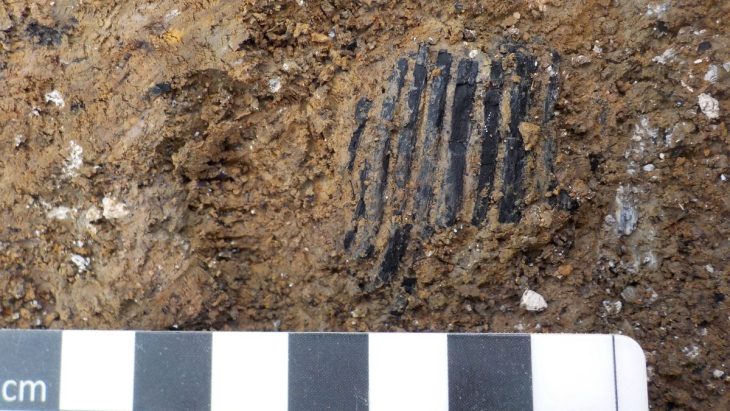
Archaeologists conducting excavations amid the renovation of the Neue Residenz in Salzburg’s Old Town have discovered a Roman ship’s bow crafted from bronze—believed to have adorned the walls or doors of a luxurious Roman city villa.
Salzburg, one of Austria’s most picturesque cities, lies in the northern foothills of the Alps along the Salzach River. Known worldwide as Mozart’s birthplace and for its UNESCO-listed baroque Old Town, the city has now added a remarkable new layer to its story. During renovations at the Neue Residenz in the historic center, archaeologists uncovered an ornamental bronze ship’s prow believed to have once adorned the walls or doors of a luxurious Roman villa.
A Bronze Relic of Roman Iuvavum
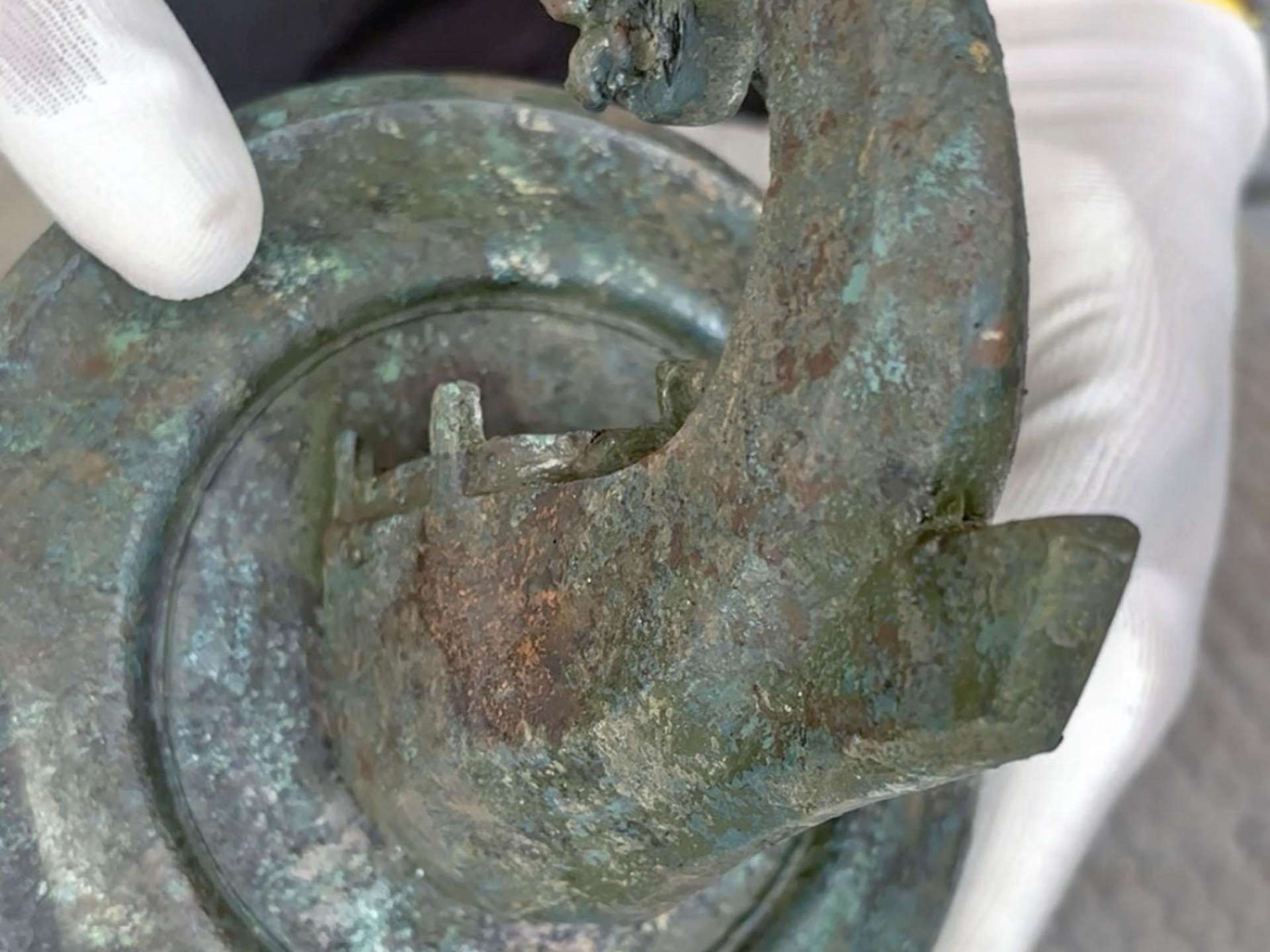
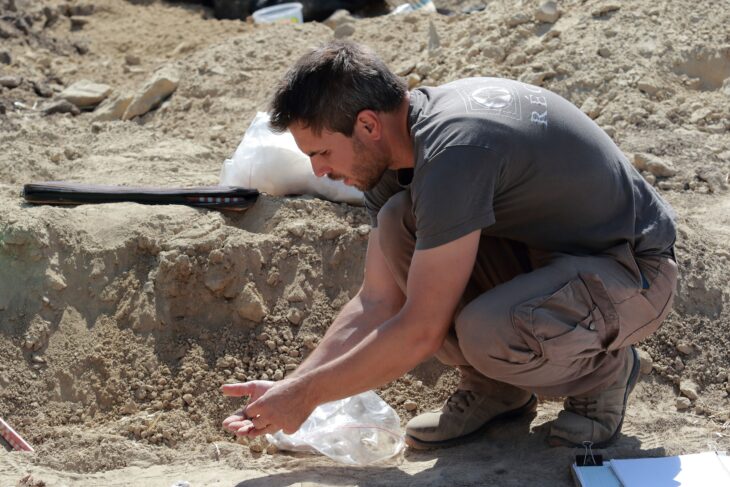
The object, weighing about one and a half kilograms, was unearthed in the second courtyard of the Neue Residenz. Beneath layers of rubble, researchers identified the remains of a Roman city villa dating to the 2nd or 3rd century AD. Within this protective layer lay the bronze ship’s bow—a piece that archaeologists immediately recognized as extraordinary.
Experts describe the find as the largest bronze artifact discovered in Salzburg’s ancient predecessor, Iuvavum, since the mid-20th century. Large bronze objects from antiquity rarely survive intact, as most were melted down and recycled for their material value. That this ornate fragment survived beneath collapsed walls is considered nothing short of remarkable.
From Mystery Object to Maritime Symbol
When first examined, the misshapen and fragmented artifact puzzled archaeologists. Because of its curved form, some thought it might have been an oil lamp shaped like a ship’s prow. Only after careful restoration did the true nature of the object emerge.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Under the microscope, conservators worked with scalpels and ultrasonic chisels to remove soil and corrosion. The fragile bronze was stabilized with custom acrylic resins, and its surface coated with microcrystalline wax to preserve it. Once secured, specialists created plastic replicas that allowed them to reconstruct the original shape.
The result was a clear image of a Roman warship’s prow, complete with a ramming spike. The level of detail even captured the delicate outline of the ship’s railing, confirming that this was no functional object but a decorative piece of high artistic quality.
