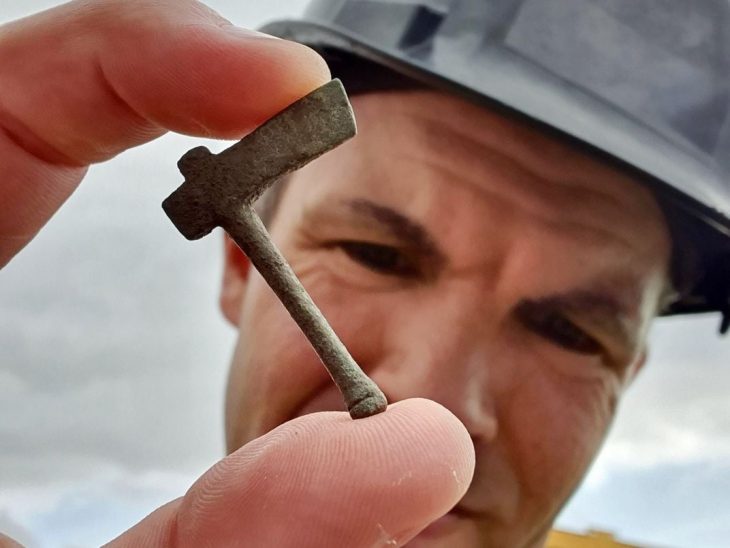
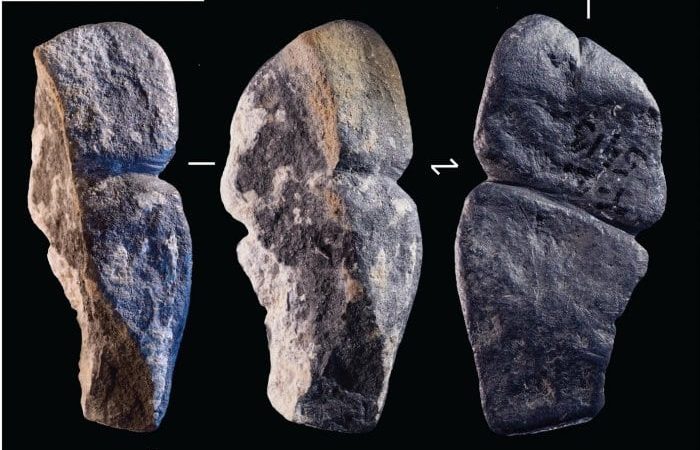
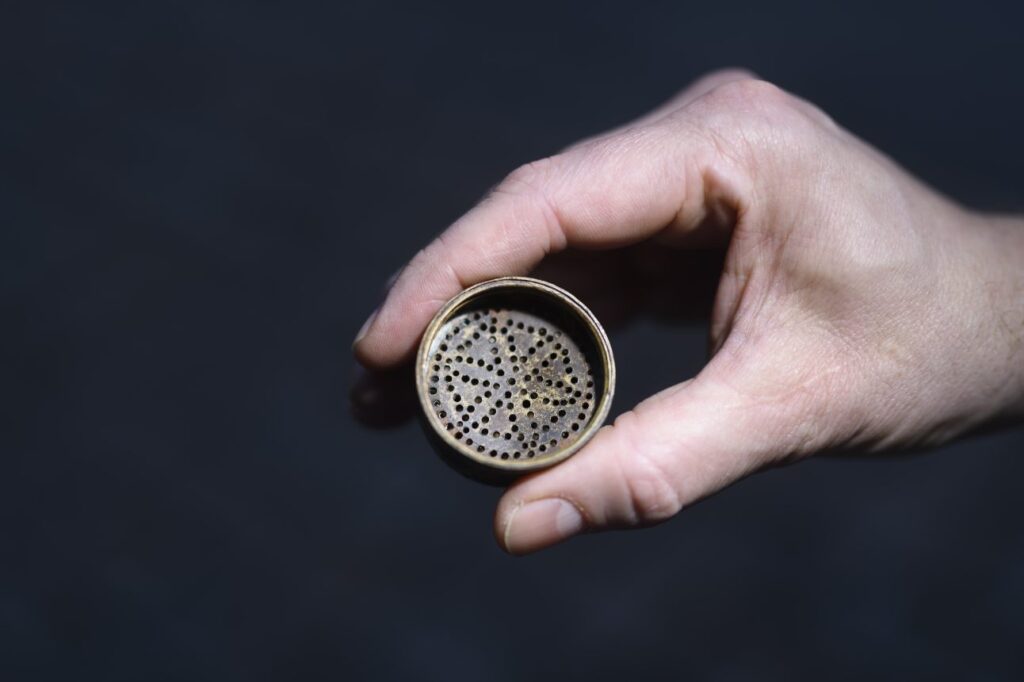
Archaeologists in Gothenburg, southwestern Sweden, have made a rather striking discovery at the site of the ancient Gullberg Fortress: a “testicle dagger” dating back to the mid-1400s. This unique style of knife, named for the distinctly phallic shape of its hilt, offers a fascinating glimpse into both the martial and potentially more personal aspects of life within the strategically important stronghold.
The dagger, featuring an iron blade and a wooden handle crafted from curly birch and adorned with circles, was found broken, its tip missing and its edge significantly chipped. Intriguingly, it was unearthed in the same archaeological layer as crossbow bolts, strongly suggesting its use in battle conditions.
