Researchers working in the Horn of Africa, also known as the Somali Peninsula have uncovered evidence showing how Middle Stone Age humans survived in the wake of the eruption of Toba, one of the largest supervolcanoes in history, some 74,000 years ago.
Modern humans dispersed from Africa multiple times, but the event that led to global expansion occurred less than 100,000 years ago. Some researchers hypothesize that dispersals were restricted to “green corridors” formed during humid intervals when food was abundant and human populations expanded in lockstep with their environments.
But a new study in Nature led by scientists at The University of Texas at Austin suggests that humans also may have dispersed during arid intervals along “blue highways” created by seasonal rivers. Researchers also found stone tools that represent the oldest evidence of archery.
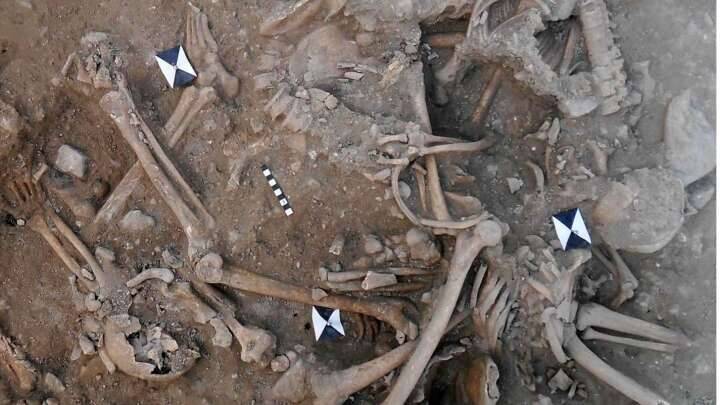
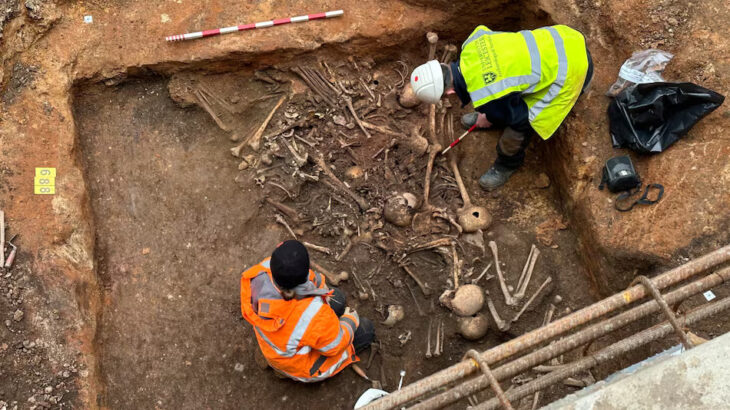
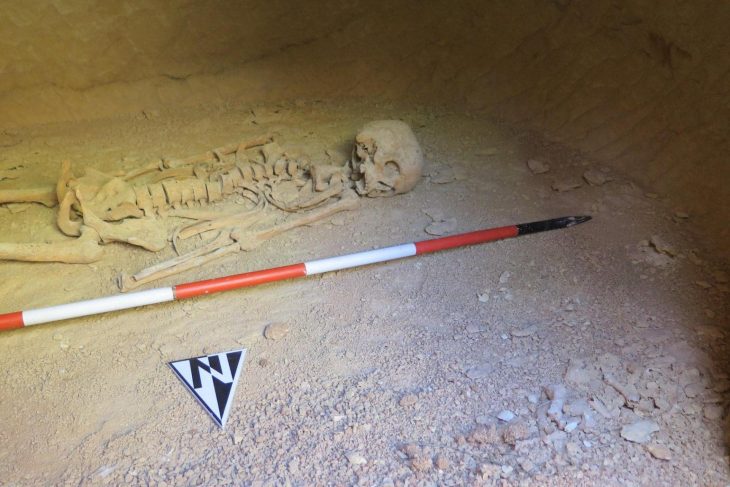
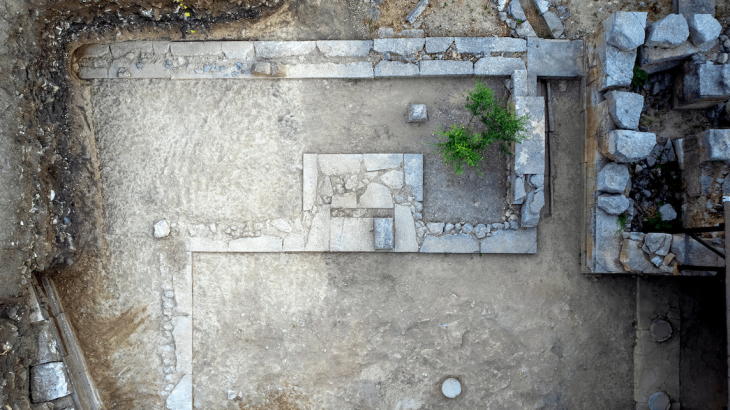
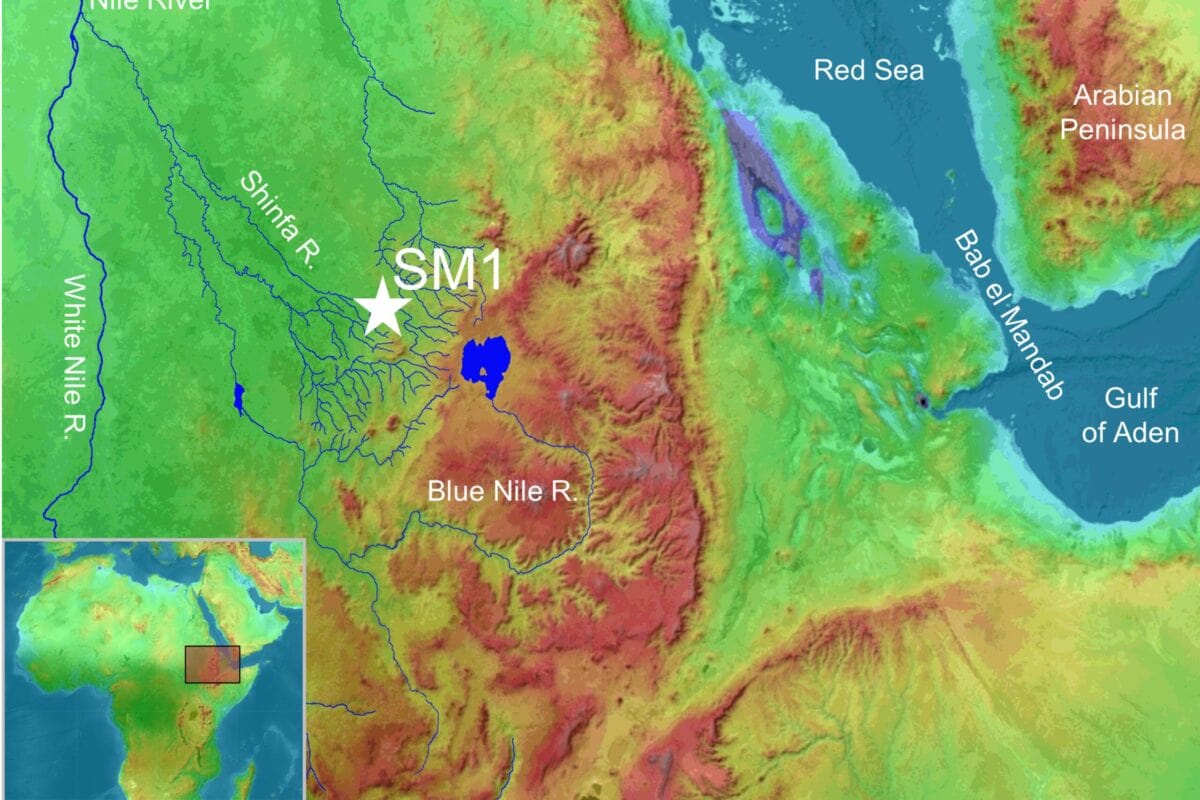
The research team examined a site called Shinfa-Metema 1 located in the lowlands of northwest Ethiopia near the Shinfa River, a tributary of the Blue Nile. They found evidence that this site was occupied during a period when the devastating Toba supervolcano erupted in Sumatra 74,000 years ago. Tiny fragments of volcanic glass, or cryptotephra, recovered from the archaeological deposits matched the chemical signature of the Toba eruption.
