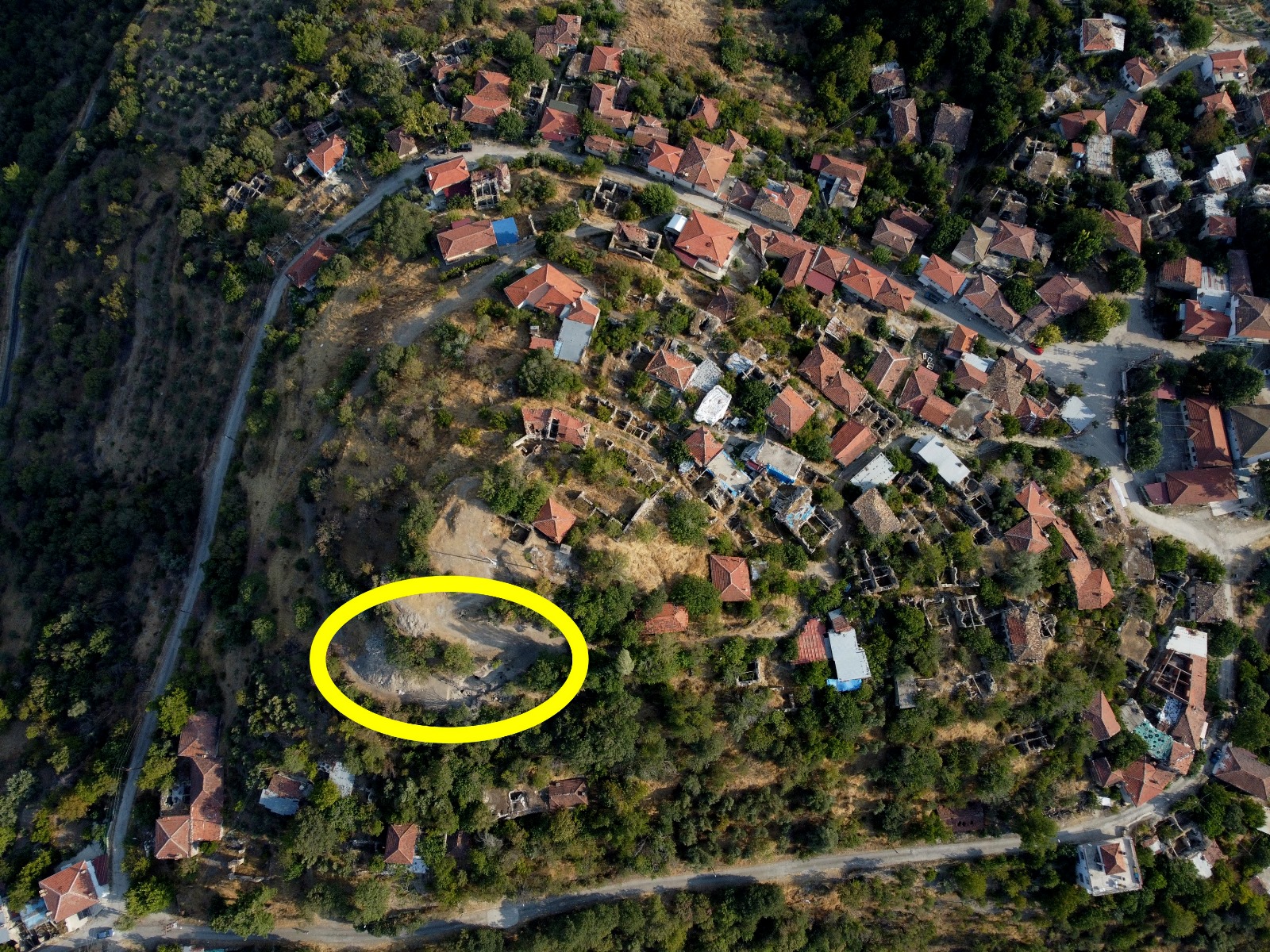
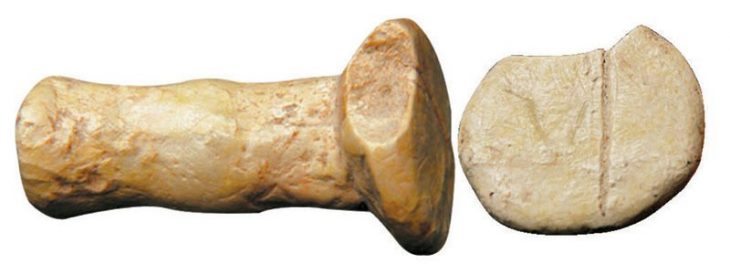
A groundbreaking archaeological discovery has been made in Attouda Ancient City, located in the Sarayköy district of Denizli, Turkey. Excavations have revealed a sacred sanctuary dedicated to the Phrygian Mother Goddess Matar (Cybele), dating back nearly 2,600 to 2,800 years. Within this sanctuary, archaeologists uncovered a monumental rock-cut shrine, a sacred cave, and a unique twin rock idol representing the Anatolian goddess of fertility and abundance.
