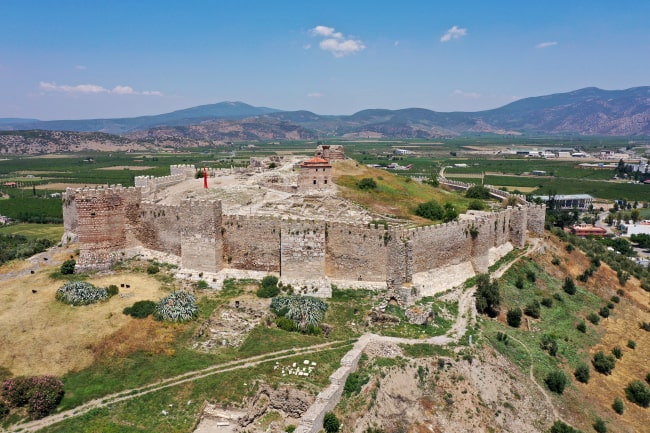
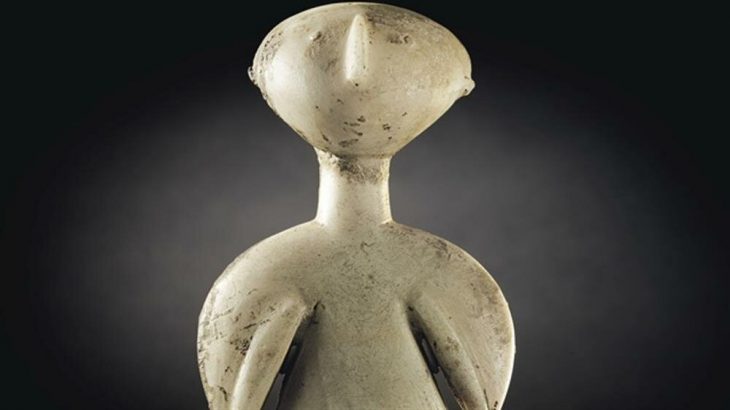
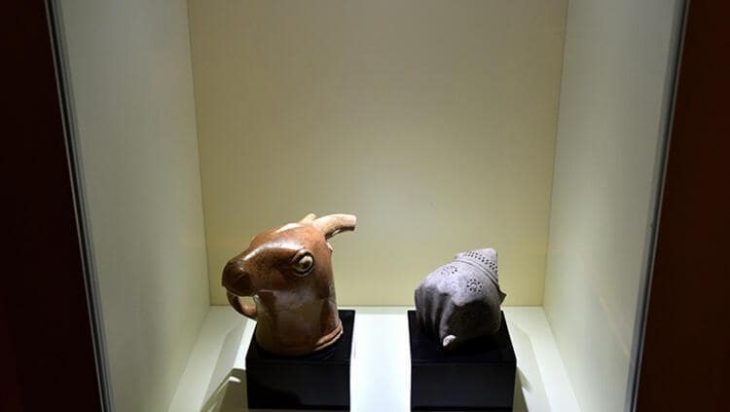
A 3,200-year-old Mycenaean figurine that could change the perspective on the history of civilization in Western Anatolia during the Bronze Age was found during the excavations at Ayasuluk Tepe in the Selçuk district of İzmir.
The statuette also strengthened the judgment that Appasas, the capital of the Arzava Kingdom, a kingdom affiliated with the Hittites, was founded in the Selçuk and Ephesus regions and that there was interaction in many areas such as trade between the Hittites and Mycenaean civilizations.
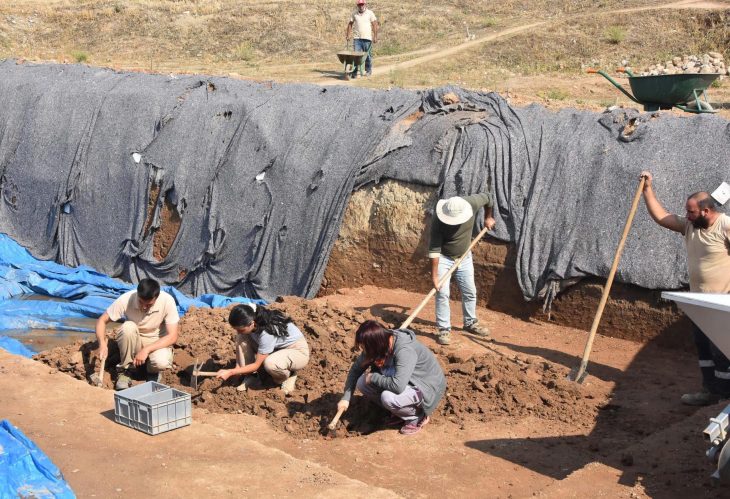
Hatay Mustafa Kemal University Art History Department Lecturer Assoc. Dr. Sinan Mimaroğlu During the excavations carried out under the direction of, a Mycenaean figurine with a height and width of 5 cm, whose head and feet could not be found, was unearthed, as well as ceramics from the Bronze Age.
