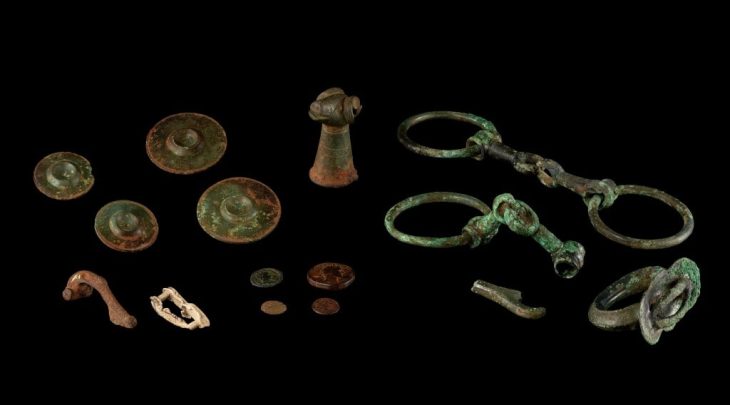
Archaeologists have uncovered a remarkable treasure dating back to the 13th century during the ongoing excavations at Molkenmarkt, the historic heart of Berlin. A team from the Berlin State Office for the Preservation of Monuments (Landesdenkmalamt Berlin) recently unveiled a small hoard of silver coins, shedding new light on the medieval history of Germany’s capital.
A Glimpse Into Medieval Berlin: The Coin Discovery
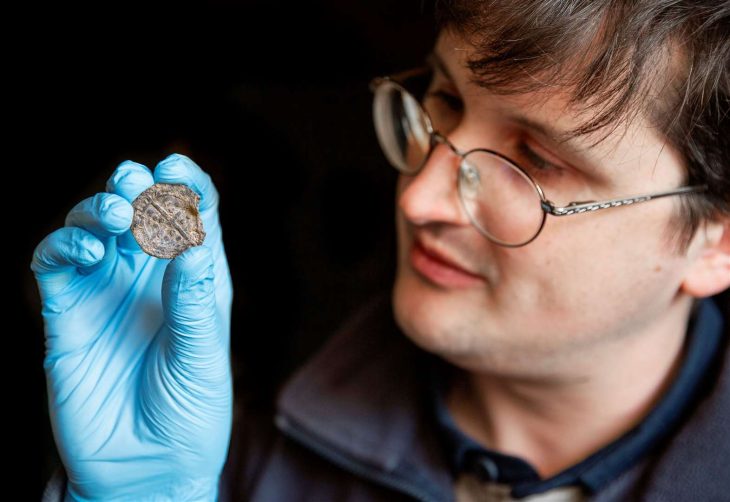
The coin hoard consists of five whole denars and one half-denar, silver coins measuring approximately 1.5 centimeters in diameter. These coins date to the latter half of the 13th century, specifically during the reign of the Ascanian margraves Otto IV and Otto V (1260/65–1293). The coins’ obverse features a standing margrave flanked by two domed towers resting on double arches, while the reverse depicts a crowned eagle—a symbol of authority and sovereignty.
Dr. Christoph Rauhut, State Conservator and Director of the Landesdenkmalamt Berlin, emphasizes the significance of the find: “These coins provide crucial evidence for the consolidation of medieval Berlin in the 13th century. For the first time, such coins have been documented at Molkenmarkt, marking an important chapter in Berlin’s urban development.”