This major find not only enriches the historical significance of Attouda but also challenges established knowledge of Phrygian religious borders, extending them further west into the Aegean region.
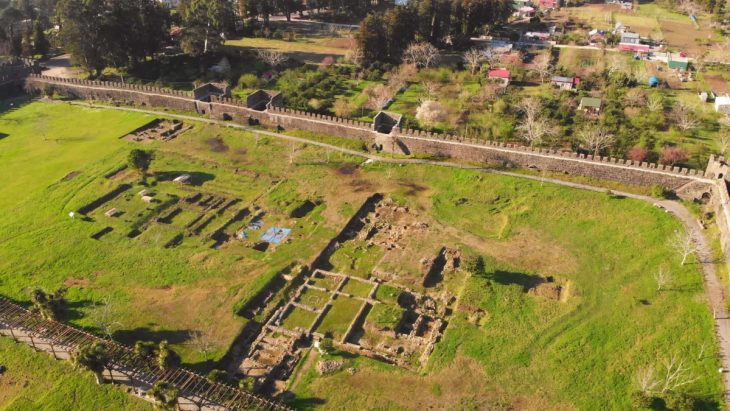
Discovery at Asar Hill, the Acropolis of Attouda
The excavation, part of the Heritage for the Future Project, is being carried out under the auspices of the Turkish Ministry of Culture and Tourism with support from the General Directorate of Cultural