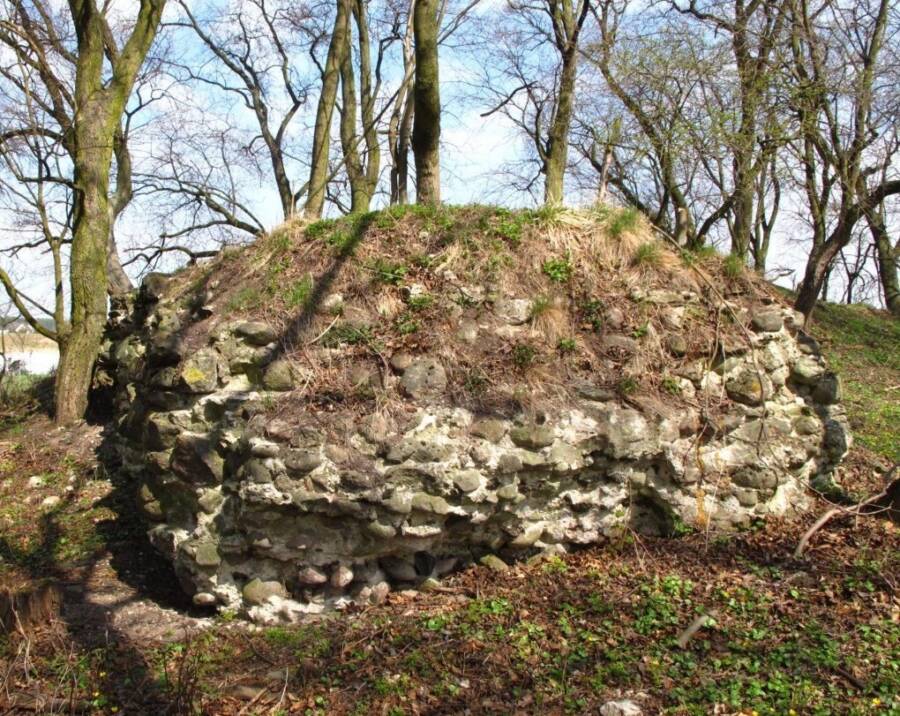
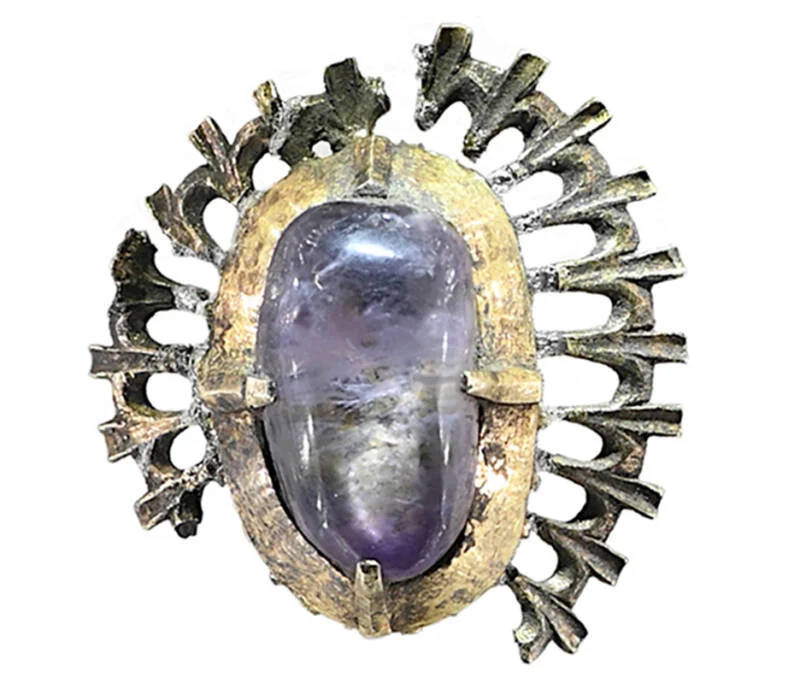
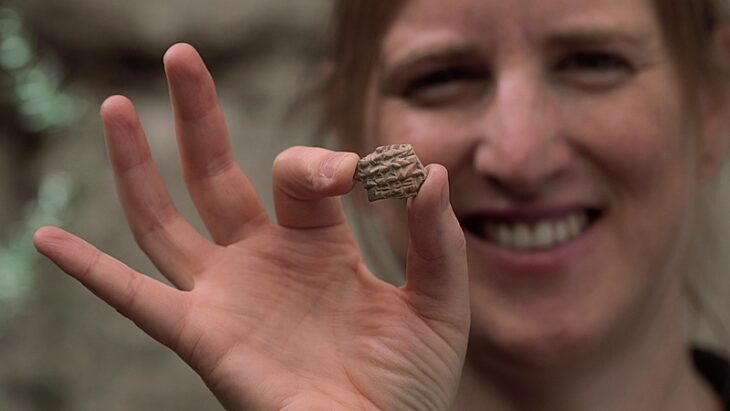A stunning medieval amethyst jewel, believed to date back over 600 years, has been discovered in the moat of the ruined Castle Kolno in southwestern Poland. This rare archaeological find offers a remarkable glimpse into the lives of the medieval aristocracy and sheds new light on the castle’s dramatic history.
