Are wars part of human nature? Do people tend to fight instinctively or do they war as a result of environmental factors? Whether war is a result of human nature or not is the main point of various disciplines such as anthropology, archeology, philosophy.
Researchers have put forward a series of ideas about why humans participate in wars. There is a long list of triggers for inter-group violence, whether it is the transition from hunting-gathering to agriculture, the development of weapons, ecological constraints, or population pressure.
The population pressure hypothesis has come to the fore recently with climate changes. The hypothesis points out that population growth will lead to scarcity of resources, leading to competition and conflicts for resources. Although this statement is widely accepted, few studies quantitatively support the origin of inter-group violence caused by population pressure based on actual archaeological data.
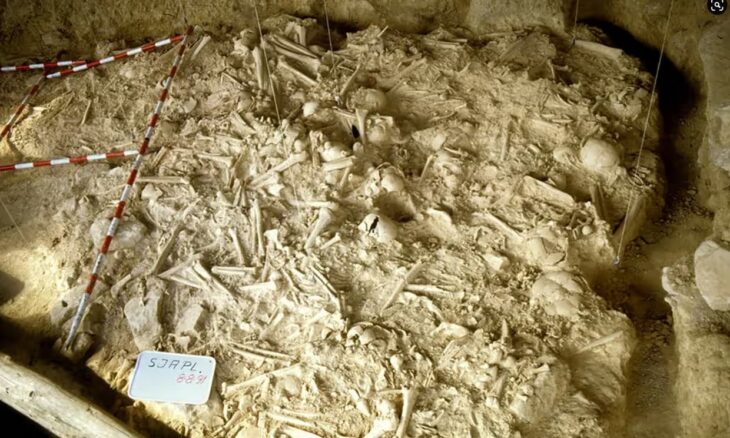
Professor Naoko Matsumoto of Okayama University and her colleagues studied skeleton remains and jar coffins, known as kamekan, from the Middle Yayoi era (350 BC to AD 25 CE) in northern Kyushu, Japan, to fill in the gaps in this hypothesis.
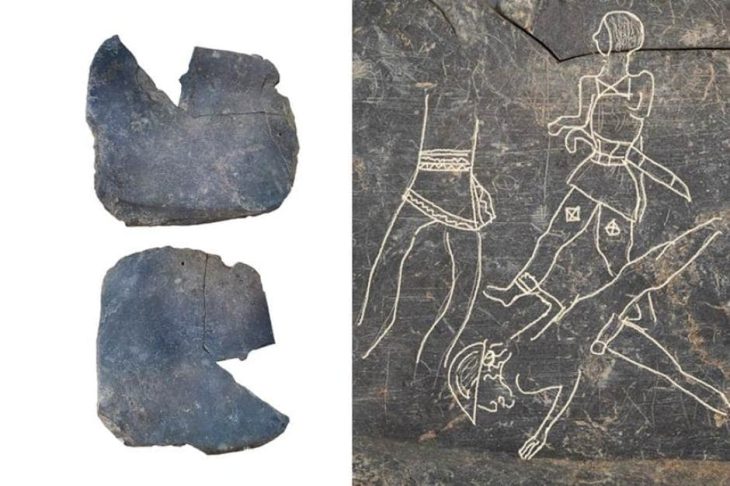
Because the skeletal remains in the Yayoi period suggest a large rise in the incidence of violence compared to those living in the preceding Jomon period, this region has been the subject of inter-group violence research.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
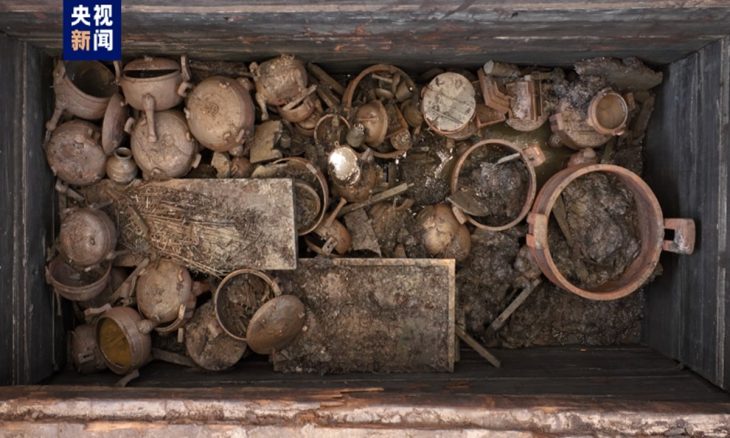
“The inhabitants of the Yayoi period practiced subsistence agriculture, in particular wet rice cultivation,” says Professor Matsumoto. “This was introduced by immigrants from the Korean peninsula along with weapons such as stone arrowheads and daggers, resulting in enclosed settlements accompanied by warfare or large-scale inter-group violence. However, those living during the Jomon period were primarily pottery-makers who followed a complex hunter-gatherer lifestyle and had low mortality rates caused by conflict.”