Heritage and Museums. The fieldwork is directed by Hulusi Ünsal, Director of Denizli Museum, with scientific supervision by Assoc. Prof. Bilge Yılmaz Kolancı from Pamukkale University’s Department of Archaeology.
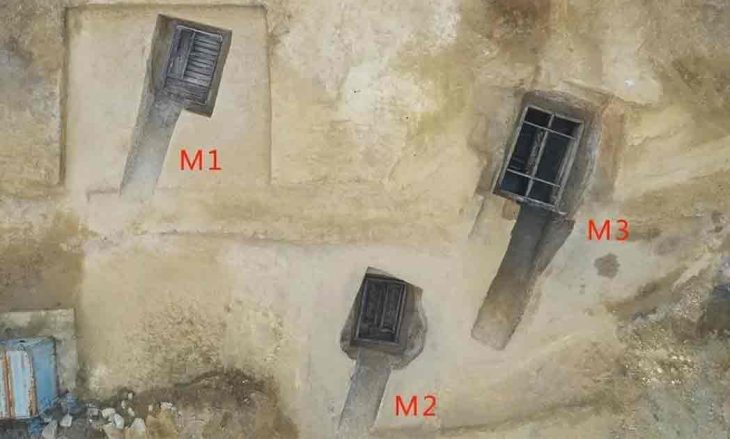
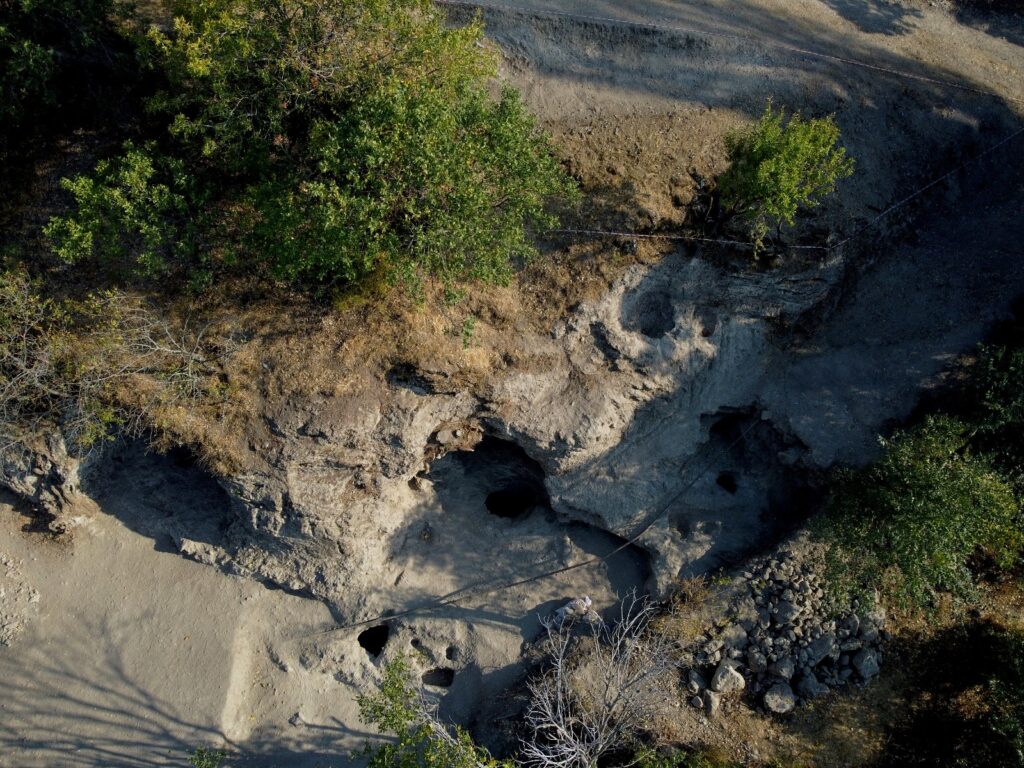
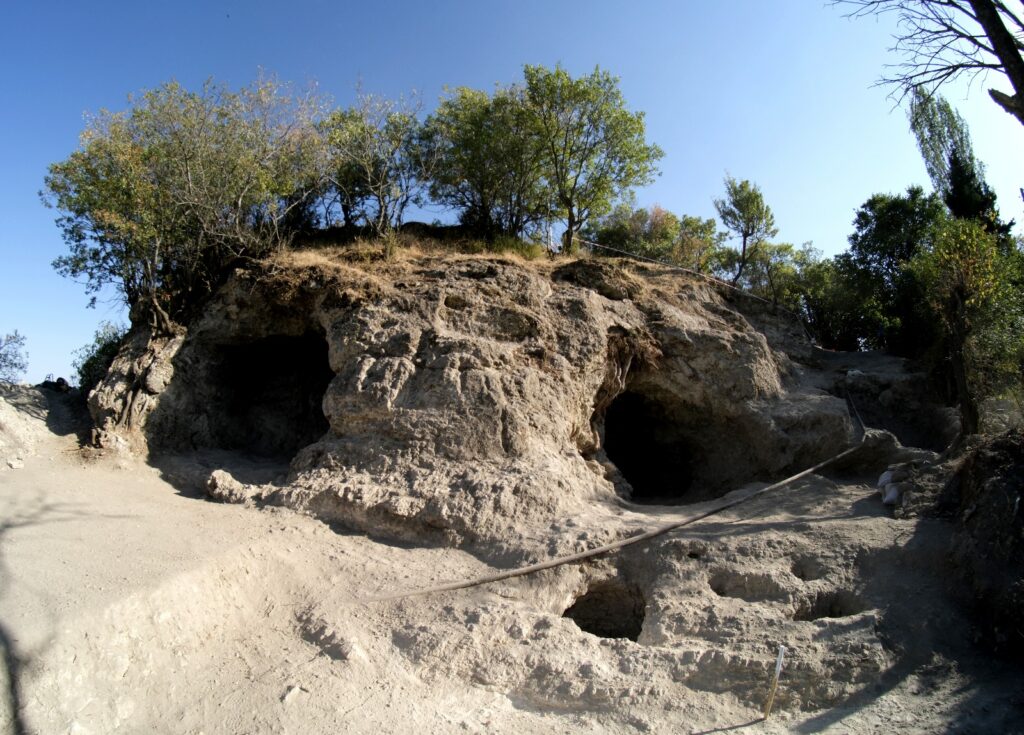
The sanctuary was unearthed on Asar Hill, the ancient acropolis of Attouda. Archaeologists identified a large religious complex used for ceremonial rituals dedicated to Matar. The complex includes:
