In Libya’s ancient city of Ptolemais on the Mediterranean coast, Polish archaeologists have uncovered a dwelling equipped with an advanced drinking water collection system, and a mysterious mask.
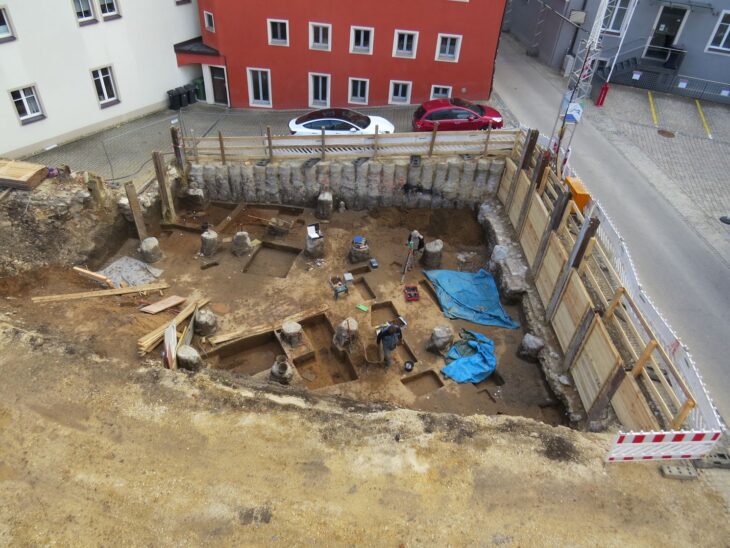
In 2023, archaeologists from Poland’s University of Warsaw made their way back to Ptolemais following a thirteen-year break due to the Libyan civil war. This city, founded by the Ptolemaic dynasty, played a significant role from the 4th century BC until the Arab conquest in the 7th century AD. The study of urban structures was the main focus of this research season, and the results were unexpected.
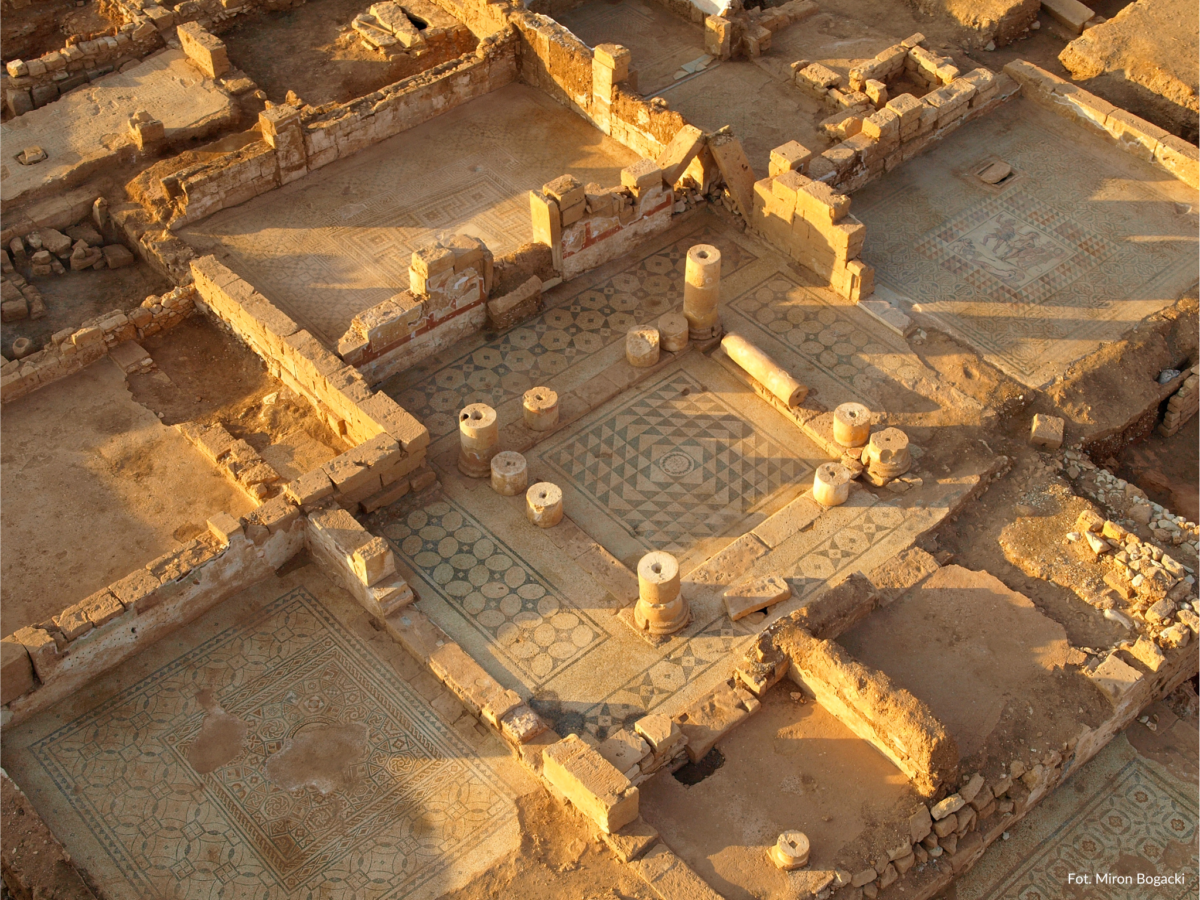
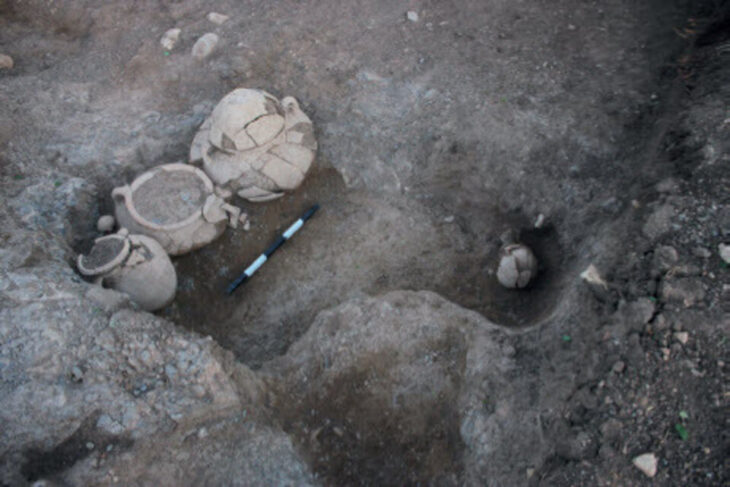
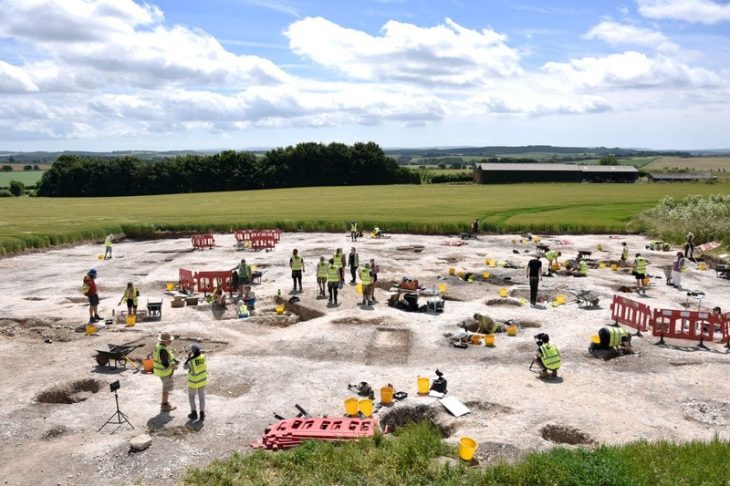
During excavations in June 2024, archaeologists from the University of Warsaw revealed part of a residential complex in the ancient city of Ptolemais. The residence, dating to the late 2nd or early 3rd century CE, featured a sophisticated rainwater collection system including an impluvium that channeled water into underground cisterns.
