Egyptian scientists have digitally unwrapped the 3,500-year-old mummy of pharaoh Amenhotep I.
For the first time, a team in Egypt used CT scans to see inside the burial wrappings of Pharaoh Amenhotep I.
The non-invasive research enabled scientists to reveal Amenhotep’s face and work out his age and health at the time of his death.
The remains of the pharaoh, who ruled approximately between 1525-1504 BC, were discovered in Deir Al Bahari in 1881 and had remained unwrapped until Egyptologist Zahi Hawass and Cairo University professor Sahar Saleem launched an in-depth study in 2019.
The mummy of ancient Egypt’s former king is the only royal mummy in contemporary history that has not been opened by scientists or tomb thieves. This isn’t due to some old curse frightening people away, but rather to Egyptologists’ refusal to damage the well-preserved decorations covering Amenhotep’s mummy.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
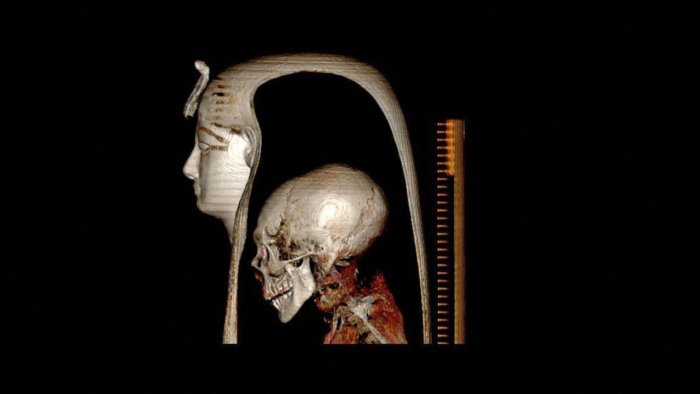
Decorated with flower garlands and a wooden face mask, Amenhotep’s mummy was so fragile that archaeologists had never dared to expose the remains before.
The remains of the pharaoh, who ruled approximately between 1525-1504 BC, were discovered in Deir Al Bahari in 1881 and had remained unwrapped until Egyptologist Zahi Hawass and Cairo University professor Sahar Saleem launched an in-depth study in 2019.
Hawass and Saleem used advanced X-ray technology, computed tomography scans, and digital software to map out the mummy in great detail, without stripping it of any of its strips.
The team also discovered that the king had been the first ruler to be embalmed with his forearms crossed in the so-called Osiris position.
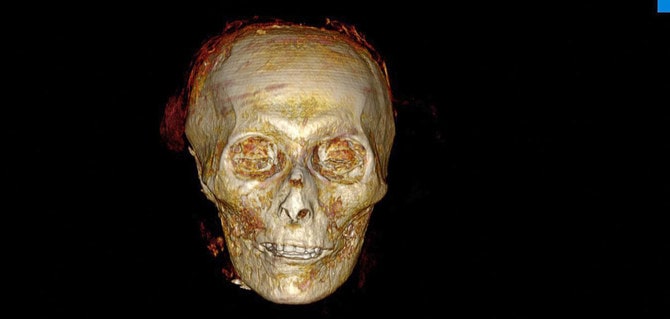
In addition, they found amulets and a girdle festooned with gold beads under the mummy’s wrapping.
To continue the tradition of leaving pharaoh Amenhotep I undisturbed, scientists turned to three-dimensional CT (computed tomography) scanning to “digitally unwrap” his tomb.
“This fact that Amenhotep I’s mummy had never been unwrapped in modern times gave us a unique opportunity: not just to study how he had originally been mummified and buried, but also how he had been treated and reburied twice, centuries after his death, by High Priests of Amun,” says Dr. Sahar Saleem, professor of radiology at Cairo University and the radiologist of the Egyptian Mummy Project, in a media release.
The scans reveal the pharaoh was a relatively young man at the time of his death, being only 35 years old. He stood between 5-foot-6 and 5-foot-7 and the team believes he was in good physical health when he died, apparently of natural causes.
Cover Photo: Facemask of the never-before unwrapped mummy of pharaoh Amenhotep I ( S. Saleem and Z. Hawass)