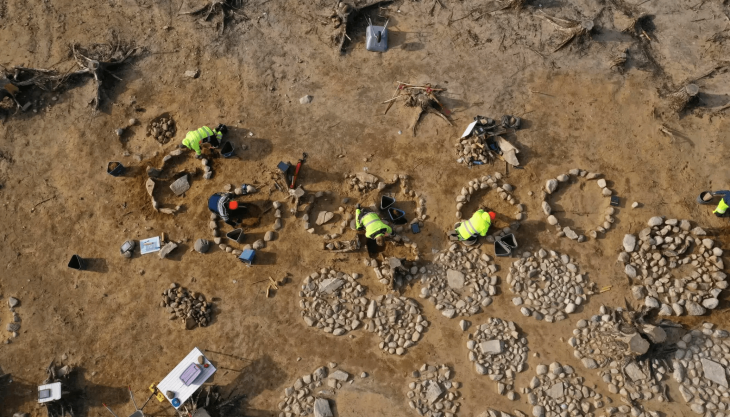
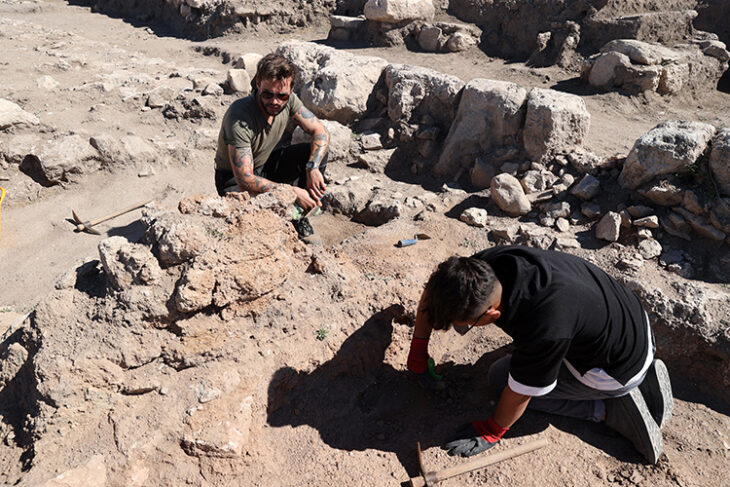
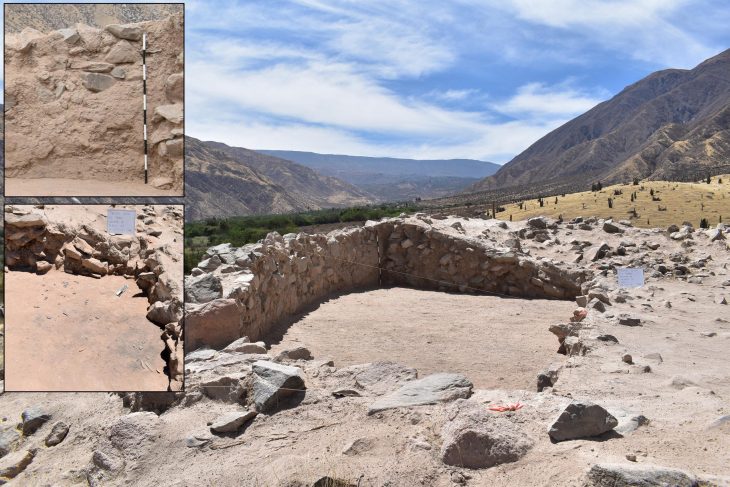
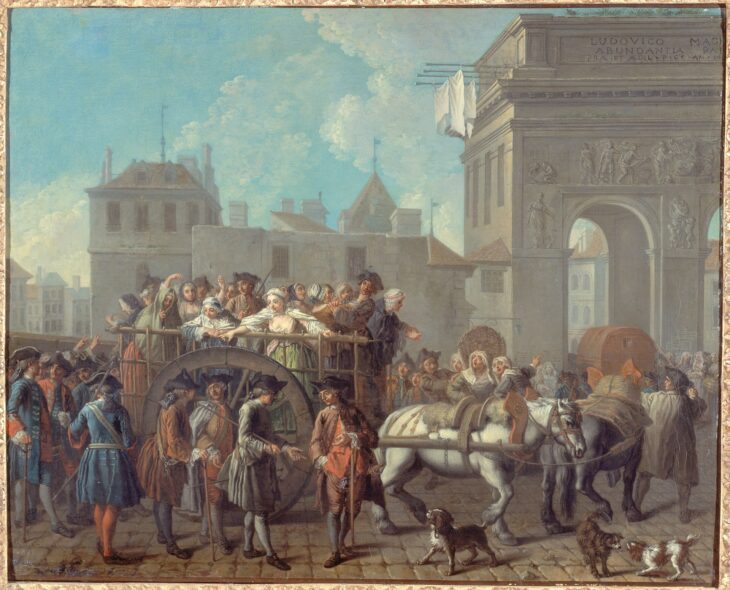
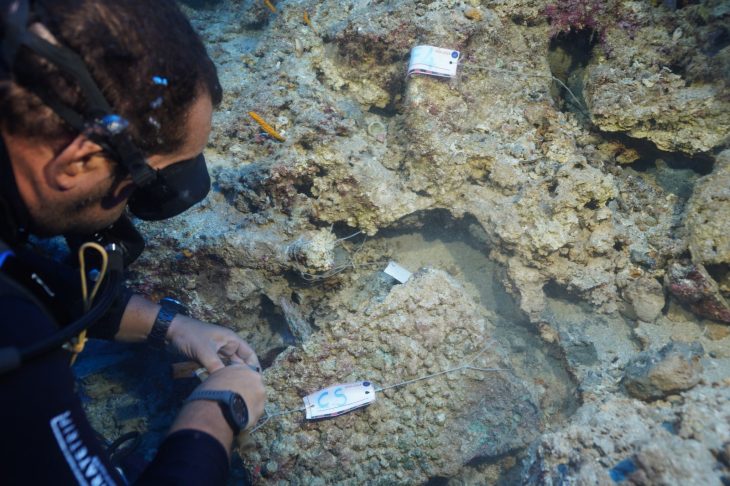
The threshing sledges, which until a few decades ago was used in many Mediterranean countries from Turkey to Spain to separate the chaff from the wheat, is estimated to have appeared in Greece as early as 6500 BC.
