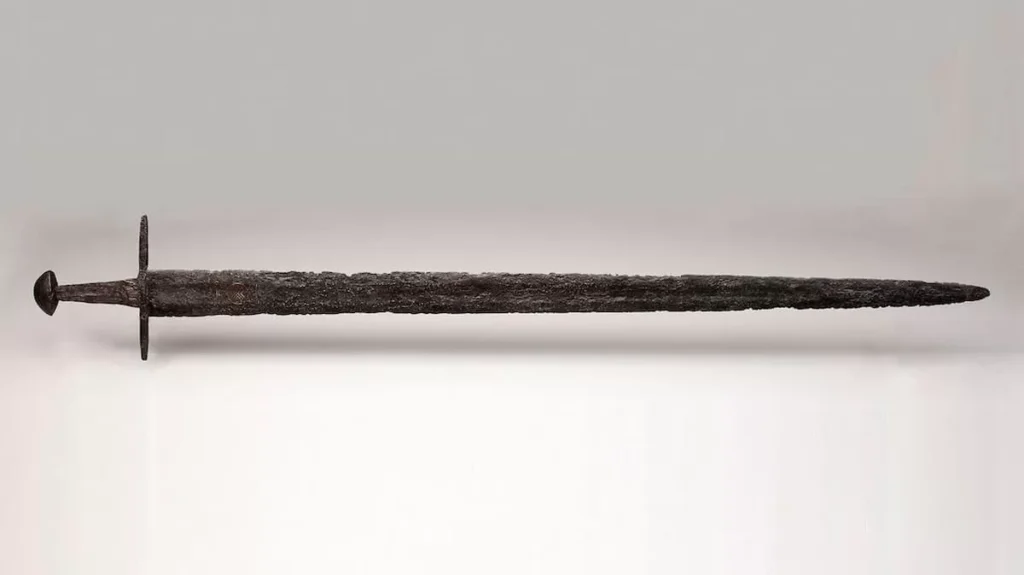
A remarkable medieval sword, dating back nearly 1,000 years, has been discovered in the Dutch province of Utrecht bearing a powerful ancient symbol of eternal loyalty and strength.
Found in March 2024 during routine dredging work in the Korte Linschoten River, the sword features a rare “endless knot” motif engraved on its blade—a powerful emblem tied to Viking and early Germanic traditions, representing unbreakable bonds, protection, and spiritual unity.
Now on display at the National Museum of Antiquities (Rijksmuseum van Oudheden) in Leiden, the sword is considered one of the most culturally significant finds in recent Dutch archaeology.
A Unique Blade With Sacred Symbols
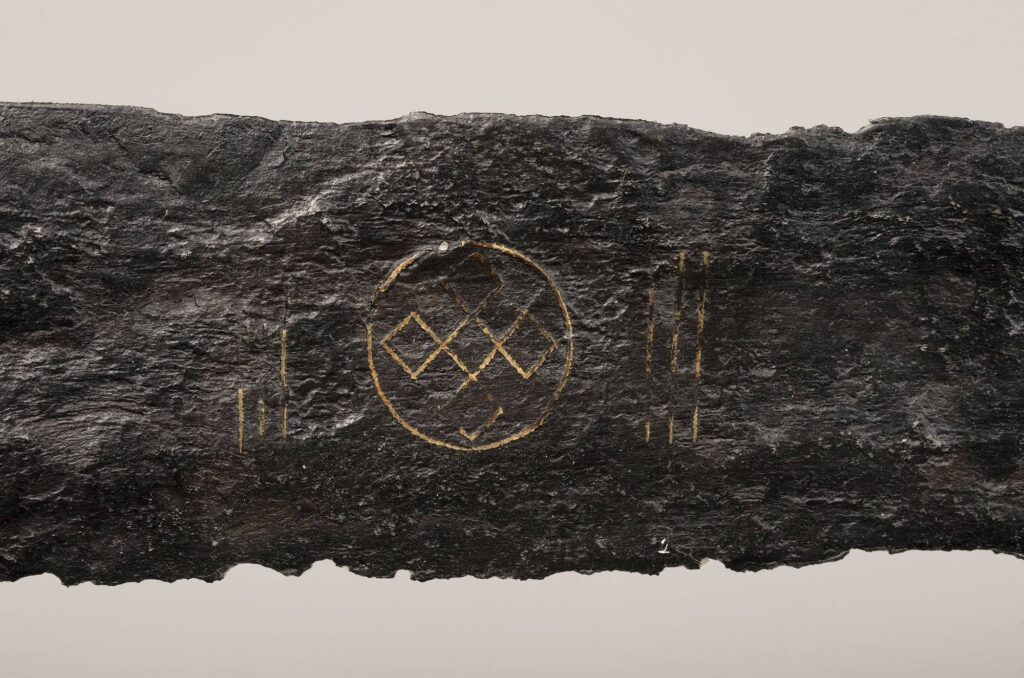
On one side of the blade, archaeologists identified the endless knot, formed by five interlaced squares inside a circle. This motif is widely associated with Viking and Germanic cultures, often representing unbreakable strength and spiritual unity. Despite being over 900 years old, the pattern is still clearly visible, delicately inlaid with copper-alloy wire.

The opposite side features another sacred symbol from medieval Europe: the sun wheel (sonnenrad)—a circle divided by a cross, historically used in church consecration rituals, particularly in Christianized frontier regions.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Experts believe the sword may have held ceremonial or symbolic significance beyond its function as a weapon. Its intricate decorations reflect the fusion of Christian and pagan traditions that characterized much of early medieval Europe.
Preservation and Possible Ritual Purpose
The sword was exceptionally well preserved due to the oxygen-poor clay in the riverbed, which prevented corrosion. After excavation, it underwent a ten-week conservation process involving salt extraction and tannin treatment to stabilize the metal.
Interestingly, no traces of a scabbard were found—leading archaeologists to believe the sword was deliberately deposited in the river as a ritual offering. At the time, the region was still being drained and colonized, and no nearby castle or estate had yet been built.

“This isn’t just a weapon—it’s a message in iron, preserved by the earth for nearly a millennium,” said a spokesperson from the Montfoort City Council.
Now on Display in Leiden
The so-called Linschoten Sword will be on view at the Rijksmuseum van Oudheden until September 2025, as part of its new acquisitions showcase. It was officially donated by the Municipality of Montfoort and Landgoed Linschoten to ensure public access and long-term conservation.
“This sword connects us directly to the people, beliefs, and artistry of medieval Europe,” said a museum spokesperson. “Its endless knot reminds us that even across centuries, symbols still carry meaning.”
Cover Image Credit: Ruben de Heer