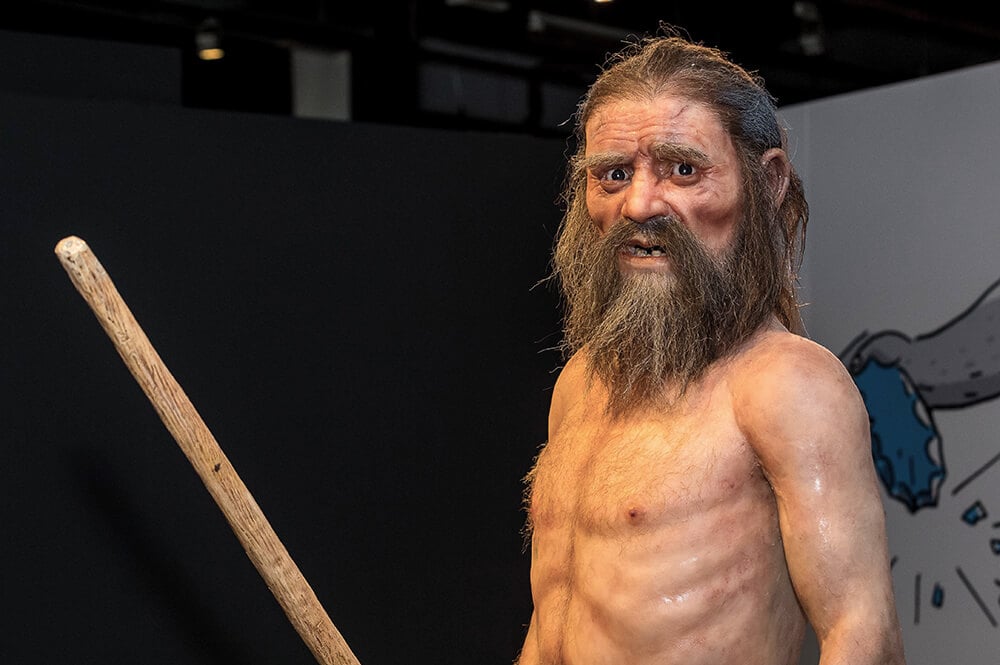
New DNA analysis by German researchers shows that the famous glacier mummy Ötzi may have had dark skin, dark eyes, a balding head, and steppe ancestry.
“Among the hundreds of early European people who lived at the same time as Ötzi and whose genomes are now available, Ötzi’s genome has more ancestry in common with early Anatolian farmers than any of his European counterparts,” the scientists said in the study, published Wednesday in the journal Cell Genomics.
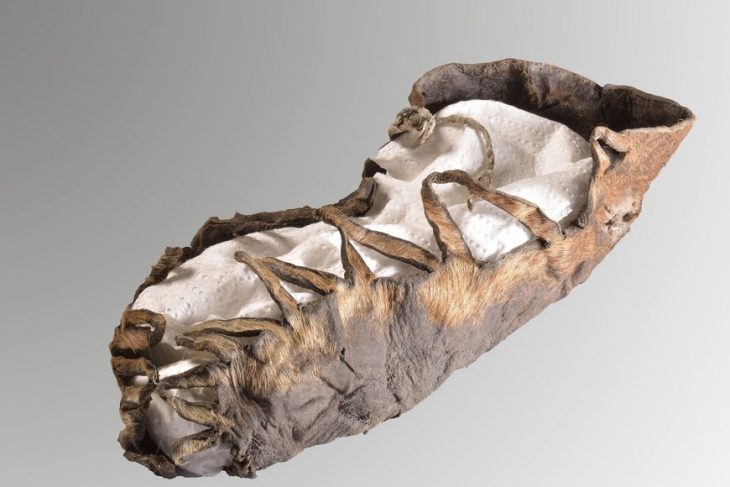
The body of Ötzi was discovered by German tourist Helmut Simon on a glacier in the Tirolean Ötztal Alps, on the Italian-Austrian border, on Sept. 19, 1991. His body was remarkably well preserved due to the cold and a natural mummification process. Radiocarbon dating indicates that Ötzi lived around 3300 BC. He was a man between 35 and 40 years old, standing approximately 5 feet 2 inches (1.57 cm) tall and weighing around 110 pounds.