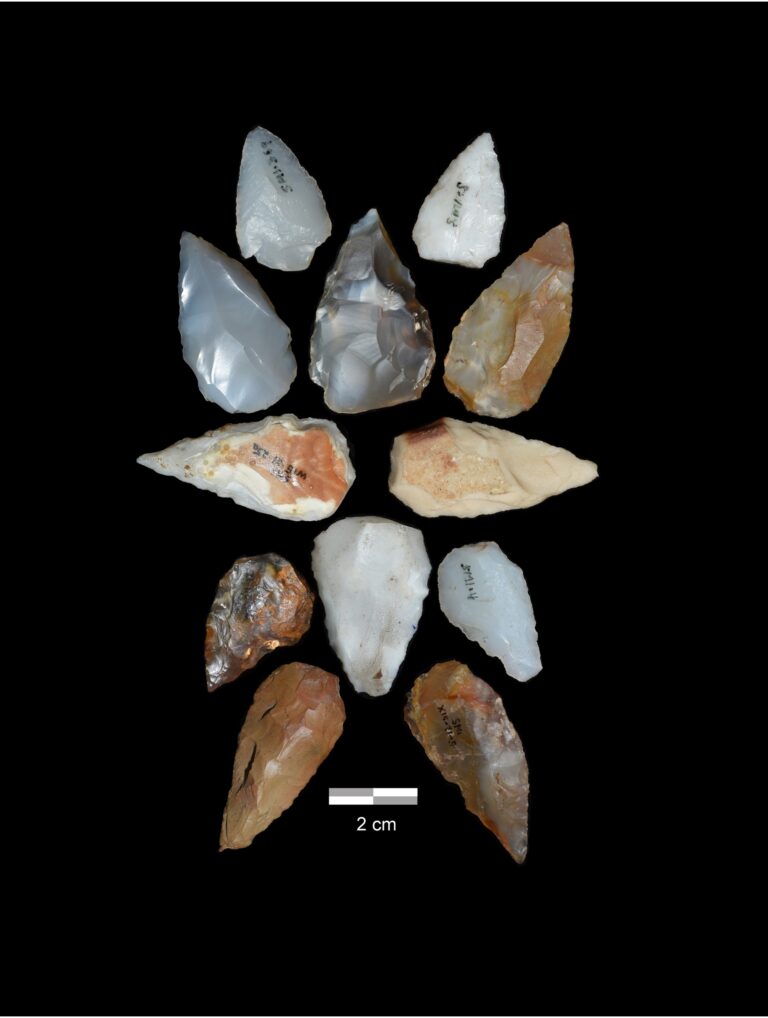

The Shinfa-Metema 1 site, shows humans were occupying the site before and after the volcano erupted more than 4,000 miles away.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
“These fragments are less than the diameter of a human hair. Even as tiny as (that) they are still big enough to analyze the chemistry and the trace elements,” said John Kappelman, a professor of anthropology and geological science at the University of Texas at Austin and lead author of the study, which published Wednesday in the journal Nature.
These microscopic shards of volcanic glass, often less than the width of a human hair, can be used to precisely date and correlate archaeological sites separated by thousands of miles.
