Archaeologists have uncovered a Roman Statue of Triton during excavations in preparation for a housing development in Kent, England.
Archaeologists from the Canterbury Archaeological Trust (CAT) have discovered artifacts, including a mausoleum which is to be buried within a roundabout, which are more than 1,700 years old during an investigative dig related to a new housing development close to London Road in Teynham.
Robert Masefield, Director for RPS, said: “We expected interesting Roman archaeology, perhaps a cemetery, but the finds including the lively and unique statue of a Triton and the mausoleum remains have by far exceeded that. These finds are now part of Teynham’s local legacy and the nations rich Roman story. Further study will place the findings in their full historical context.”
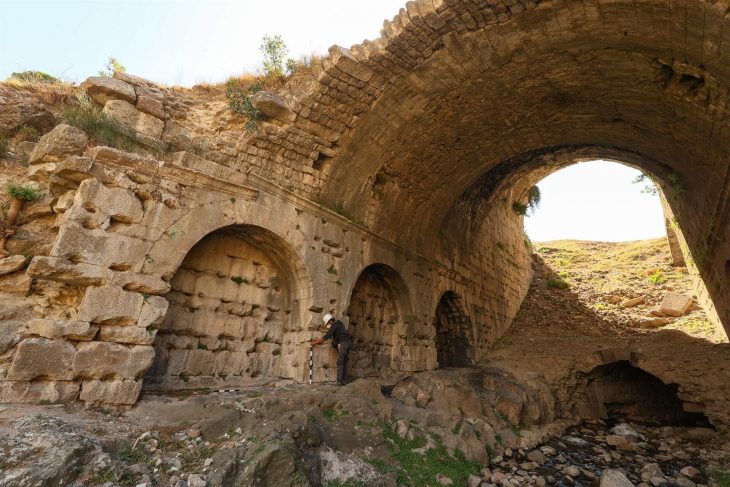
The area, which is being built on by Moat Homes and Chartway Partnerships Group for its Frognal Lane development, follows the ancient Roman Watling Street and during an initial site evaluation, fragments of chalk wall foundations and Roman cremation burials were discovered. As a result, Swale Council, with advice from Kent County Council Heritage Conservation, required a 0.5-hectare archaeological excavation at the site.
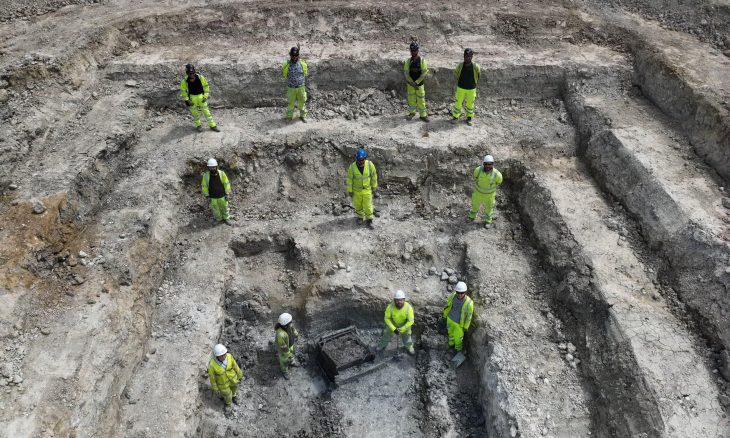
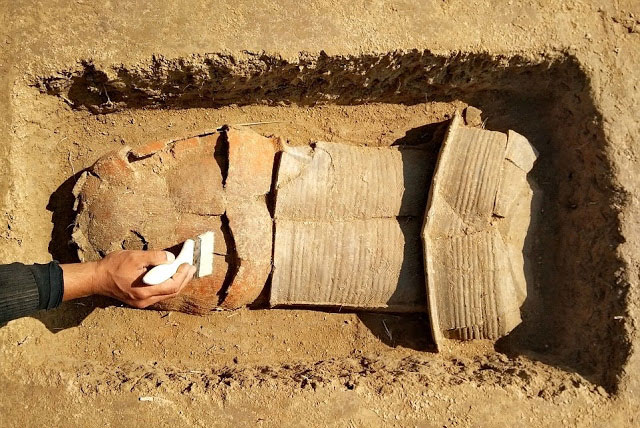
The Canterbury Archaeological Trust (CAT) was tasked with leading the dig, which revealed elements of a 30m square walled enclosure surrounding a c.7m square structure. Further excavations revealed that the structure is a Roman mausoleum containing a Roman coin dating from around 320 to 330 AD. The site also included Roman, and possibly later, burials with various grave goods.
