New research results are rewriting the history of Karanis, an ancient Greco-Roman agricultural settlement in the Fayum oasis in Egypt. The study’s findings contradict the conventional wisdom that the location was abandoned in the middle of the fifth century and indicate that this location may have been inhabited until the middle of the seventh century AD.
These dates round out the intricate picture of population swings and the renovation and repurposing of Karanis’ architectural legacy. This finding suggests that the settlement remained still active during a time of significant political and environmental changes in the region and beyond.
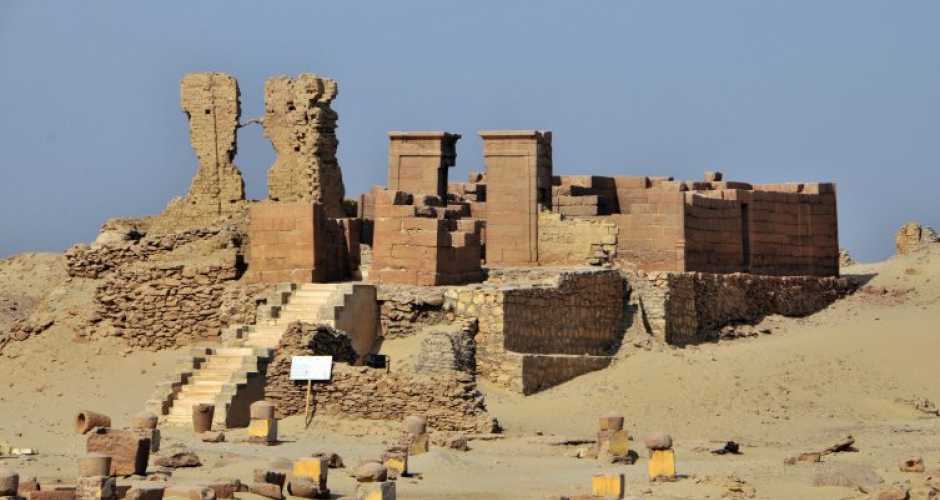
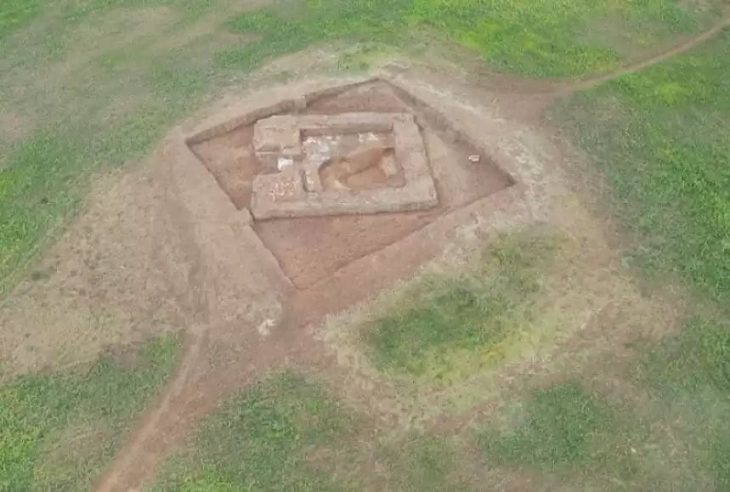
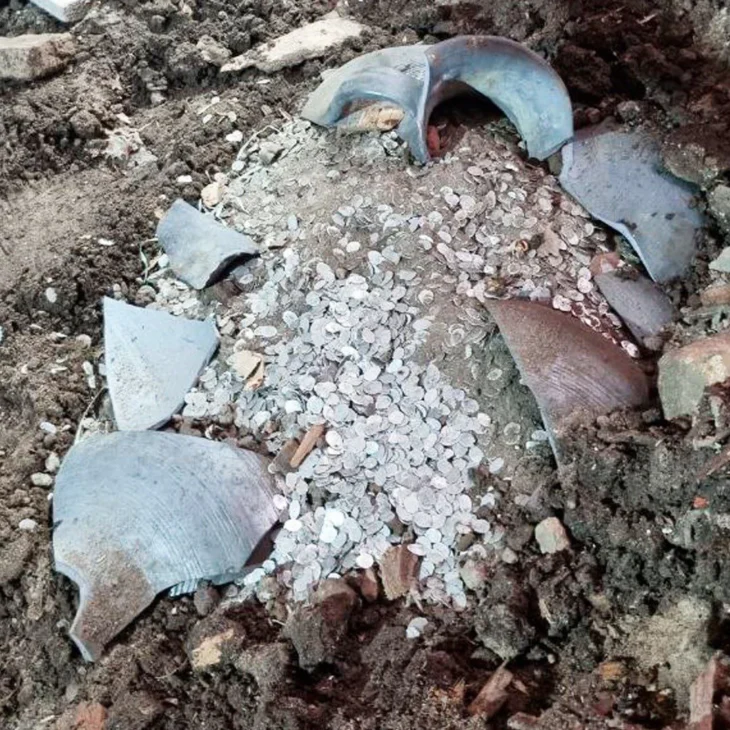
Founded in the Fayum region of Egypt circa 250 BC, Karanis was home to a farming community with a varied populace and an intricate material culture that persisted for hundreds of years. Karanis, which was eventually abandoned and partially covered by the encroaching desert, turned out to be an extraordinarily rich archaeological site, yielding tens of thousands of artifacts and papyrus texts that provide a wealth of information about daily life in the Roman Egyptian town.