Piotr Jaworski, head of the Polish Archaeological Mission to Ptolemais, explained that the heart of the eastern area of the house was a small peristyle, surrounded by a kitchen, a staircase, and a room with a mosaic.
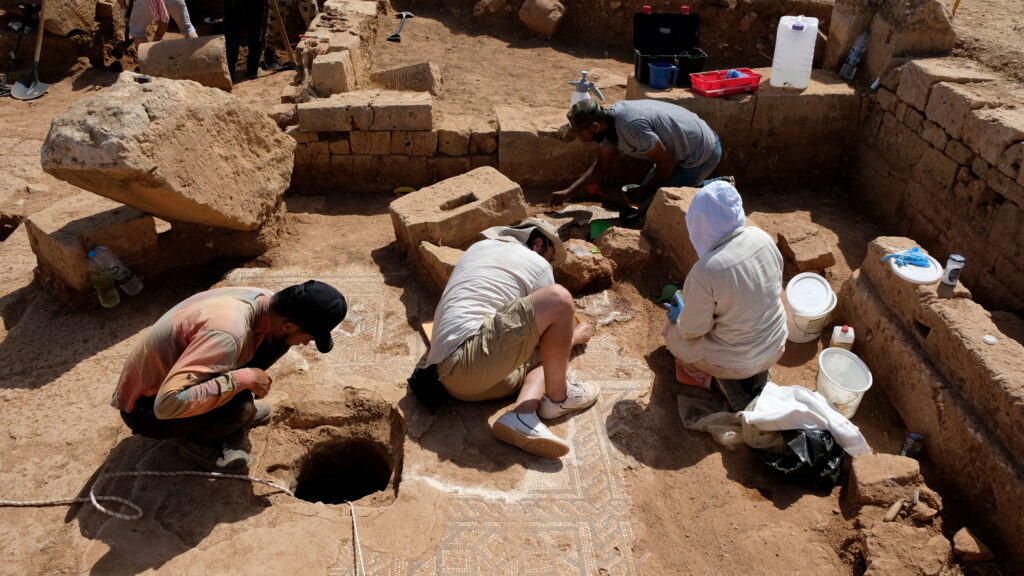

A peristyle pool that collected rainwater and routed it to two subterranean cisterns was the centerpiece of the home’s sophisticated water collection system. The house was rebuilt in the late Roman era after being damaged by earthquakes in the third century. Three stone containers at the entrance serve as proof of this and may have been used for offerings or taxes, according to researchers.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
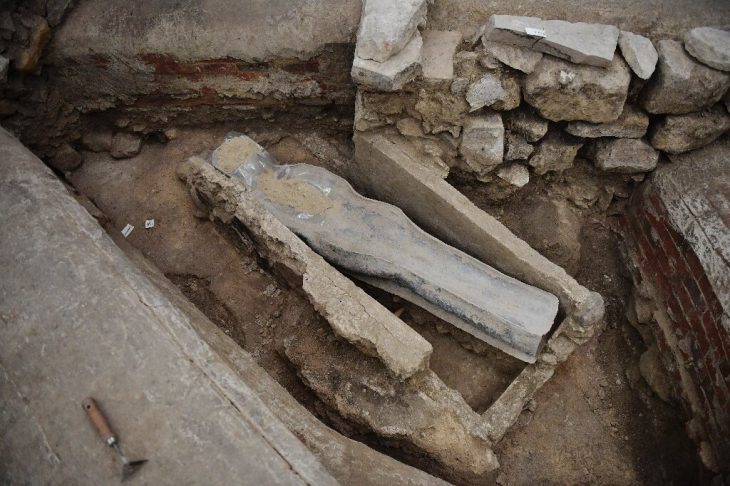
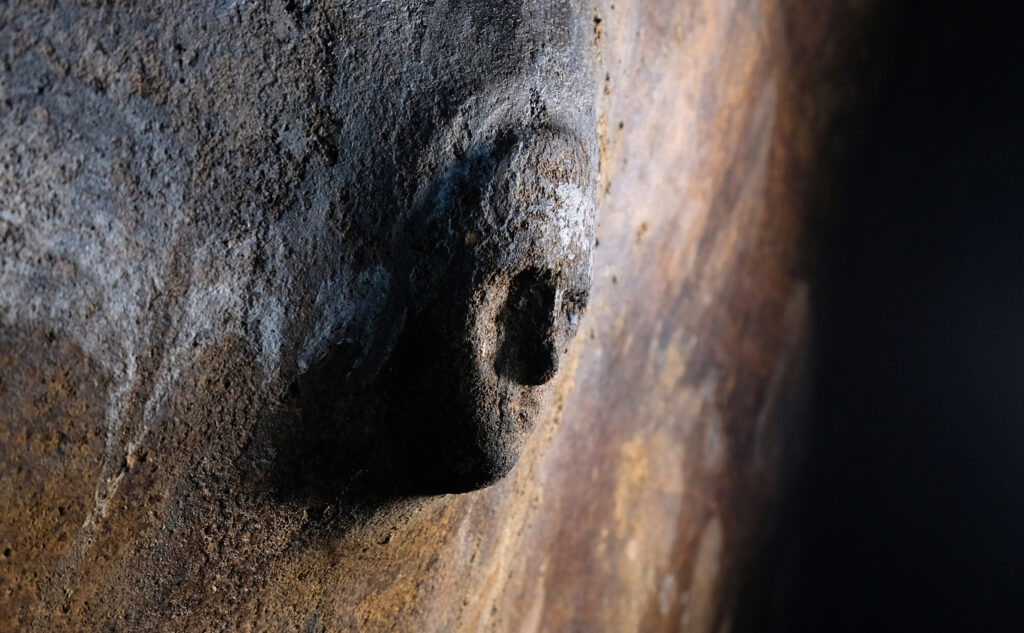
A human face carved in hydraulic mortar inside a cistern was among the most fascinating discoveries. The mask’s origins are unclear due to its lack of distinguishable features, leading to a variety of interpretations. Similarities to carvings found in Libyan sanctuaries are noted by archaeologists, indicating potential local connections or influences. It is possible that the owner of the house or those involved in its creation were of Libyan origin, but this remains speculative.

Ptolemais, founded in the 3rd century BC, was an important cultural and religious center in Cyrenaica. This place attracts researchers, among others, because of its historical complexity. It most likely still holds many secrets.
With ongoing archaeological efforts, researchers aim to better understand the function of structures on the acropolis and uncover insights into life in ancient Ptolemais.
Cover Image Credit: Ruins of the House of Leukaktios in Ptolemais discovered by a University of Warsaw expedition between 2001 and 2010. Website of the Republic of Poland