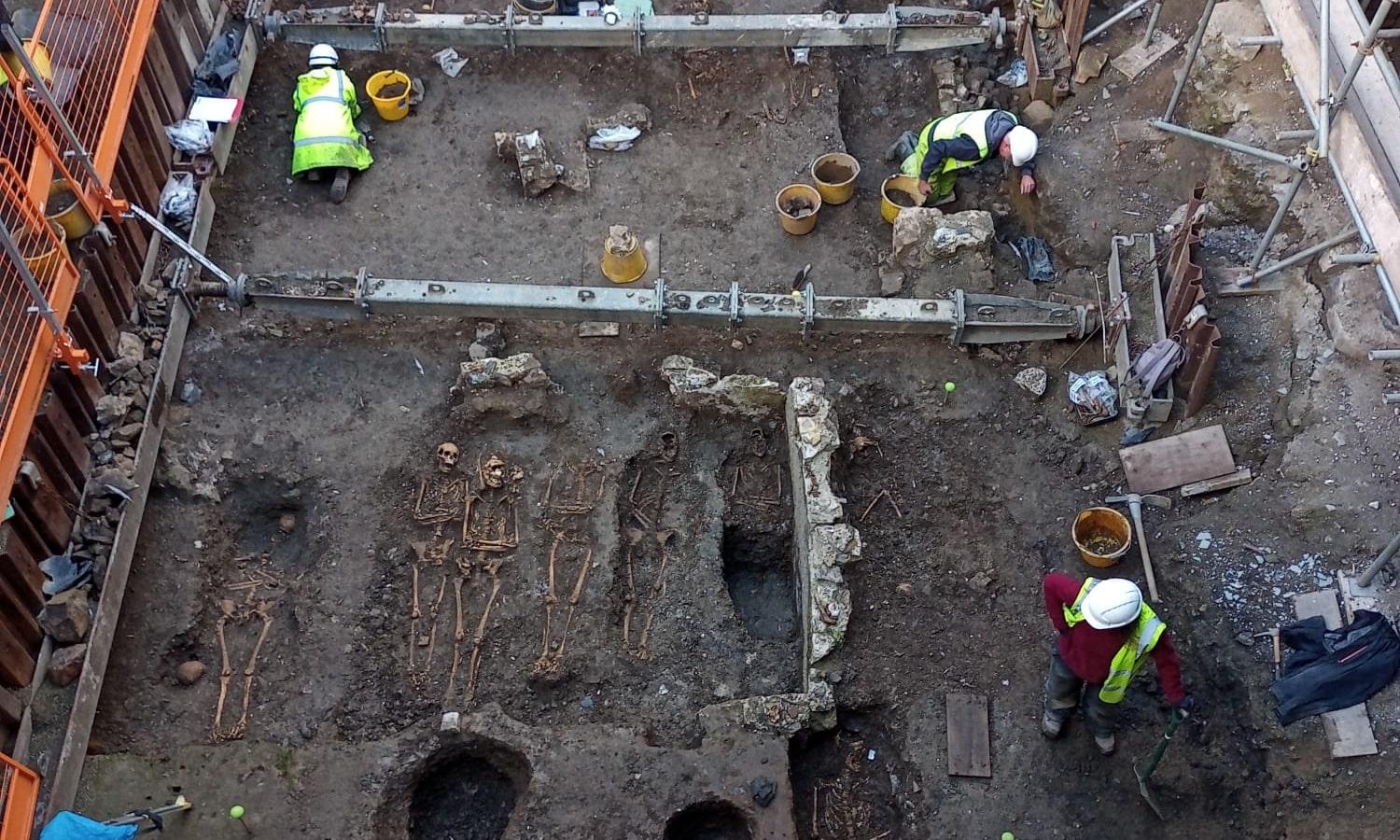
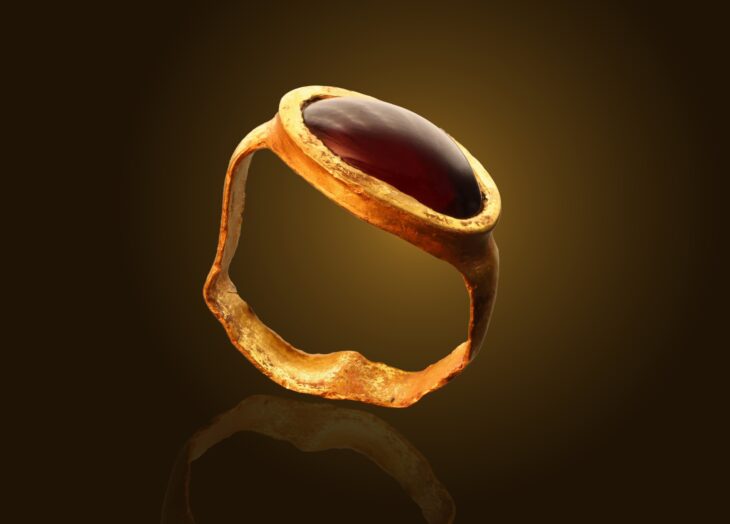
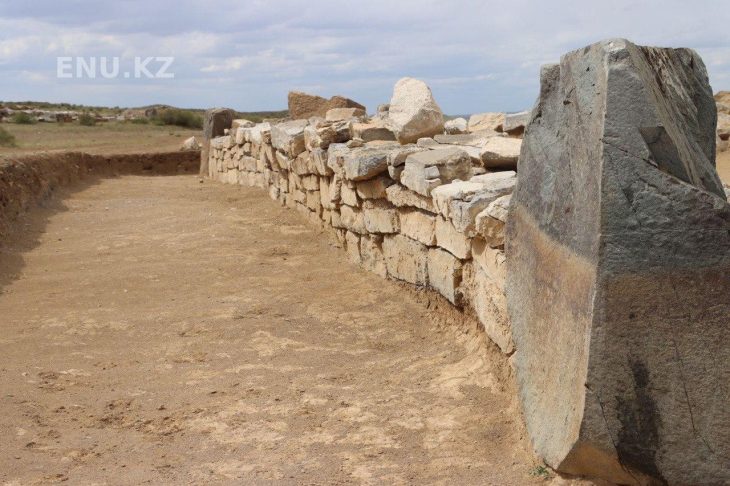
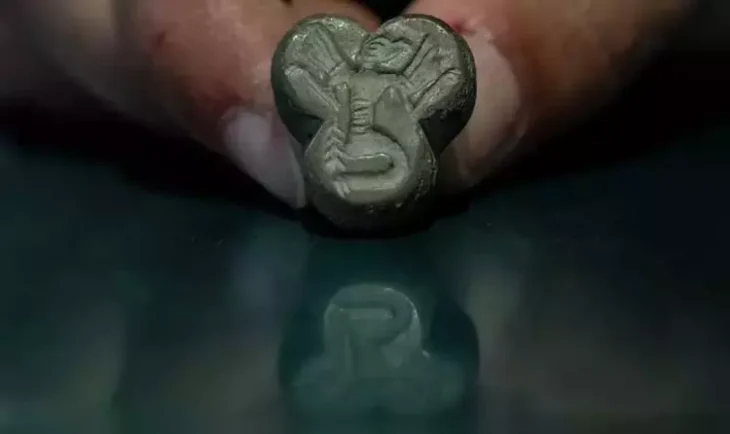
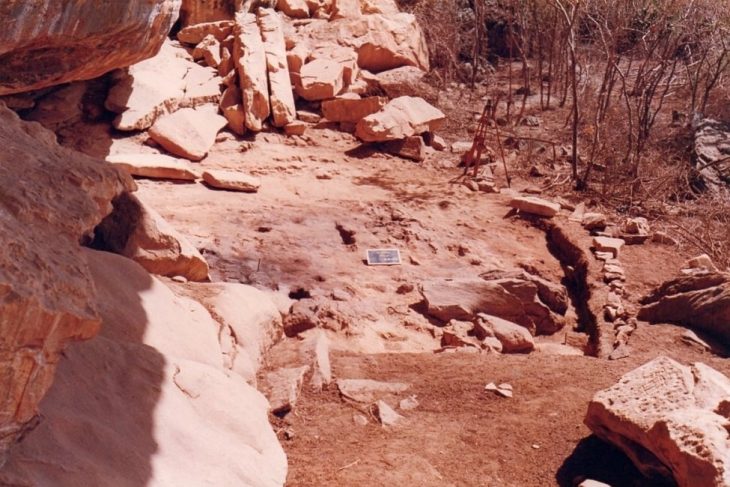
Archaeologists found skeletal remains of over more than 240 people, from beneath a former department store in Pembrokeshire in Wales, UK among remnants of a medieval priory.
More than a hundred of them are children, the majority of whom are infants under the age of four. The bodies were unearthed at the site of the one-time Ocky Whites department store, closed since 2013 and now slated for redevelopment.
The discovery has been described as “hugely significant” by experts. They believe the site is that of a priory named St Saviour’s, which dates to about 1256.
In addition, experts who stated that about half of the remains belonged to children, pointed out that this was a reflection of the high mortality rates in the past.
Henry III gave the friars 10 marks to build a church in 1246, according to the earliest known account of the Dominican friary of St. Saviours in Haverfordwest. Ten years later, they received an additional 15 marks to relocate to a new location, where they constructed a larger friary. Over the years, St. Saviors received numerous gifts and bequests, but by the early 16th century, as was the case with many monastic communities, its finances were deteriorating. In 1526, it began renting out its lands, and in 1535, it began to accept tenants.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
In the second round of monastic dissolutions, the friary saw its end. The forced visits, confiscations, and formal dissolutions that destroyed monasticism in England and Wales did not target more modest friaries like St. Saviors. By 1538, the goal was to persuade the last few settlements to voluntarily (?) hand over their homes to the Crown. On September 2, 1538, the eight remaining friars at St. Saviors signed the document, though the final signer appears to have changed his mind because his name is smudged off the document.
St. Saviours vanished from the landscape, leaving only names like Friars Lane and the Friars Vault pub in its wake. There were no historical records indicating its precise location, and the knowledge had faded over time. The discovery of the burial ground has contributed to the unraveling of the mystery.
It is thought to have comprised a complex of buildings including dormitories, a hospital, and stables, along with a graveyard that could have been used until the early 1700s.
Site supervisor Andrew Shobbrook, from Dyfed Archaeological Trust, told the BBC: “It’s quite a prestigious place to be buried. You have a range of people, from the wealthy to general townsfolk.”
Mr. Shobbrook added that the remains uncovered on the site show evidence of the type of injuries that might be sustained during battle.
He theorized some of the deceased could have been victims of a siege carried out on Haverfordwest in 1405 by French and Welsh rebels.
The remains are due to be analyzed by experts before being reinterred nearby.