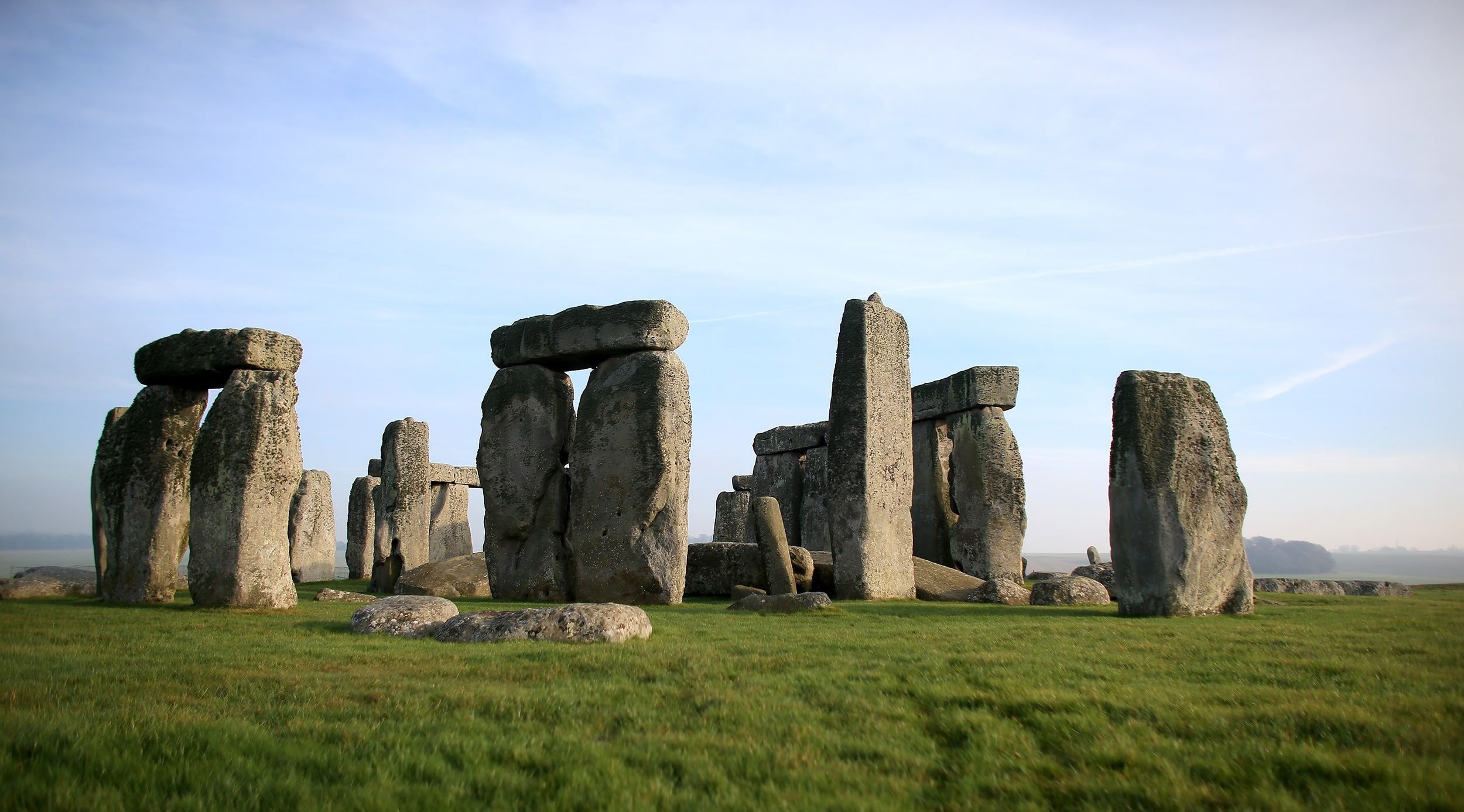
A new study posits that the Stonehenge circles served as a calendar that tracks the solar year of 365.25 days, calibrated by the alignment of the solstices.