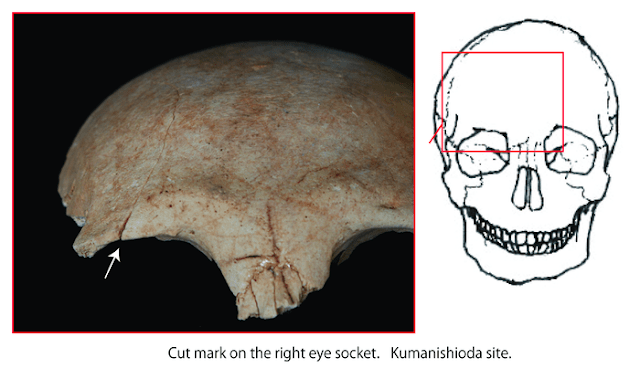
Professor Matsumoto and her team assessed population pressure from the ratio of population to arable land, using numbers of well-dated burial jars as a proxy for population size. The frequency of violence was determined using percentages of wounded people found among the skeleton population, followed by a statistical study of the relationship between population pressure and the frequency of violence.
The results of the investigation were published in the Journal of Archaeological Science. The researchers uncovered 47 skeletal remains with trauma, in addition to 51 sites containing burial jars in the Itoshima Plain, 46 in the Sawara Plain, 72 in the Fukuoka Plain, 42 in the Mikuni Hills, 37 in the east Tsukushi Plain, and 50 in the central Tsukushi Plain, encompassing all six study sites. They found that the highest number of injured individuals and the highest frequency-of-violence levels occurred in the Mikuni Hills, the east Tsukushi Plain, and the Sawara Plain. Interestingly, the Mikuni Hills and the central Tsukushi Plain also showed the highest overall values for population pressure. Overall, statistical analyses supported that population pressure affected the frequency of violence.
However, the peak population did not correlate with the frequency of violence. High levels of population pressure in the Mikuni Hills and the central Tsukushi Plain showed low frequency-of-violence values, while the relatively low population pressures of the east Tsukushi Plain and Sawara Plain were linked to higher frequency-of-violence levels.
Professor Matsumoto reasons there may be other factors that could have indirectly influenced such high levels of violence in the Middle Yayoi period. “I think that the development of a social hierarchy or political organization might also have affected the level of violence. We have seen stratified burial systems in which certain members of the ruling elite, referred to as ‘kings’ in Japanese archaeology, have tombs with large quantities of prestige goods such as weapons and mirrors”, she says. “It is worth noting that the frequency of violence tends to be lower in the subregions with such kingly tombs. This suggests that powerful elites might have a role in repressing the frequency of violence.”
The evidence collected by Professor Matsumoto and her team undeniably confirms a positive correlation between population pressure and higher levels of violence and may help devise mechanisms to avoid seemingly never-ending conflicts in motion today. Further research based on these insights could identify other variables at play in determining the root causes of inter-group violence and actively prevent them.
The study is published in the Journal of Archaeological Science.