One of the revolutionary implications of this study is that with the new cryptotephra methods developed for our previous work in South Africa, and now applied here in Ethiopia, we can correlate sites across Africa, and perhaps the world, with a time resolution of weeks, said researcher Christopher Campisano.

The supereruption occurred during the middle of the time when the site was occupied and is documented by tiny glass shards whose chemistry matches that of Toba. Its climatic effects appear to have produced a longer dry season, causing people in the area to rely even more on fish. The shrinking of the waterholes may also have pushed humans to migrate outward in search of more food.
Some scientists suspected a volcanic winter resulting from the eruption was a big enough shift to wipe out most early humans due to genetic evidence suggesting a steep drop in the human population.
But now this cutting-edge study on an archaeological site in northwest Ethiopia once occupied by early modern humans has added to a growing body of evidence that suggests the event might not have been so apocalyptic.
DOI: 10.1038/s41586-024-07208-3
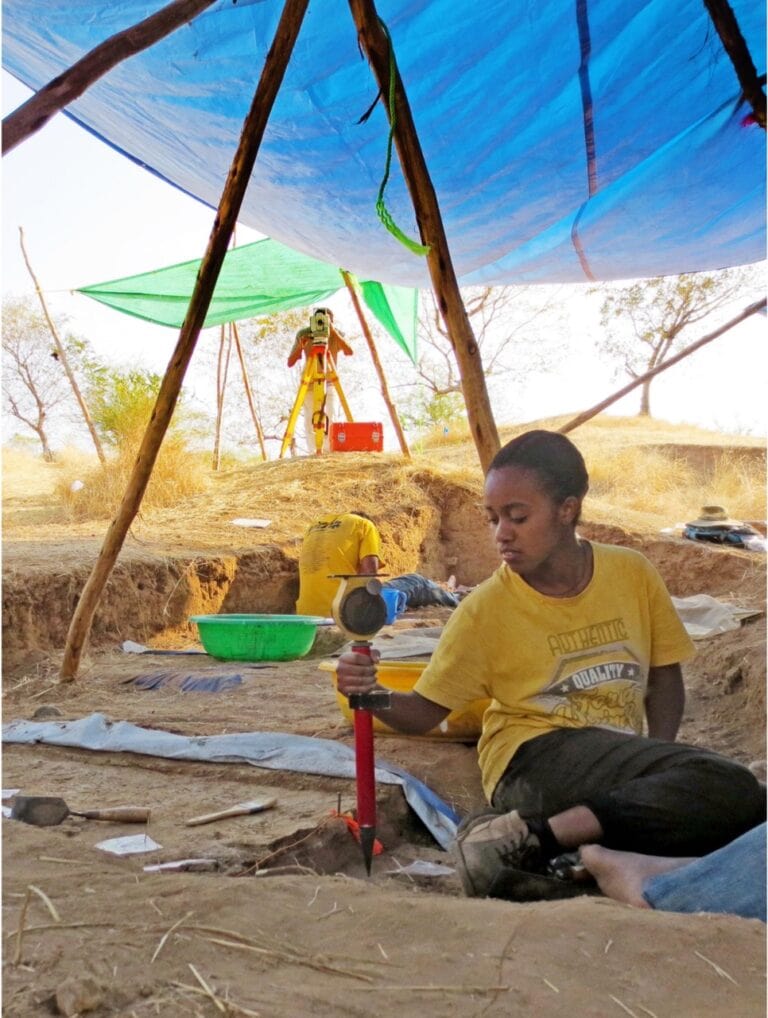
Cover Image: Excavations at a Middle Stone Age archaeological site, Shinfa-Metema 1, in the lowlands of northwest Ethiopia, revealed a population of humans at 74,000 years ago that survived the eruption of the Toba supervolcano. Credit: From topographic-map.com Open Database License (ODbL) v1.0