Stonehenge may have served as a calendar to keep track of the yearly movements of the sun. In this case calendar, one with 12 months of 30 days, divided into 10 day weeks. Such calendar designs were previously seen in ancient Egypt. This suggests a prehistoric link to sun worship in the eastern Mediterranean.
While Stonehenge has long been thought to have some sort of calendar function, none of the theories adequately explained how it might have worked — and the new research is only possible because of a better understanding of the ancient site, according to Timothy Darvill, a professor of archaeology at Bournemouth University in the United Kingdom and the study’s author.
In a paper published in the journal Antiquity, Prof Darvill deduced that the stones are displayed to represent a solar year of 365.25 days and were once used to help people keep track of time.
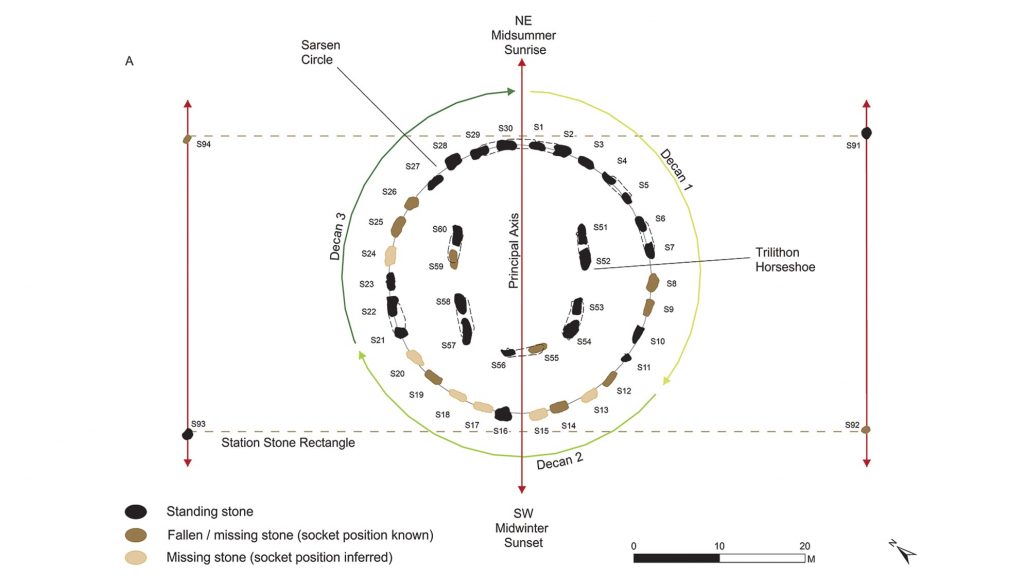
It seems Stonehenge was primarily aligned to the winter solstice in the Northern Hemisphere — Dec. 22, according to the modern calendar — when the sun rises and sets at its southernmost points, resulting in the longest night and the shortest day of the year.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
By aligning Stonehenge to the solstice and then using it to count the days in a year, the ancient monument could have accurately reflected the annual solstices and seasons for hundreds of years, Darvill said.
Professor Darvill said: “The proposed calendar works in a very straightforward way. Each of the 30 stones in the sarsen circle represents a day within a month, itself divided into three weeks each of 10 days.”
The main circle of Stonehenge today consists of 17 enormous stones known as sarsens, a term originating from the medieval English word “saracen,” which originally referred to Arabs but has since come to denote anything pagan. However, empty holes in the ground reveal that it was constructed as a complete circle of 30 sarsens; the others have since been carted away, most likely for other structures or roadways.
The solar calendar was developed in eastern Mediterranean countries after 3000BC and adopted in Egypt as the Civil Calendar around 2700BC. It was widely used around 2600BC, at the start of the Old Kingdom. This information raises the possibility that the calendar that Stonehenge tracks may be influenced by other cultures.