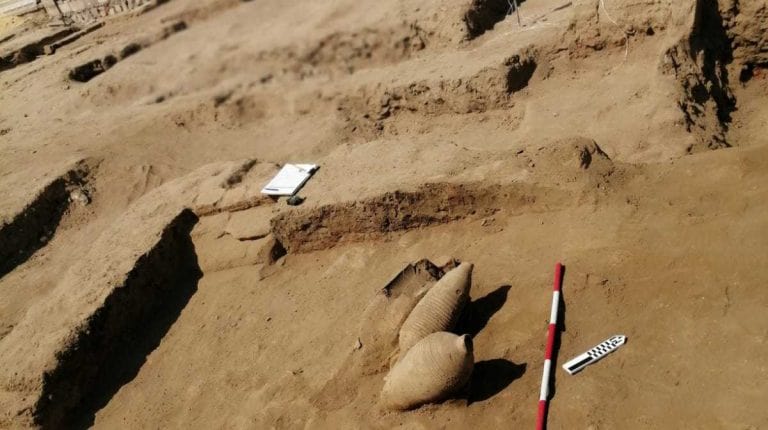
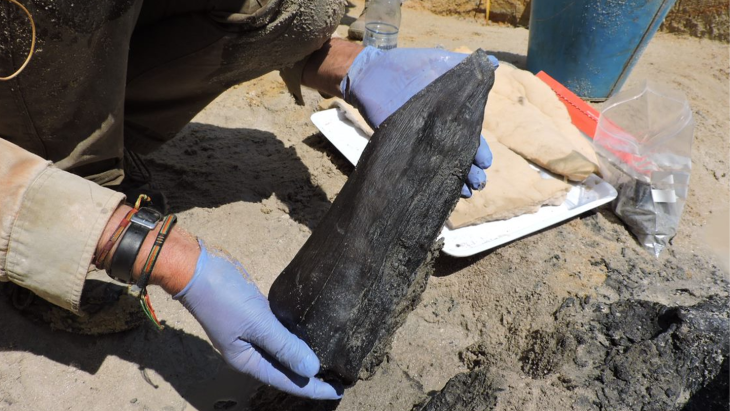
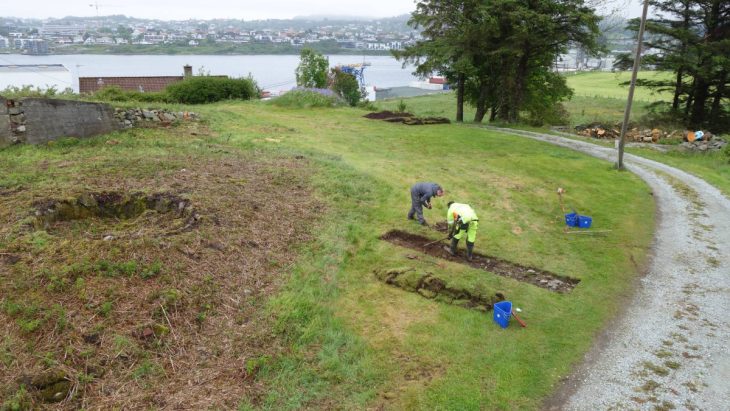
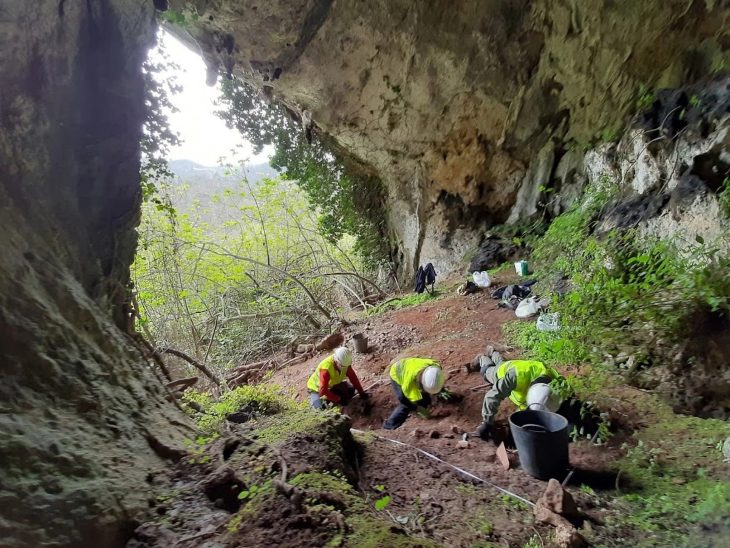
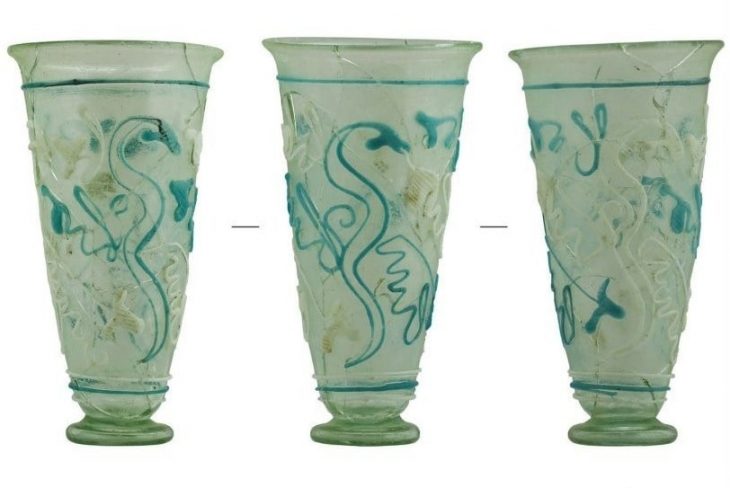
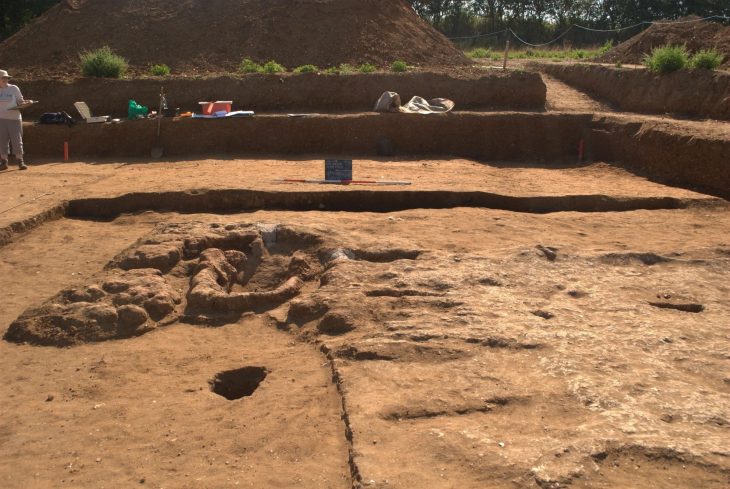
An Egyptian archaeological mission excavating at the site of the recently demolished Tawfiq Pasha Andraos Palace discovered a number of Byzantine-era amphorae and lamps.
The demolition of the 120-year-old Tawfiq Pasha Andraos Palace in Luxor had received a lot of criticism.
On Oct. 17, Mustafa Waziri, secretary-general of the Supreme Council of Antiquities, revealed that this find is part of a sequence in Luxor, Egypt’s southernmost city. Excavations on the property, he said, are nearing completion.
In August, Egyptian authorities demolished the 120-year-old Tawfiq Pasha Andraos Palace, located near the Luxor Temple and overlooking the Nile River, based on a decision by the Ministry of Antiquities that archeological sites were under it.
But the move was controversial. “Even the Louvre Museum has monuments below it and was never demolished,” Bassam al-Shammaa, an Egyptologist and a tourist guide told Al-Monitor. “Nothing justifies destroying antiquity for the sake of another, especially considering that Egypt has witnessed successive historical civilizations. It is just unthinkable to demolish antiquity because there is another one below it.”