The Basilica Cistern, one of the magnificent ancient structures of Istanbul, was restored. Besides being the greatest work of the Roman period, the cistern is the focus of interesting narrations.
The two Medusa heads, used as supports under the two columns at the northwest end of the cistern, are considered the reason why the cistern is mentioned in strange rumors, except that it is a great work of the Roman period.
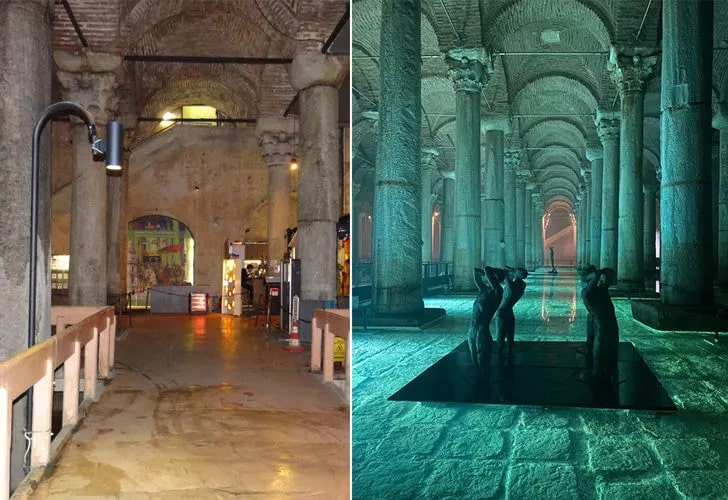
The Basilica Cistern is located southwest of Hagia Sophia. This large subterranean water reservoir was built for Justinianus I, the Byzantium Emperor (527-565), and is known as the “Yerebatan Cistern” among the public due to the buried marble columns. It is also known as Basilica Cistern since there used to be a basilica at the location of the cistern.
In 2017, Istanbul Municipality started restoration work on the Basilica Cistern. Istanbul Municipality President Ekrem İmamoğlu announced on his Twitter account that the restoration work, which lasted for 4 years, has ended and the visits to the Basilica Cistern will begin at the weekend.
The entrance and exit sections of the Basilica Cistern, which have not undergone extensive restoration work for 1,500 years, were arranged.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Due to the large number of people who wanted to visit the cistern and the narrowness of the entrance area, the visitors were forming long queues at the gate. The restoration covered the entrance area with glass eaves and a waiting area was made. Necessary plan changes were made in the exit section of the cistern, and a suitable and useful area was created for the building.
The Basilica Cistern is located in a rectangular area 140 meters long and 70 meters wide. The building, which has a water storage capacity of approximately 100,000 tons in an area of 9,800 m2, is accessible by a 52-step stone staircase.
There are 336 columns, each 9 meters high, inside the cistern. The columns are 4.80 meters long, forming 12 rows of 28 columns each.
Majority of the columns, most of which is understood to have been compiled from the ancient structures and sculpted of various kinds of marbles, is composed of a single part and one of it is composed of two parts. The head of these columns bear different features in parts. 98 of them reflect the Corinthian style and part of them reflect the Dorian style.
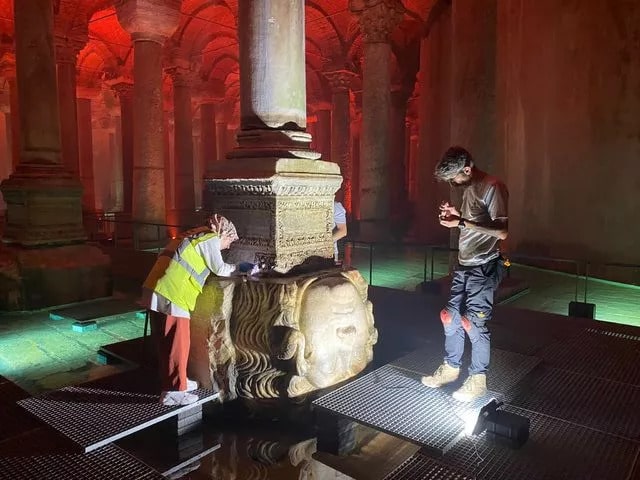