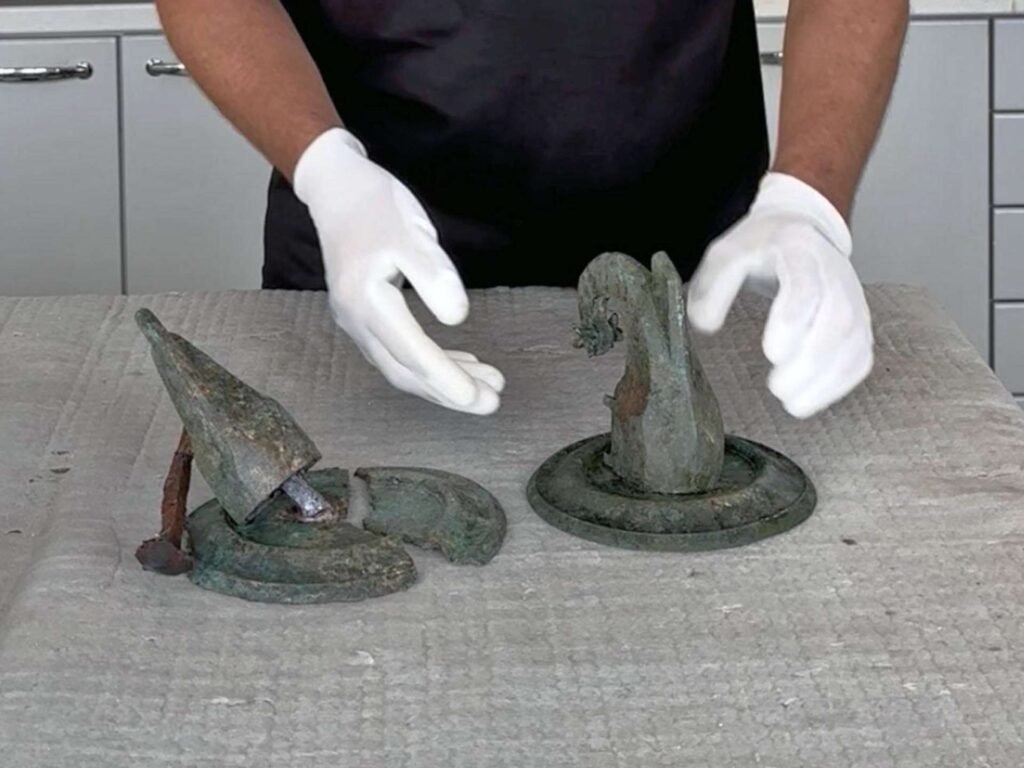

A Status Symbol of Roman Power
The ship’s bow would have been mounted onto a wall or door by means of an iron pin, secured with advanced casting techniques. Between the wall and the prow, an ornamental disc added to its visual appeal. For archaeologists, the placement of such a symbol within a Roman villa was highly significant.
In Roman culture, miniature representations of warships were potent emblems of strength and triumph. Historical texts describe wealthy households adorned with bronze ship prows, fasces, and axes—symbols associated with authority and state power. The Salzburg find fits seamlessly into this tradition.
Even in Rome itself, the term rostra—the famous speaker’s platform in the Forum—was derived from captured ship prows that decorated its façade. Displayed as trophies, they broadcast Rome’s military victories to all who passed by. For the owner of the Salzburg villa, displaying a ship’s bow would have been a clear statement of wealth, influence, and alignment with imperial values.
A Journey Through Time and Craft
The discovery also highlights the advanced craftsmanship of Roman artisans. Casting such an object in bronze required not only skill but also considerable resources, underscoring the villa owner’s elite status. The combination of detailed modeling, iron reinforcement, and ornamental integration illustrates both artistic ambition and technical mastery.
For archaeologists and historians, the artifact provides fresh insight into the cultural and social life of Iuvavum. It reveals how deeply Roman identity and symbolism penetrated even provincial centers far from the heart of the empire.
A Future on Display
The restored bronze ship’s bow will not remain hidden in museum storage. Plans are underway to present it to the public in 2028, when Salzburg opens its new Iuvavum Archaeology Museum. Alongside the original, a gleaming golden reconstruction will allow visitors to appreciate how striking the piece would have looked when newly cast.
For Salzburg, the find bridges past and present. The city that today charms visitors with baroque palaces and Alpine scenery once stood as a thriving Roman settlement. This bronze prow, buried for nearly 1,800 years, now resurfaces to tell a story of power, artistry, and cultural pride.

More Than Just a Discovery
Beyond its archaeological value, the ship’s bow has already captured the imagination of the public. It is not just a fragment of bronze—it is a symbol of continuity. From the Roman legions who once patrolled the Danube frontier to the modern city that thrives on history and tourism, Salzburg remains a place where culture, power, and art intersect.
The miniature prow reminds us that history often reveals itself when least expected. Hidden under layers of rubble, waiting through centuries of silence, it now speaks again—of Roman ambition, of craftsmanship, and of the enduring legacy of a city where past and present meet.
Cover Image Credit: Eram Khan – Salzburg Museum