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
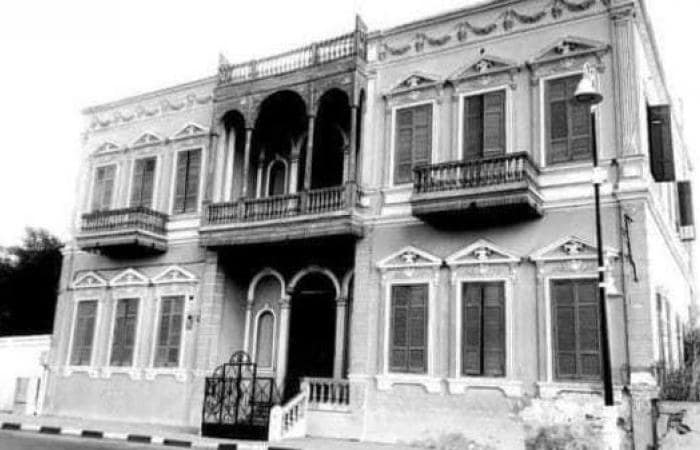

Shammaa added that the palace in Luxor was just steps away from notable Roman structures and in front of the Luxor Temple’s initial western superstructure. Emperor Hadrian’s most renowned monument is dedicated to the deity Serapis, and a statue of him may be seen in the northwest corner of the courtyard of the Luxor Temple, quite near to the Andraos Palace. According to Shammaa, the Roman monument was constructed around 126 AD.
According to Ahmed Amer, an archaeological specialist at Egypt’s Ministry of Antiquities, the finds herald a new era in archeology. According to him, the fresh discoveries provide new information on the religious and secular lives of the ancient Egyptians.
Other recent discoveries under the Tawfik Pasha Andraos Palace, Amer said, include a set of Roman bronze coins, a part of a wall from the Roman era, and an old storehouse. The lamps are made of different materials, and pottery is probably the most common, he said.