The two Medusa heads, used as supports under the two columns at the northwest end of the cistern, are considered the reason why the cistern is mentioned in strange rumors, except that it is a great work of the Roman period.
The fact that the structure from which the Medusa heads were taken is not known is a very remarkable detail.
The researchers often consider that it has been brought for being used as supports to the column at the time of construction of the cistern. However, this has not prevented myths for the heads of Medusa.
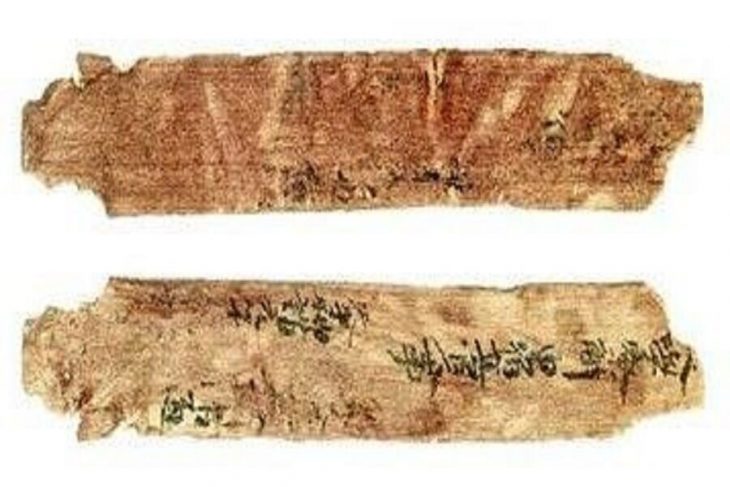
During the research on the Medusa heads in the Basilica cistern, some documents mentioned in Kara Kaplı, a diary kept by Sultan Abdülhamit II, were found. These documents in Kara Kaplı have carried the Medusa narrative to a very different dimension.
In 1456, a delegation of Italian origin income from Venice to meet with Fatih Sultan Mehmet. They demand to meet with the Sultan, but the Sultan assigns the grand vizier to meet with the delegation. The delegation tells the vizier about the treasure in the Basilica Cistern, but they say that they can only tell the Sultan the location of the treasure.

The subject attracts Sultan’s attention and he agrees to meet with a member of the delegation. The chosen representative tells the Sultan that the treasure in the Basilica Cistern is not a material thing, but a corpse. The committee, which offered a lot in return for this corpse and the sarcophagus (coffin) in which it was found, could not get what it wanted. According to what is mentioned in Kara Kaplı, this delegation is a member of a paganist sect.
After Fatih Sultan Mehmet, Abdulhamit Han took a close interest in the Medusa sarcophagus. When a delegation was sent to Abdülhamit Han to discuss this issue several times, the Sultan’s interest in Medusa increased and he asked for research on this subject. Abdülhamit Han, who decided to take out the sarcophagus in line with the information learned from the research and the delegations, and the people he assigned in this regard, find the sarcophagus in one of the corridors of the Basilica Cistern.
Inside the sarcophagus is the deteriorated mummy of a terrifying creature. The head of this creature resembles a human head, but with its entire body curves, it resembles a giant snake. This sarcophagus is taken under protection by the order of the Sultan. It is decided that the sarcophagus, which is wanted to be hidden from the public first, will be brought to light later on the condition that its cover is not removed.

One day, a child entered one of the corridors and saw the corpse inside and said to the people of Istanbul, “I saw Şahmeran!” event is heard. This sarcophagus weighing tons is brought to light with great difficulty and taken to the courtyard of Fatih Mosque and shown to the public for a short time.
By order of Abdülhamit Han, the photograph of the corpse was taken and published in the newspapers of that period. Today, there is no trace of the newspapers in which the photographs of this sarcophagus were published.
Although it is known that many foreigners are after the Medusa sarcophagus, it is also said that the delegations that came to the Sultan held rituals around this sarcophagus for years. It is a matter of curiosity whether these delegations have anything to do with the confiscation of the newspapers and the cover-up of the event.

The legend of Şahmeran: The legend tells about the great love of Şahmeran, a half-snake half-human woman, with Tahmasp. He mentions that Şahmeran is hidden in a cave, that he knows the secret of the world and that the one who eats his flesh will be healed. Those who seek Şahmeran for the health of the sick sultan find him thanks to Tahmasp and at the end of the legend, the vizier kills Şahmeran. Although it is not known what happened to Şahmeran’s body after he died, Tahmasp may have hidden Şahmeran’s body in a sarcophagus.
Perhaps we will never find out if Şahmeran and Medusa are the same woman. However, these legends, which have been going on for centuries, will continue to circulate centuries later.