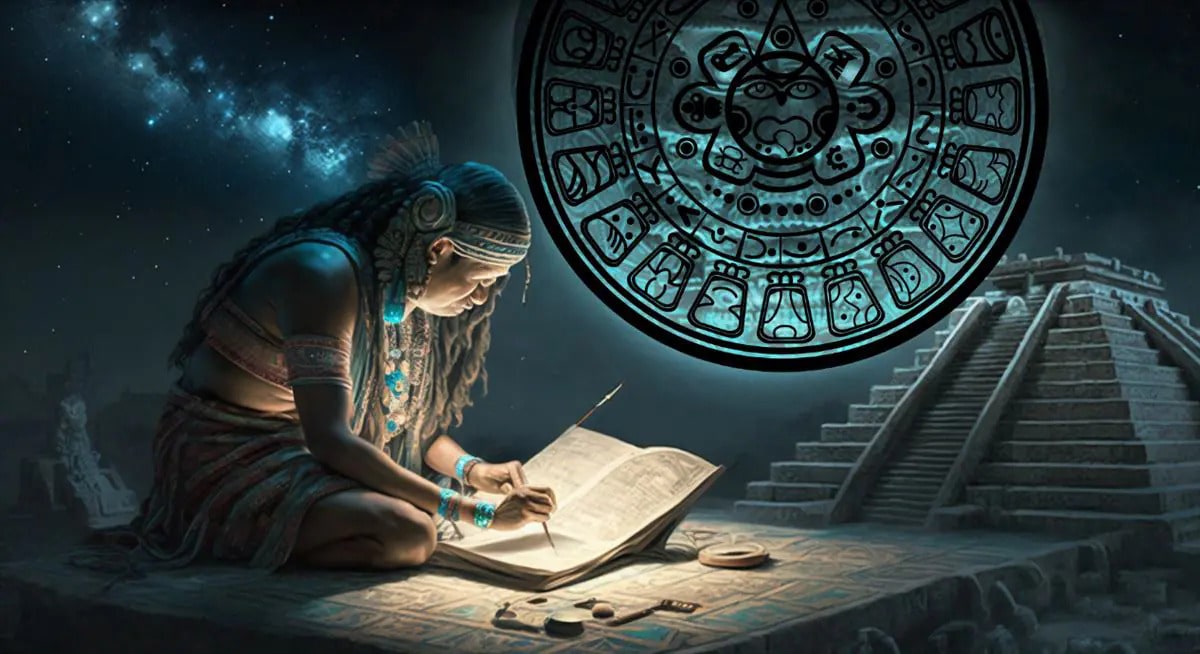
Researchers at Tulane University in Louisiana have solved the mystery of the 819-day ancient Mesoamerican calendar used by ancient Mayans.
The researchers were able to match the planetary cycles of every planet that might have been visible to ancient astronomers using a 45-year period.
Multiple calendars that were likely used by scholars at the time have been discovered during research on the ancient Mayan civilization, but not all of them make sense in today’s world. One such calendar was discovered in glyphic texts – the Mayans’ native writing system – and piqued the interest of researchers.
However, the astronomers did not leave behind any additional text or definitions explaining how it might work with their regular calendar system.
819-day calendar
The 819-day count and the motions of the celestial bodies, particularly Venus and Mars, were tracked by the Mayans using a calendar system. The synodic period, which is the amount of time it takes for these planets to return to their original positions with respect to the sun as seen from Earth, served as the foundation for this system.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The 819-day count was divided into 13 cycles, each lasting 63 days, and each cycle was based on a particular Venus or Mars phase. The cycles were given specific god names and were connected to various characteristics and traits. For instance, while the second cycle is named after the god of war and is associated with conflict and aggression, the second cycle is named after the maize god and is associated with growth and fertility.

This calendar system, which the Mayans found and developed, could not be adapted to any calendar system we use today, which made the number 819 mysterious.
Anthropologists John Linden and Victoria Bricker from Tulane University have studied the mystery of the Mayan 819 daily count, a type of ancient Mesoamerican calendar system, and have come up with important findings.
The study was published in the journal Ancient Mesoamerica.
When the researchers bumped into the idea of extending the time that the 819-day count can be used to represent the synodic period for all known planets, they found that the planets lined up perfectly. For example, they found that multiplying 819 by 20 equals 16,380 (about 45 years). And the 378 cycles of Saturn’s 13-day synodic period add up to 914,819 days, which is the same as six times 4.
Likewise, the same process can be used to show when all known planets will appear in the sky over the next 45 years. They also note that the number of days (16,380) used in mathematics is a multiple of 260, meaning that 819 rounds of 20-day periods match the Tzolk’in (general Mayan calendar).
According to the researchers, rather than focusing on just one or two planets, the ancient Mayans developed a large calendar system that could be used to predict the synod periods of all visible planets.