By applying advanced analytical methods, including co-orientated microscopy, to the flint industries, researchers led by the University of Pisa were able to trace the early adoption of such technology and the adaptation of what can be considered among the first agricultural machines in Europe.
The research, conducted as part of several research projects funded by the European Union, Italy, and Spain and directed by the University of Pisa in collaboration with the CSIC in Spain and the Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, predates previous records of this technology in Europe by at least 3,000 years, providing new insights into Neolithic society’s technological innovations.
We have been working for years to reconstruct the routes and mechanisms of the spread of agriculture from the Near East to the rest of the Mediterranean, explains Professor Niccolò Mazzucco, of the University of Pisa, principal investigator of the work, discovering the processes of technological innovation and how new machines were introduced is fundamental to reconstructing past technological systems.
The use of the threshing sledge, also known by the Roman term tribulum, allowed for a considerable increase in the amount of grain processed and accelerated its processing. In the past, it was believed that this innovation was linked to the birth of the first states, but our study shows that its first use is much older.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
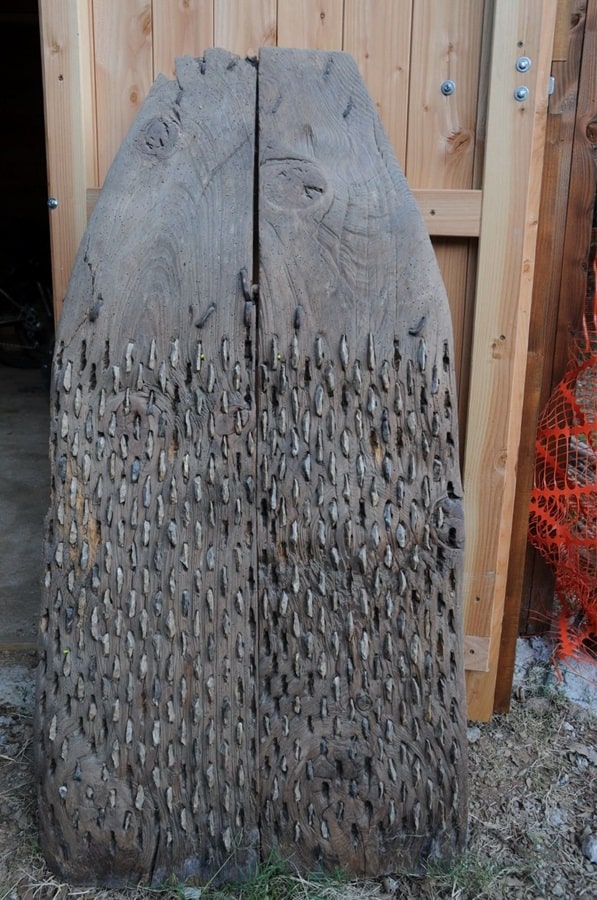

In recent years – adds Mazzucco – more and more evidence has emerged that the first domesticated animals were not only used as a source of food but also as labor. And threshing sledges are part of a broader process of technological innovation that involved the use of animals in this sense. The detailed analysis of archaeological findings and the use of advanced methodologies thus add a crucial chapter to the history of agricultural development and underline how the Neolithic was a period of significant technological advances.
The researcher concludes that this understanding of agricultural technologies’ spread and their effects on the social structure and economy of the time allows us to better understand the development dynamics of the first European agricultural societies.
The University of Pisa-led study’s findings, which were published in the most recent issue of the Journal of Archaeological Science: Reports, show that technological innovation has been present in the agricultural sector since prehistory and raises important questions regarding the dissemination of technological knowledge across the Mediterranean.
What until a few decades ago was considered a late innovation, today proves to be, in fact, a practice that has existed since the earliest Neolithic stages in Europe.