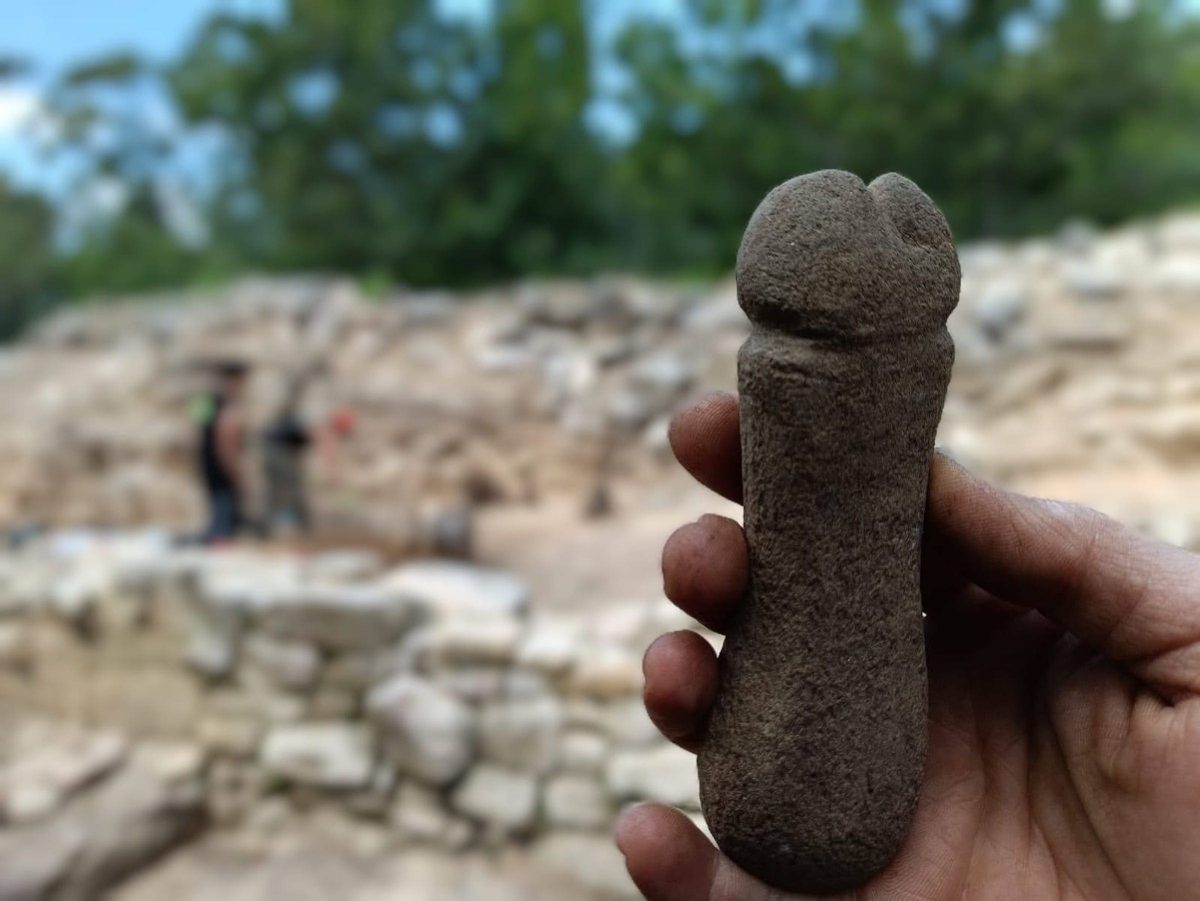
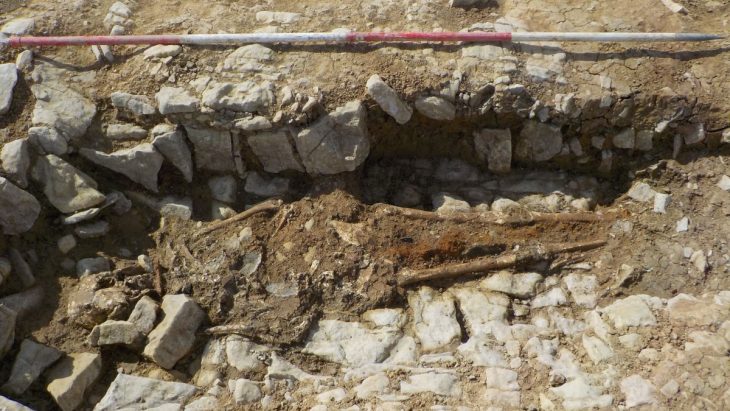
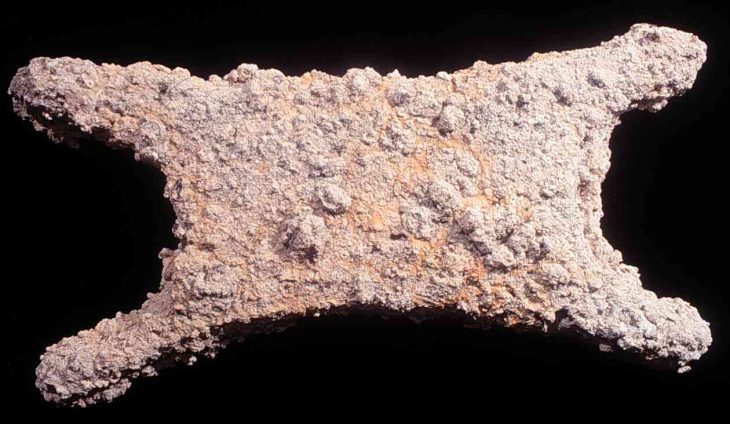
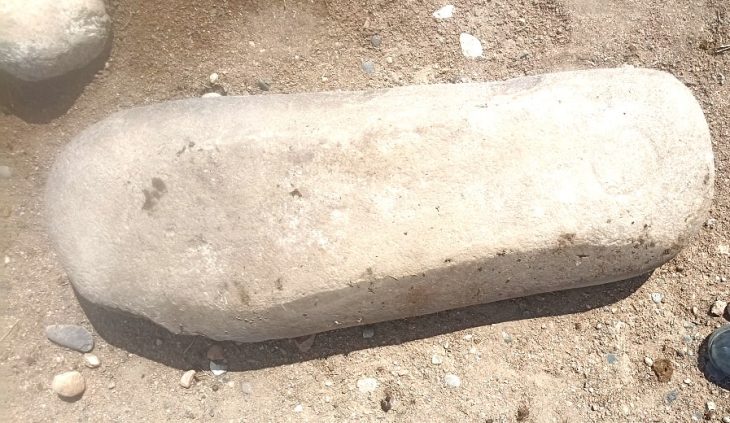
Archaeologists found a six-inch stone penis while excavating the Tower of Meira (Torre de Meira) in the city of Ría de Vigo in the northwest region of Spain.
Phallic symbolism is commonly found in prehistoric artifacts, but it is less common in finds from the medieval era. That’s why archaeologists couldn’t understand why this object was in medieval grounds.
But now the relic stands out, not just for its phallic form, but for its violent purpose – to sharpen weapons in preparation for bloody battles during the Irmandiño War in Spain.
Experts said this kind of symbolism may have been related to the violent uprisings taking place in the region around the time when the tower was demolished.
Torre de Meira was brought down in 1476 during the Irmandiño revolts when peasants rose up against the Spanish nobility. Some 130 castles and forts suffered the same fate.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
According to Darío Peña from the Árbore Arqueoloxía team, sharpening stones are commonly discovered at medieval sites, and can have different forms. The archaeologists determined the function of the stone penis by observing a distinct pattern of wear on one side of the phallic whetstone.