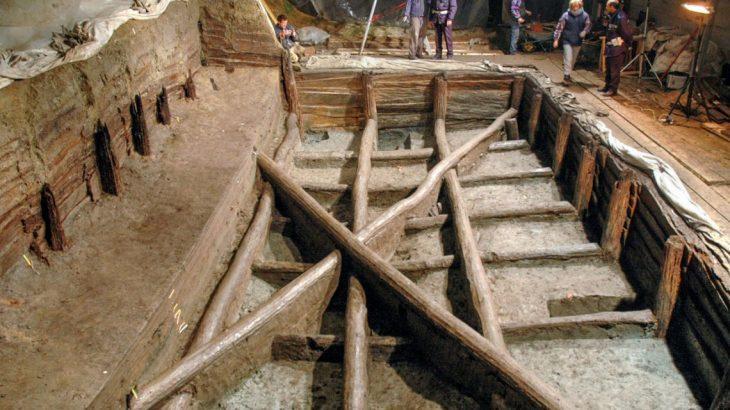
The jewel was unearthed in the sediment between the timber posts of a collapsed bridge that once spanned the castle’s moat. Based on stratigraphic and dendrochronological evidence, experts have dated the artifact to between the early 14th and mid-15th centuries—a time when Castle Kolno was an active stronghold and aristocratic residence.
An Uncommon Jewel in an Unlikely Place
The discovery is extraordinary not only because of the jewel’s craftsmanship but also due to its context. Medieval jewelry is rarely found in settlement sites. Typically, gold and silver ornaments from this period are recovered from graves or hidden hoards, not from domestic environments such as castles or urban dwellings.
Archaeologists believe the amethyst may have been lost by its noble owner while crossing the bridge that once connected the castle to the surrounding area. The find challenges common assumptions about the circulation and deposition of high-value items in medieval Poland.
“This is a unique object to discover in a moat,” said Dr. Lech Marek, an archaeologist at the University of Wrocław. “The artifact likely belonged to a noble visitor and may have been part of a brooch, or possibly a coronet.”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

Analysis and Craftsmanship
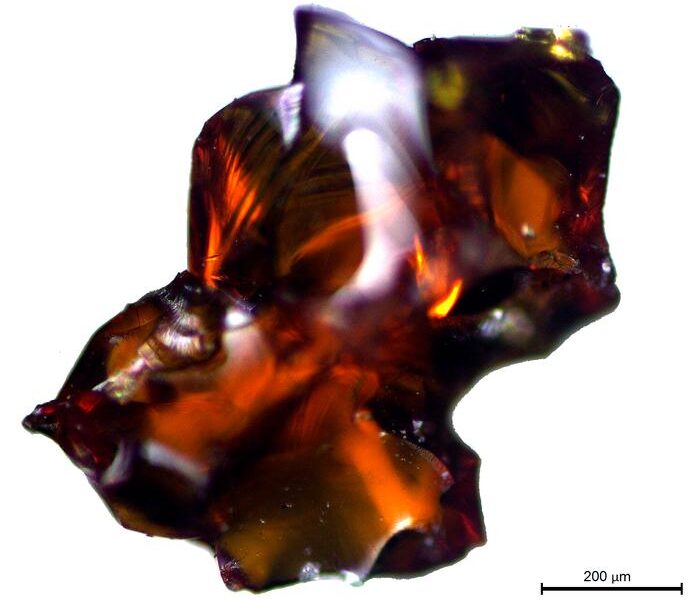
The jewel was identified as a cabochon-cut amethyst using Raman spectroscopic analysis, a technique that determines a gem’s molecular composition with laser light. The surrounding metal was confirmed to be fire-gilded silver through X-ray fluorescence analysis.
The design features a central amethyst encircled by a radiating pattern resembling petals or palmettes, suggesting the piece was once part of a larger decorative setting. Remnants of a silver pin and lead solder on the back support the theory that it was originally affixed to another item—most likely a luxurious brooch.