Molkenmarkt Excavations: Germany’s Largest Urban Archaeological Site
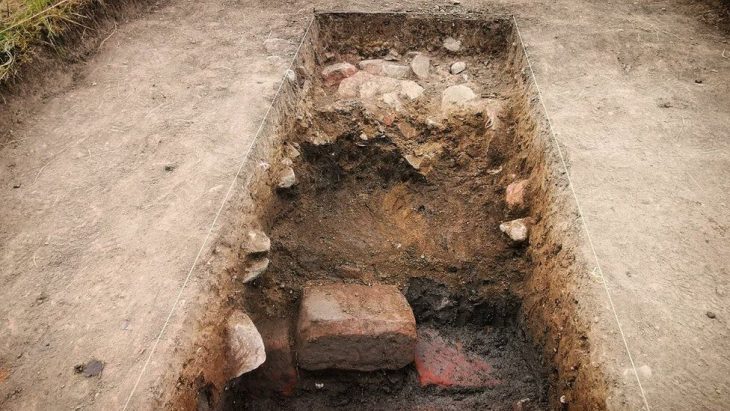
The Molkenmarkt excavation spans approximately 22,000 square meters in Berlin-Mitte, making it the largest city center archaeological project in Germany. Excavations delve down to depths averaging four meters, moving over 88,000 cubic meters of historic soil, which remains exceptionally well preserved due to 20th-century surface sealing.
This extensive archaeological endeavor uncovers layers of Berlin’s development from its medieval founding through the 20th century. Key findings include a 50-meter-long and seven-meter-wide plank road dating back to around 1230, defensive ditches from the 13th century, and hundreds of wells and latrines spanning the 13th to 18th centuries. Researchers have also discovered remnants of medieval wooden cellars, houses, mud dome ovens, and smithies, along with prehistoric artifacts, particularly from the Stone Age.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Christian Gaebler, Senator for Urban Development, Construction, and Housing, comments: “Molkenmarkt continues to surprise us with fascinating finds. Visitors can now admire many of these discoveries at the newly opened PETRI Berlin museum, offering a unique window into Berlin’s rich history.”
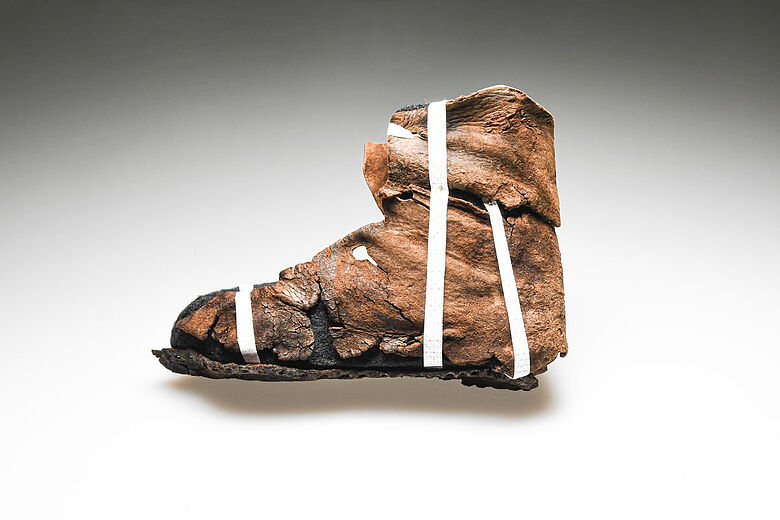

Beyond Coins: Everyday Life in Historical Berlin
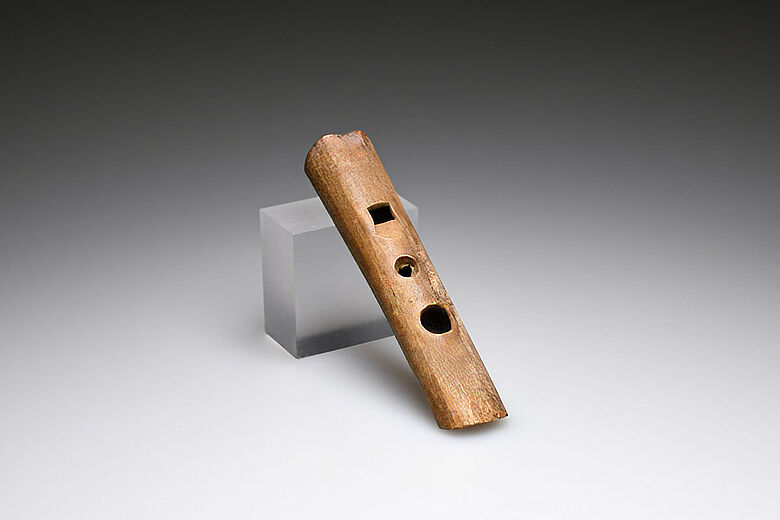
The coin hoard is just one highlight among more than 700,000 artifacts uncovered at Molkenmarkt, which together paint a vivid picture of Berlin’s social and cultural history. Among these finds are a 14th-century fishing net sinker, a bone flute from the same era, a sock and leather shoes dated around 1450, a silk ribbon from the mid-15th century, 17th-century toys including marbles, and 18th-century flintstones used in flintlock firearms.
These artifacts collectively illuminate the daily life, craftsmanship, and traditions of Berlin’s past residents over several centuries. The preservation of such a diverse range of objects is exceptional, largely thanks to the protective measures taken during Berlin’s urban modernization in the mid-20th century.

Scientific Documentation and Future Insights
Currently, over 70% of the excavation area has been thoroughly documented and researched. Following the completion of fieldwork, a comprehensive scientific evaluation of all findings will take place, promising new insights into Berlin’s medieval and early modern urban landscape.
The Molkenmarkt site stands as a testament to the city’s layered history—from its medieval beginnings through its evolution into a modern metropolis—offering archaeologists and historians an unparalleled resource to understand Berlin’s past.

Visiting Molkenmarkt and PETRI Berlin
For those interested in exploring this history firsthand, many of the Molkenmarkt finds, including the rare coin hoard, are exhibited at PETRI Berlin, a recently opened cultural venue dedicated to showcasing the city’s archaeological treasures.
As the Molkenmarkt project progresses, it continues to deepen our understanding of Berlin’s origins and development, making it a focal point for both scholars and the public alike.
Cover Image Credit: Rare 13th-Century Coin Hoard Discovered at Berlin’s Molkenmarkt Excavations. Landesdenkmalamt Berlin, Julia-Marlen Schiefelbein