Ever since his discovery more than 30 years ago, he has been a fascinating source of information for historians and anthropologists. Ötzi was armed with a copper ax and a longbow and wore a bearskin hat.
Scientists have been able to conclude that he had a big meal of ibex meat and fat not long before his death, and that he died after being shot with an arrow between his rib cage and shoulder blade. Originally, it was believed that Ötzi had succumbed to exposure or exhaustion while crossing the Alps, freezing to death.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
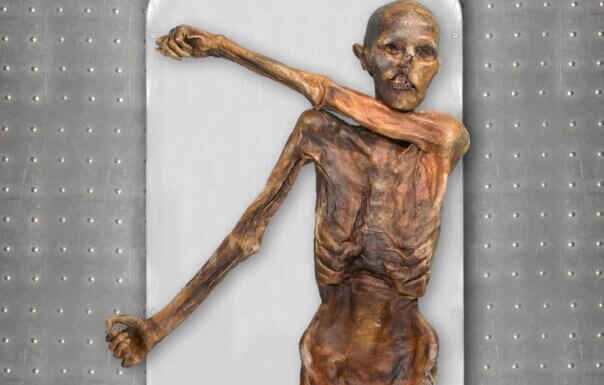
Scientists also previously believed the Iceman was lighter-skinned and hairier, and that his mummified corpse had changed over time in the ice.
The results provided important insights into the genetic makeup of prehistoric Europeans. Advances in sequencing technology have now enabled a research team from the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology and Eurac Research to reconstruct Ötzi’s genome more accurately. The results of this recent analysis refine the Iceman’s genetic picture: compared to other contemporary Europeans, Ötzi’s genome has an unusually high proportion of genes in common with those of early farmers from Anatolia.
The study published Wednesday suggests Ötzi had no traces of the eastern European tribes.
Johannes Krause, head of the Department of Archaeogenetics at the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology, said his team was “very surprised” by the results.
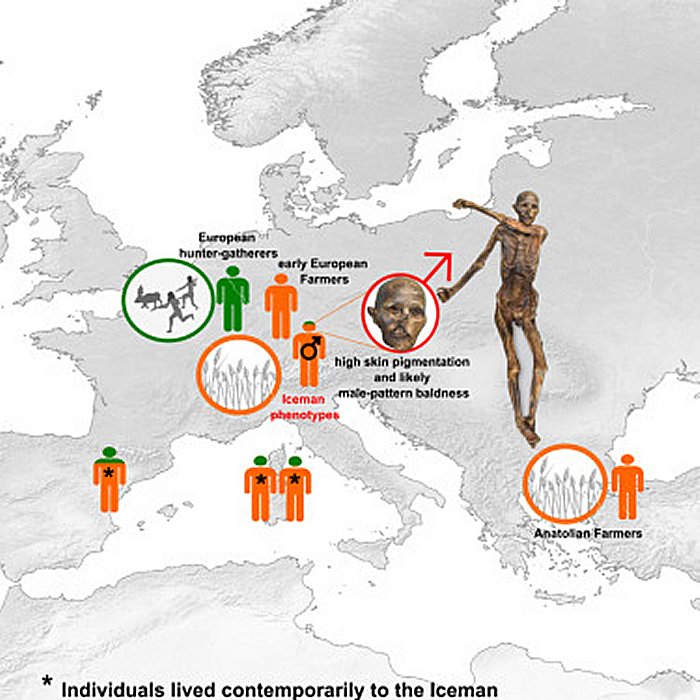
“Genetically, his ancestors seem to have arrived directly from Anatolia without mixing with hunter-gatherer groups,” he said.
The researchers also deduced that Ötzi was bald, or almost bald, when he died. This was genetic, as his genes show a “predisposition for baldness,” the study said. The team also concluded that the Iceman was darker-skinned than initially thought. In life, his original skin color was likely similar to his body’s present color.
