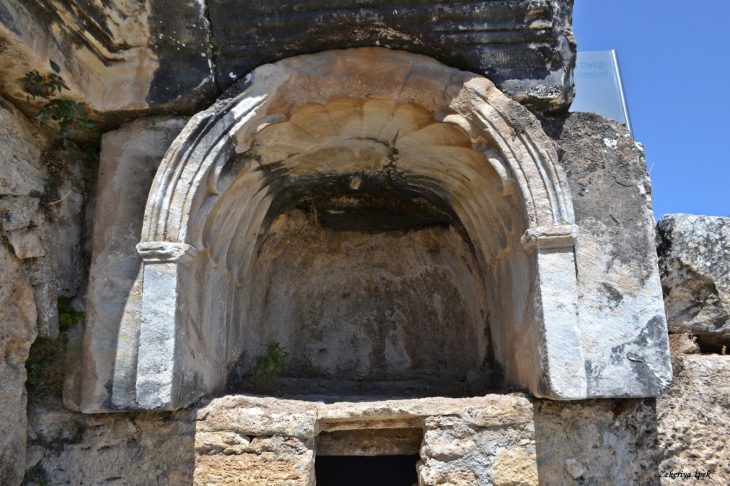
A Phrygian rock monument (8th–6th century BC), serving as an open-air temple.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
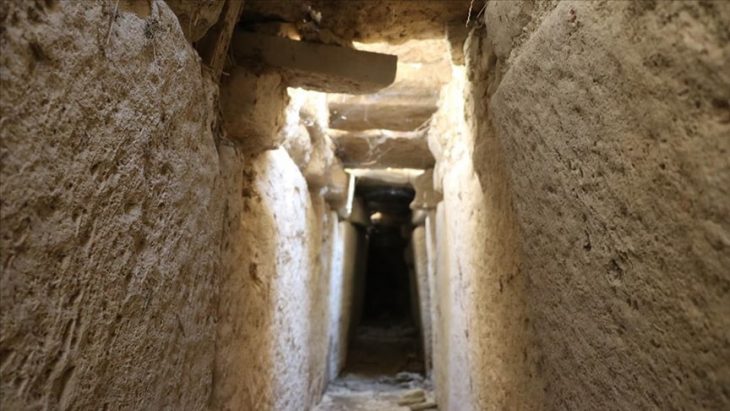
A sacred cave, thought to have been used for initiations and fertility rites.
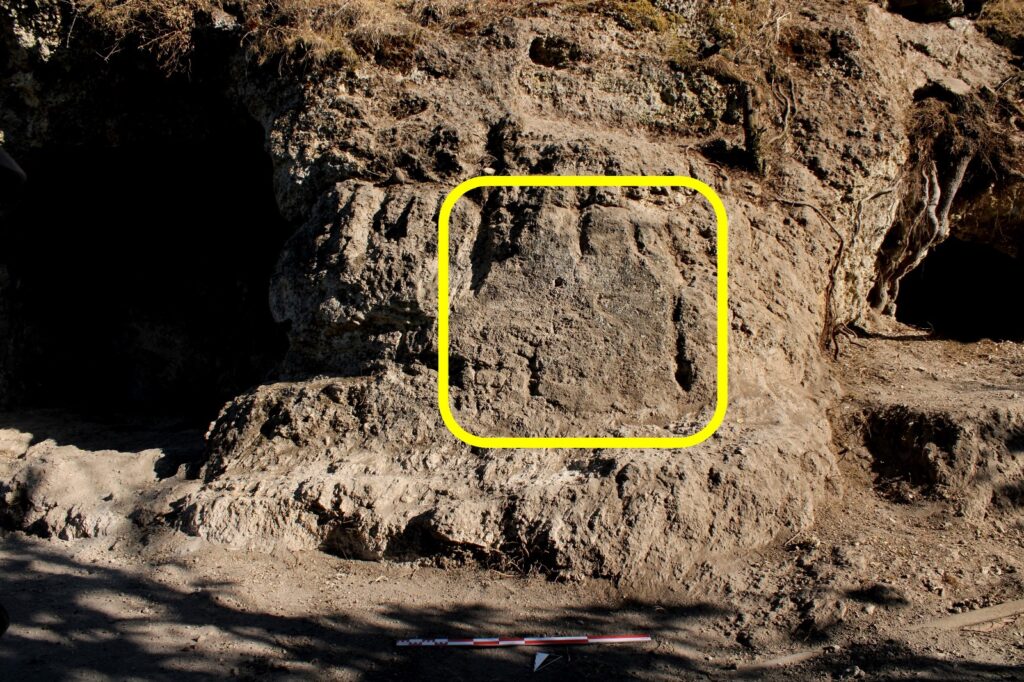
A twin rock idol, symbolizing the dual nature of the goddess and her association with fertility, life, and rebirth.