This style of gem setting was popular in the international courtly tradition of the 13th and 14th centuries. Comparable examples can be found in royal collections and cathedral treasuries across Europe, such as those from Toledo, Cracow’s Wawel Cathedral, and Środa Śląska, reinforcing the jewel’s aristocratic association.
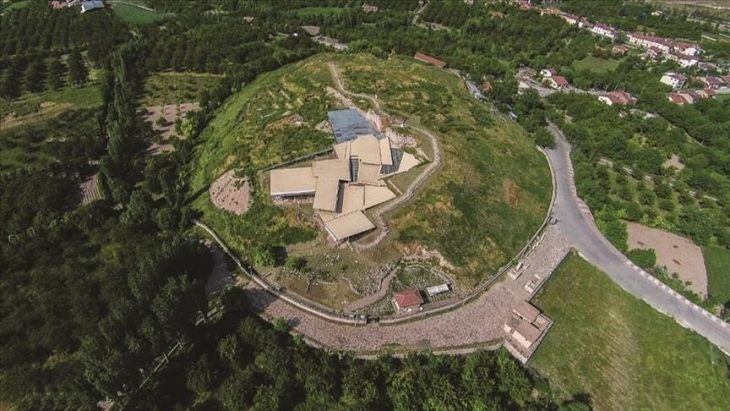
Castle Kolno: A Site of Power and Conflict
Castle Kolno was established in the 13th century by Duke Bolesław III of Brzeg. Initially serving as a fortress and administrative hub—particularly for regulating the timber trade—it was later sold to local nobles. The castle changed hands several times before being burned down in 1443, likely during violent clashes between rival duchies in the aftermath of the Hussite Wars.
Since 2010, archaeologists have been excavating the ruins, uncovering artifacts ranging from military gear to ceramics, most dating to the castle’s 14th- and 15th-century heyday. The amethyst jewel stands out as one of the most significant and symbolic discoveries to date.
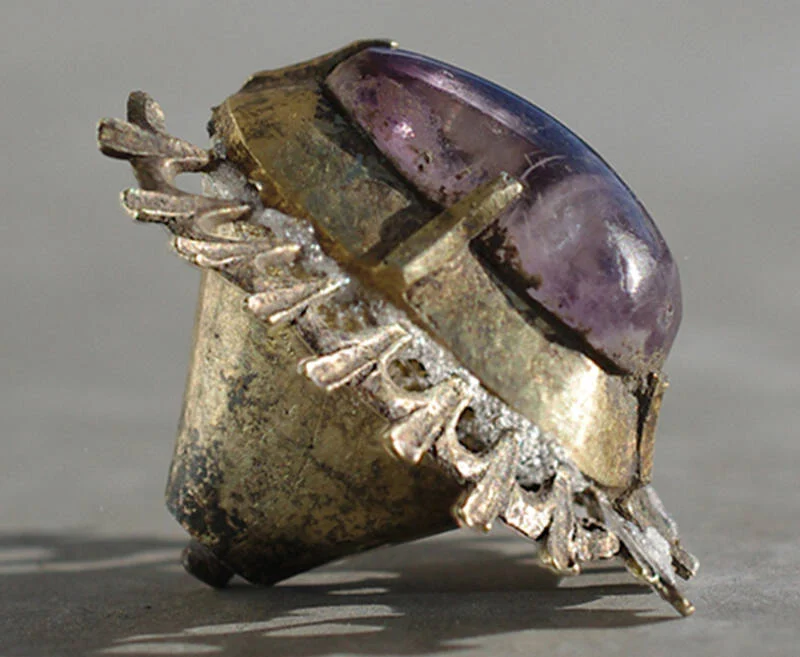

More Than Just a Gem
Beyond its aesthetic value, the amethyst carries symbolic significance. In the medieval period, amethysts were believed to have protective and spiritual powers, defending the wearer from various dangers—including intoxication, treason, and even enchantment. Such symbolism would have increased the jewel’s importance to its original owner.
“In the sophisticated medieval play of symbols, the choice of gems always had a deeper meaning,” said Marek. “A stone believed to possess supernatural powers quickly rose in both social and monetary value.”
An Ongoing Mystery
Despite the insights the jewel provides, one key question remains unanswered: how and why was it lost? Whether dropped accidentally or intentionally discarded, the jewel’s journey into the moat remains a mystery.
Excavations at Castle Kolno continue, with archaeologists hopeful that more artifacts will emerge to help reconstruct the rich and complex narrative of this once-powerful medieval site.
Marek, L., & Miazga, B. (2025). A jewel worthy of a duke from the moat of Castle Kolno. Antiquity, 1–6. doi:10.15184/aqy.2025.10097
Cover Image Credit: Castle Kolno was destroyed in the 1400s, and only its ruins remain today. Credit: National Institute of Cultural Heritage