25 scientists, who are experts in different disciplines such as art history, anthropology, and genetics, agreed as a result of the preliminary study that the Mycenaean figurine is strong evidence of a Bronze Age settlement on Ayasuluk Tepe.
Head of the excavation, associate professor Sinan Mimaroğlu, said that they were excited to find a Mycenaean figurine during the drilling in the ground they called bedrock.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
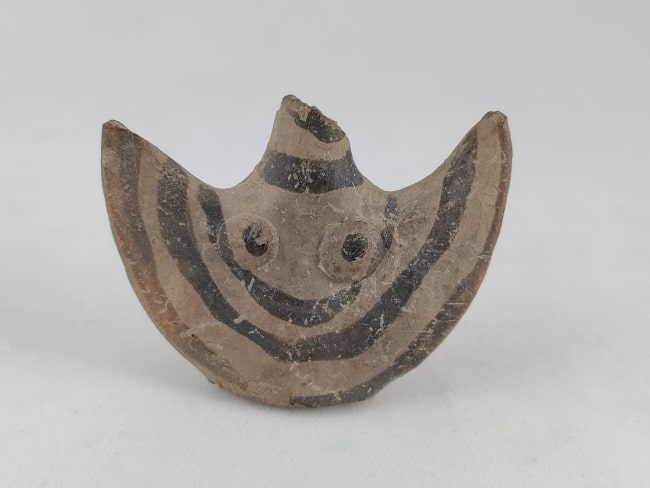

Noting that figurines in similar forms have been found in 5 more centers in Western Anatolia to date, Mimaroğlu said, “During the drilling work, we found a piece of a Mycenaean figure when we went down to the bedrock of the castle. The Mycenaean figurine is dated to 1200 BC. I can say that this find is another proof that Ayasuluk Hill is associated with Appasas, which was the capital city during the Hittite period.” used the phrases.
Despite the acceptance of many historians, Mimaroğlu stated that they could not scientifically match Ayasuluk Hill and Appasas without a seal, and gave the following information:
“The Mycenaean figure indicates that there was a strong Bronze Age settlement here. There were important centers and settlements in Western Anatolia, especially during the Hittite period. For example, Appasas, the capital of Arzava, is matched with Ephesus and Ayasuluk Hill. But scientifically, we need seals to make that nomenclature. I hope it will come out in the coming seasons. If those seals say it’s Appasas for sure, then we’ll be able to say for sure. With the pieces found so far, we’re on our way to calling it Appasas.”
Sinan Mimaroğlu reminded that similar Mycenaean figurines were found in Troy, Limantepe, Kadıkalesi, Miletos, and Iasos, which are Bronze Age settlements.
“This is where Ephesus was first established”
Emphasizing that Ayasuluk Hill was an important center for the late Bronze Age, Mimaroğlu said, “This is where Ephesus was first established. After all, it was a place on the seaside and they were trading.
“In the Late Bronze Age, we can say that there was a trade-in of ceramics, other materials, and mine between Western Anatolia and the islands or between continental Greece,” said.
“The material from which the figurines are made, namely the attribute of the clay, shows where they came from. According to our first observations, we think that the sample recovered was an imported material. It may have come from the islands,”.
We think that the people of that period also had this financial power since it was quite expensive to bring materials from abroad at that time. We found a large number of eaten oysters at the same level. The findings suggest that the upper class, that is, the class with monetary power, could access this food. The Mycenaean figure, these oyster shells, and the ceramics recovered actually complement each other like a vase.”
Known as the first settlement in Ephesus, where there has been an uninterrupted settlement for approximately 9 thousand years, starting from the prehistoric period, Ayasuluk Hill is located in the city center of Selçuk, approximately 3 kilometers from the Ancient City of Ephesus.