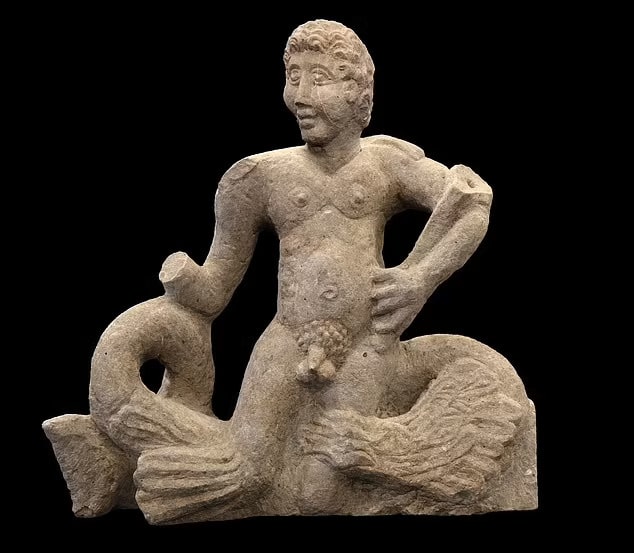

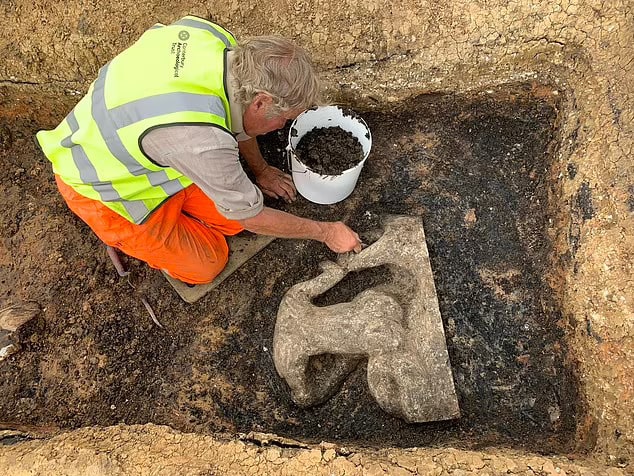
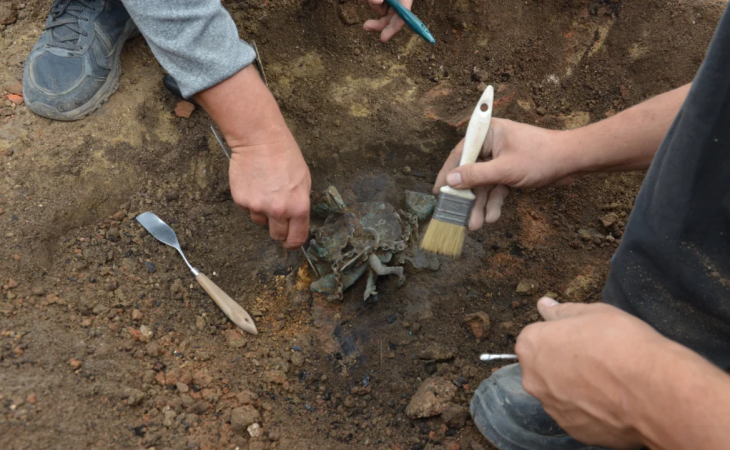
However, the highlight of the findings was the discovery of a stone statue, representing the sea god Triton.
The Triton statue is substantial, appropriately 70cm (27.5 inches tall) and 70cm wide. It weighs more than 132lb (60kg). Archaeologists did not need to dig far. It was only 1.3 feet (40cm) below ground.
In Roman mythology, Triton was the son of Neptune, the god of the sea. The unique stone statue depicts Triton – a merman with the torso of a man and the tail of a fish – riding on a sea monster.
As a demi-god, he could calm the waves by blowing on his conch shell, which he appears to be holding in the uncovered sculpture. That part has been broken off, but the artifact is otherwise in incredible condition. It was carved between the late first century and second century AD.
Dr. Richard Hobbs, senior curator of Roman Britain at the British Museum, told MailOnline it is ‘spectacular’.
He said that, although a few fragments of Triton sculptures are known from Roman Britain, ‘nothing quite like this has been discovered before’.
Excavations are continuing at the site.
Canterbury Archaeological Trust
Cover Photo: Canterbury Archaeological Trust