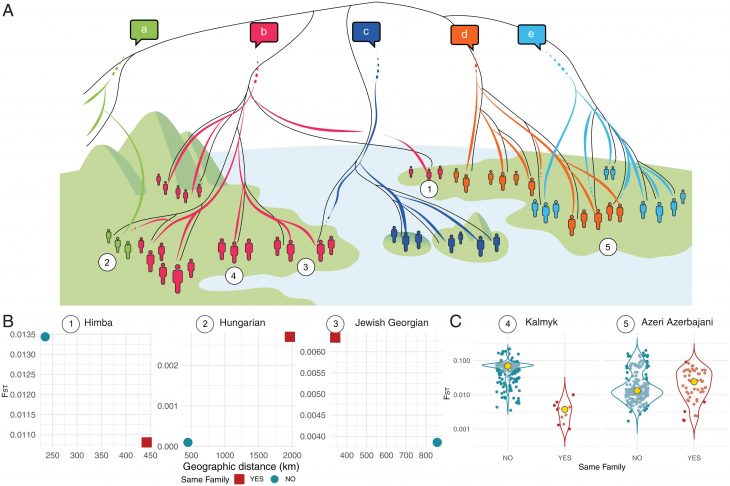
New research by a group of Austrian and Israeli scholars has finally deciphered a 1,900-year-old scroll describing a tense court case during the Roman occupation of Israel.
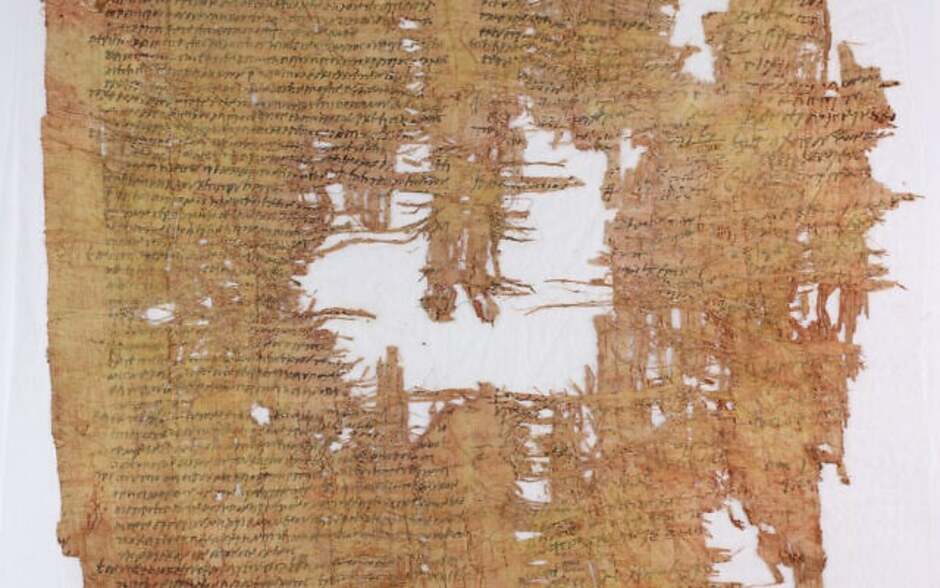
A recently deciphered papyrus, believed to have been stored with the Israel Antiquities Authority since the 1950s, has revealed significant insights into life in ancient Israel just before the Bar Kochba revolt (132-135 CE). Initially thought to be a Nabataean document, this Greek papyrus is the longest of its kind ever found in the Judean Desert. It contains crucial prosecutor’s notes related to a fraud trial and the minutes of proceedings before a Roman official nearly 2,000 years ago, shedding light on the legal and social dynamics of the time.
A chance rediscovery in 2014 has brought to light a remarkable papyrus, initially misclassified as Nabatean, by Hannah Cotton Paltiel, professor emerita at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem. While volunteering in the archives of the Israel Antiquities Authority, Cotton Paltiel identified the artifact as being written in ancient Greek. As scholars began to decipher the text, they uncovered details of a criminal trial involving two Jewish defendants, Saulos and Gedalias, who may have had ties to the planning of the Bar Kochba revolt.
Dr. Anna Dolganov from the Austrian Academy of Sciences emphasized the significance of the papyrus in a recent interview with The Times of Israel, stating, “We are talking about an extraordinary papyrus from many points of view.” The academic paper detailing these findings was co-authored by Dolganov, Prof. Fritz Mitthof of the University of Vienna, Cotton Paltiel, and Dr. Avner Ecker of the Hebrew University, and was published in the journal Tyche earlier this month. Dolganov also published a blog on the extraordinary find, “Romans go home!” in Der Standard.
“This is the best-documented Roman court case from Judaea apart from the trial of Jesus,” study co-author Avner Ecker, an epigrapher, or researcher of ancient inscriptions, at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem, said in the statement.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
In a fitting tribute to its discoverer, the newly uncovered papyrus has been named “Papyrus Cotton.” This significant artifact features 133 lines of text that provide a glimpse into the legal proceedings of the time. Researchers have determined that the papyrus likely contains notes used by a prosecutor preparing for a trial before Roman officials during the reign of Emperor Hadrian (A.D. 117 to 138), just prior to the onset of the Bar Kokhba revolt in A.D. 132—a pivotal Jewish uprising against Roman rule.

“Forgery and tax fraud carried severe penalties under Roman law, including hard labor or even capital punishment,” study co-author Anna Dolganov, a papyrus expert at the Austrian Academy of Sciences, said in the statement.
The court case detailed in the papyrus revolves around two individuals, Gadalias and Saulos, who allegedly forged documents related to the sale and emancipation of slaves in an attempt to evade Roman taxes. The study reveals that the document also includes a hastily written transcript of the trial and strategic notes exchanged between prosecutors.
However, researchers face challenges in fully deciphering the text due to significant portions of the papyrus being missing. Key details, such as the location of the trial, the residences of the defendants, and their status as Roman citizens, remain elusive, complicating efforts to grasp the complete context of this intriguing legal case.
The newly translated papyrus offers compelling evidence regarding a contentious issue: the ownership of slaves among ancient Jewish communities. According to the study, the document reveals that at least one Jewish family—specifically that of Saulos and his father—owned multiple slaves, although it remains uncertain whether these slaves were Jewish themselves.
Furthermore, the papyrus does not provide a definitive conclusion to the court case it references, which may have been disrupted by the Bar Kokhba rebellion. This significant uprising could have led the scroll’s owner to hastily abandon it in the caves of the Judaean Desert, where it remained for nearly two millennia alongside other Dead Sea Scrolls.
The discovery of the “Papyrus Cotton” not only enriches our understanding of ancient legal practices but also challenges long-held perceptions about social structures within Jewish communities of the time. As scholars continue to unravel its contents, this remarkable artifact serves as a crucial piece of evidence in the ongoing discourse about slavery in ancient Israel.
Cover Image Credit: Israel Antiquities Authority