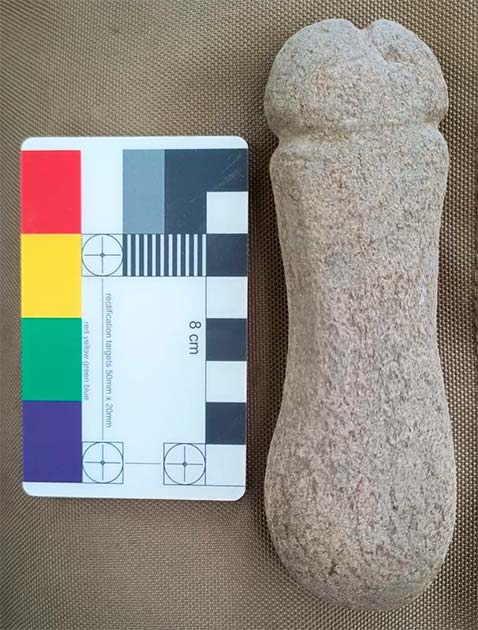

The artifact’s cultural significance is unknown, but its proximity to the fortified tower may provide some insight. It might have had a symbolic significance in relation to the war or served a useful function during that trying time.
“It materializes the symbolic association between violence, weapons, and masculinity,” archaeologist Darío Peña told Hyperallergic. “An association that we know existed in the Middle Ages and that is present in our culture today.”
The phallic stone was found among other artifacts including pottery and stone spindles according to Árbore Arqueoloxía e Restauración S. Coop. Galega, the group leading the excavations.
Excavations at this site began around 3 years ago. In the first phase of excavations, the tower was excavated and restored by Arbore. Just last year, the focus was shifted to the structure’s surrounding wall, and finally, the focus was shifted to the excavation of the main building. Archaeologists plan to continue excavations at the site, after seeking permission from the landowners in the municipality of Moaña.
Cover Photo: Árbore Arqueoloxía S.Coop.Galega