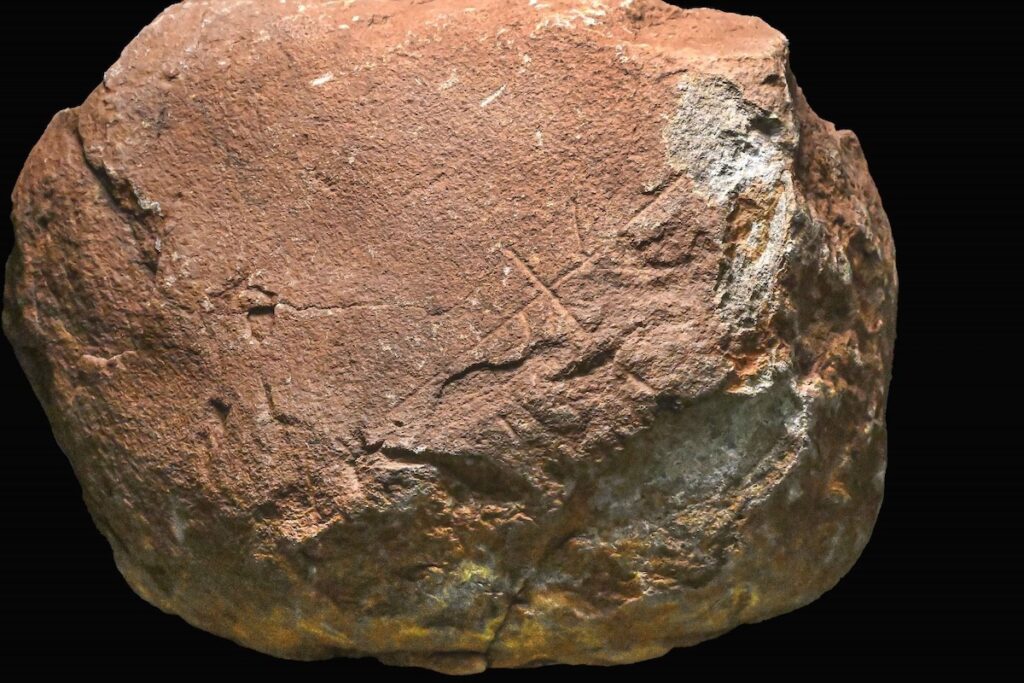
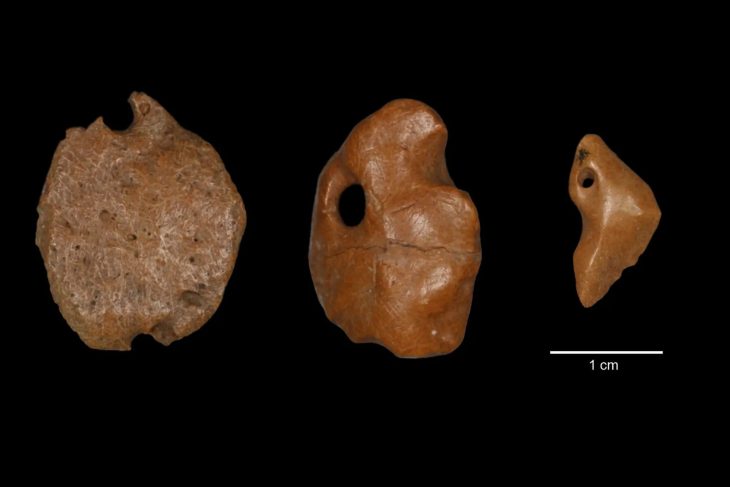
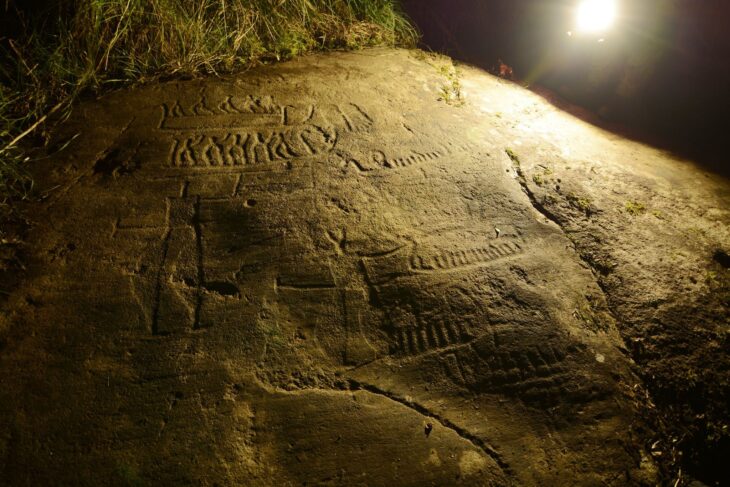
Marbella has just made an incredible discovery that could change everything we thought we knew about prehistoric Europe. Archaeologists working in the Las Chapas area have found a stone at the Coto Correa site, which is protected and has been recognized for its historical significance since the 1950s. This stone features carvings that might be over 200,000 years old! If this is confirmed, it would make these markings some of the oldest human-made art in Europe, predating Spain’s earliest known cave art by a staggering 100,000 years.