Thanks to the radiocarbon dating of thirteen samples of plant remains taken from the settlement’s structures, the chronology of Karanis was reexamined. The crops’ age was determined with the assistance of the 14CHRONO Centre at Queen’s University Belfast, which carried out the dating. These findings suggest that the site was occupied for a longer period of time than previously believed.
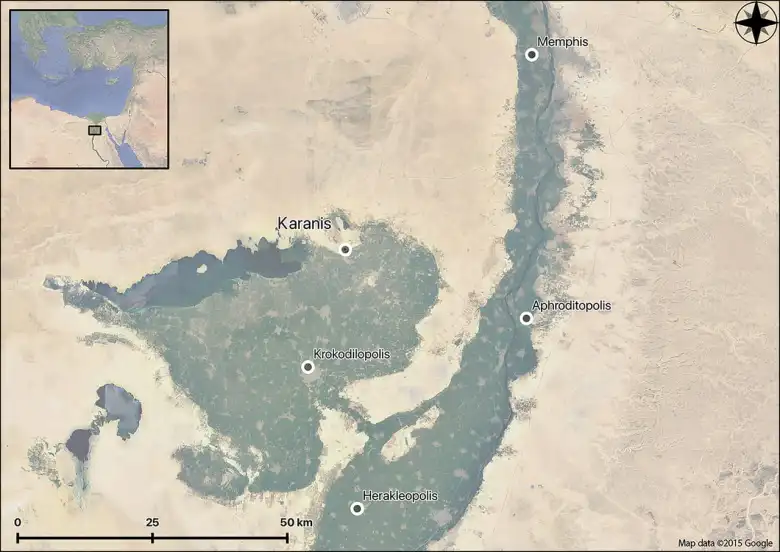
The chronological framework for the site was established by the first excavators through papyrological and numismatic evidence. Based on papyri and coins from the first excavations conducted between 1924 and 1935, as well as the materials’ scarcity after approximately 460 AD, researchers came to the conclusion that Karanis was abandoned at that time. This implies that events such as the Antonine Plague (AD 165–180) and the ensuing economic downturn caused the settlement to be abandoned.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The research indicates that while there may have been depopulation in certain parts of the settlement by the middle of the 5th century, there were still inhabited areas up until the 7th century, which coincided with the Islamic conquest of Egypt. This result defies earlier inferences that suggested an early decline based on papyri and coins.
The settlement appears to have changed gradually over time, with buildings being renovated and repurposed. It is known that there were notable variations in the climate and Nile levels during this time, and that Byzantine and Arab conquests also altered the political landscape. These dynamics may have allowed some areas of Karanis to remain active while abandoning others, thereby influencing the survival and transformation of the region.
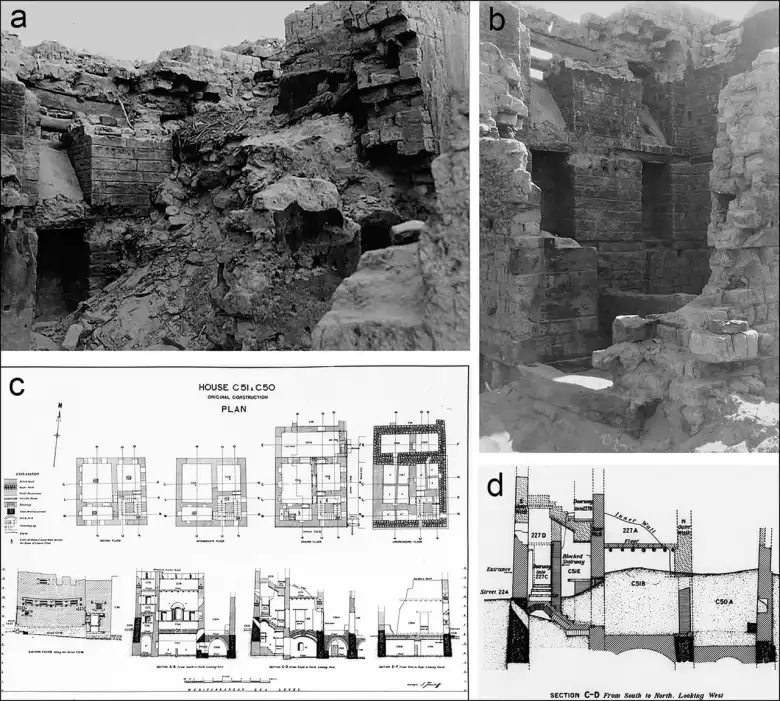
The settlement was continuously inhabited beginning in the sixth century, and it seems to have endured in some capacity at least until the Islamic conquest in the seventh century AD, according to the researchers. With the available data and without a deeper understanding of its shifting urban fabric, it is challenging to determine how much of its prosperity it retained.
However, researchers do concede, though, that it is also unclear how and when Karanis was ultimately abandoned; the lack of coins and papyri does not necessarily mean that there was no population there.
Cover Photo: Karanis is one of the Largest Greco-Roman Cities in the Fayoum. Source