These discoveries suggest that Attouda was not only a regional power in antiquity but also a significant religious center.

Expanding the Boundaries of Phrygian Religion
Until now, rock idols dedicated to Matar had only been found in Mountainous Phrygia (covering present-day Eskişehir, Afyonkarahisar, and Kütahya). The discovery in Denizli, far from the traditional Phrygian heartland, reveals that the influence of the Mother Goddess cult extended much farther than previously believed.
Assoc. Prof. Kolancı emphasized the importance of this find:
“The presence of twin rock idols and a sacred sanctuary dedicated to Matar in Attouda proves that the religious boundaries of the Phrygians extended into western Anatolia. This is a remarkable breakthrough for understanding the spread of Phrygian spiritual traditions.”
The sanctuary also contained numerous rock-carved libation vessels, channels, and wells. These features were used in rituals of grain and liquid offerings, symbolic of honoring fertility, harvest, and the abundance bestowed by the goddess. Such findings provide valuable insight into how ancient communities celebrated agricultural prosperity and divine blessings.

The Legacy of Attouda Ancient City
Attouda, known in antiquity as a city of Caria and Phrygia, was strategically positioned between Laodicea and Hierapolis. It flourished during the Hellenistic, Roman, and Byzantine periods, with coins minted in its name and inscriptions linking it to various Anatolian cults.
The city’s location gave it both military and cultural importance, as it acted as a bridge between inland Anatolia and the Aegean coast. Over the centuries, Attouda became a vibrant center for trade, religion, and politics.
Key highlights of Attouda’s history include:
Its strong cultural ties with surrounding cities, particularly Hierapolis and Laodicea.
The spread of local Anatolian cults, including that of Matar, which coexisted with Greco-Roman deities.
Archaeological remains such as city walls, necropolises, and temples, reflecting its long urban history.
The recent discovery adds another chapter to Attouda’s legacy, positioning it as a vital hub for the worship of the Phrygian Mother Goddess, whose cult later evolved into the widespread worship of Cybele in the Greco-Roman world.

A New Era for Denizli’s Archaeological Tourism
The discovery of the Matar sanctuary in Attouda is expected to significantly boost both academic interest and cultural tourism in Denizli. Already home to the world-famous Pamukkale and Hierapolis, the region now holds yet another treasure that highlights the richness of Anatolia’s ancient civilizations.
Experts believe that continued excavations will uncover even more details about the ritual practices of the Phrygians and their cultural integration with Carian and Roman traditions.
Assoc. Prof. Kolancı expressed optimism about future work:
“Every layer we uncover tells us more about the spiritual life of ancient communities. The sanctuary of Matar is not only a religious discovery but also a bridge between cultures, showing how beliefs spread and evolved across Anatolia.”
Attouda’s Secret Reveals a New Face of Phrygia
The unearthing of the Matar sanctuary in Attouda Ancient City is a milestone in Anatolian archaeology. It not only reveals the depth of Phrygian spirituality but also cements Attouda’s place as a crossroads of civilizations where religious traditions converged.
As excavations continue, Attouda promises to shed more light on the interplay of cultures, gods, and rituals in the heart of Anatolia—offering a new perspective on how ancient peoples worshiped, celebrated fertility, and sought divine favor nearly three millennia ago.
Cover Image Credit: Arkeoloji Haber