The Marbella cave, known as the Coto Correa site, is located in the Las Chapas area of Marbella, in the province of Málaga, Spain. This site has been recognized for its archaeological significance and is situated near the Mediterranean coast, making it an important location for understanding prehistoric human activity in the region.
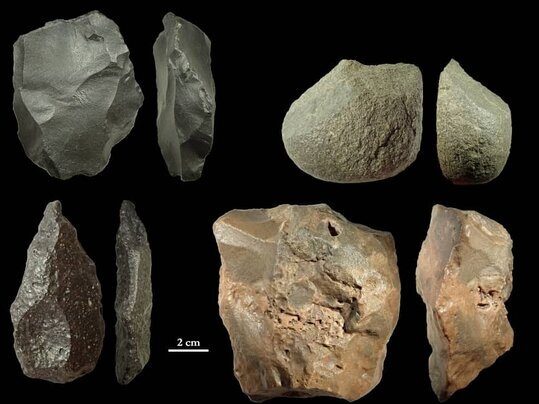
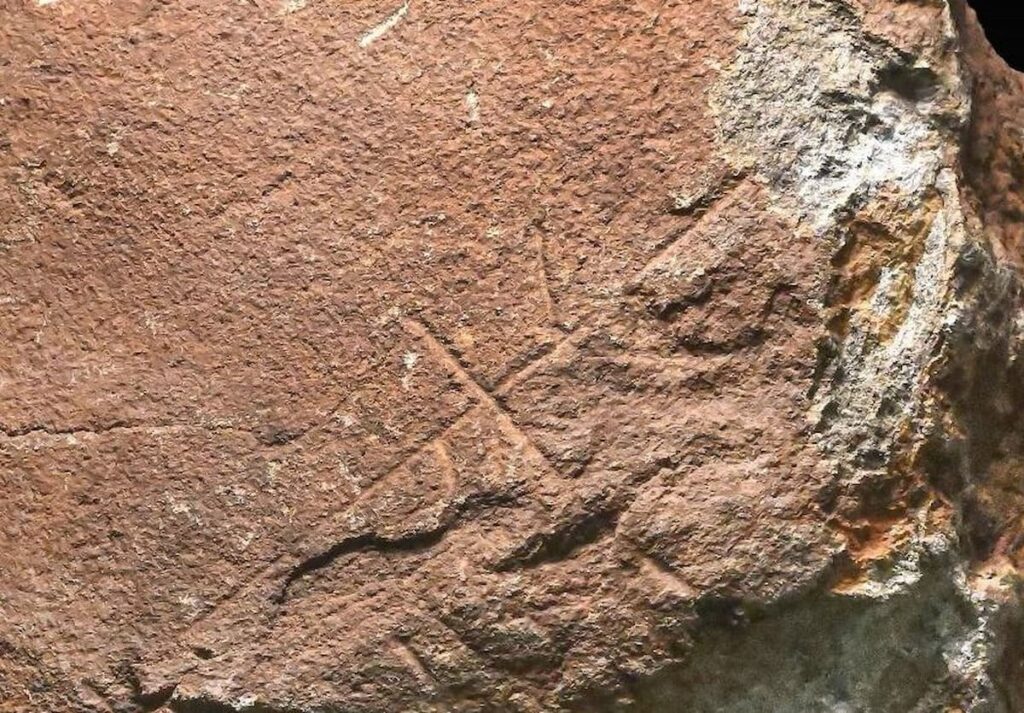
The excitement kicked off during a recent archaeological survey at Coto Correa, where previous digs had already uncovered ancient stone tools used by Marbella’s earliest inhabitants. But this latest find takes things to a whole new level. The star of the show is a piece of gabbro, a dark, coarse rock, adorned with a series of engraved lines.
Experts believe these markings could represent one of the earliest forms of symbolic expression, possibly the oldest graphic representations ever found on the Iberian Peninsula.
If ongoing studies confirm the age of these engravings, they could completely reshape our understanding of when and how early humans began to express themselves artistically. While Spain is home to other significant prehistoric art sites, like the famous painted caves in Cantabria, the age of these Marbella carvings sets them apart and raises intriguing questions about the cognitive and creative abilities of early humans, including Neanderthals or their ancestors.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

To determine the exact age of the carvings, researchers are employing advanced geoarchaeological techniques. They’re analyzing quartz in the surrounding sediments to create a clear timeline, while cutting-edge 3D digital mapping helps distinguish between natural wear, tool marks, and intentional engravings.
This digital documentation will not only assist scholars in verifying the origins of the markings but will also serve as a valuable resource for museums, allowing experts, students, and curious visitors to explore this remarkable find for years to come.
Local authorities have set aside €8,000 to support this vital research—a modest investment that could redefine not just Marbella’s history, but our broader understanding of human evolution and creativity. Once the results are in, the cultural department plans to share this scientific milestone through public events and exhibitions, ensuring that everyone can catch a glimpse of Marbella’s newly uncovered ancient past.
Could Marbella soon be known for more than just its luxury lifestyle? This potential breakthrough in Paleolithic research might just give the town a new kind of prestige—one that stretches back hundreds of thousands of years.
Cover Image Credit: 200,000-year-old rock carvings found in Marbella. Some of the oldest known human-made carvings in Europe. Credit: Ayuntamiento de Marbella (Marbella Town Council)