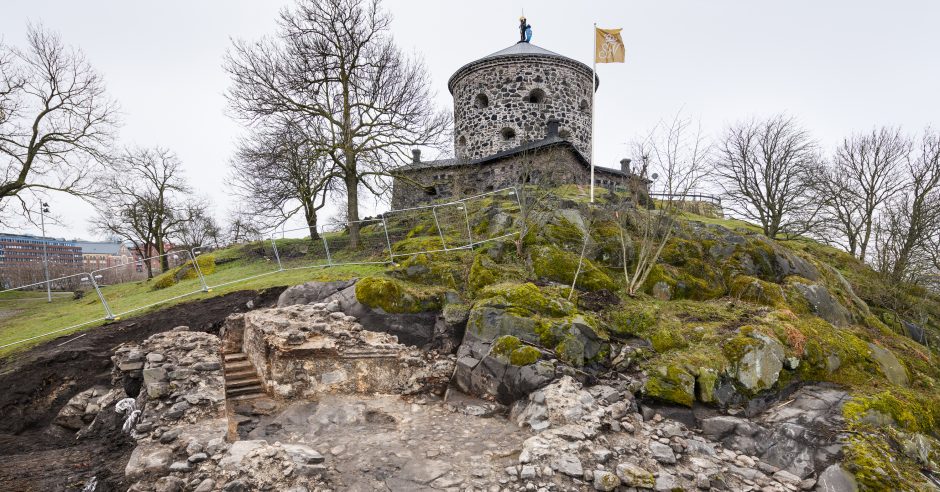
Gullberg Fortress, overlooking the mouth of the Göta River, held immense strategic significance for centuries. As Sweden’s sole direct access point to the North Sea when the rest of the western coast belonged to Denmark-Norway, the hill was fortified as early as the 14th century. The fortress predates the modern city of Gothenburg, founded in 1621, and served to protect its predecessor, Lödöse, a Viking settlement that blossomed into a major trade hub by the 13th century.
The history of Gullberg is marked by conflict, with evidence indicating multiple phases of destruction and reconstruction between the 14th and 17th centuries. It was ultimately destroyed by Danish forces in 1612. A vivid eyewitness account from ten-year-old Cecilia Krakow, who lived at the fortress during the attack, describes the desperate attempts to fend off the invaders.

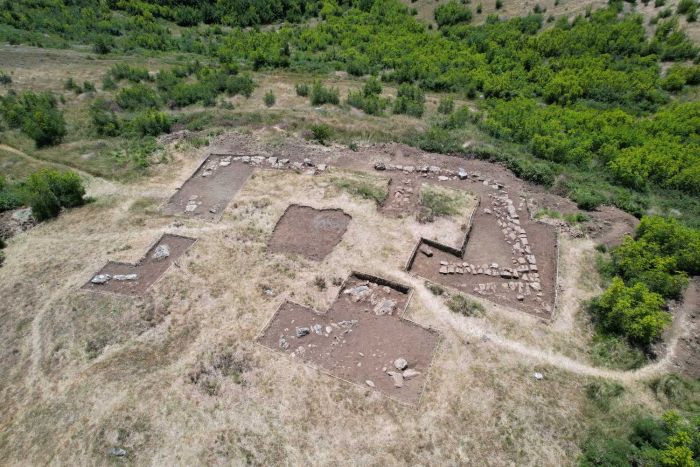
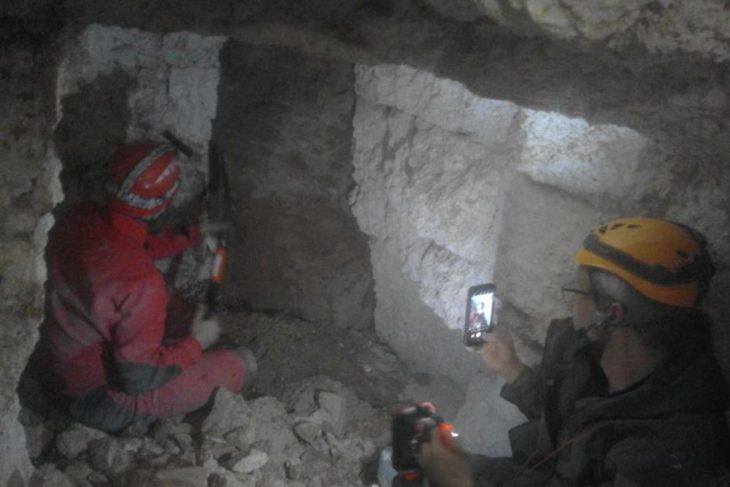
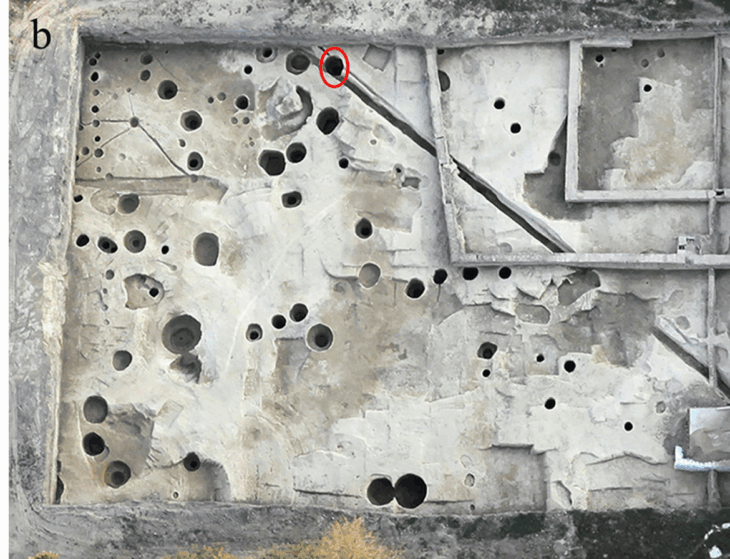
The archaeological excavations at the fortress site, conducted between 2014 and 2023 as part of a railway construction project, have yielded a wealth of artifacts. Unsurprisingly, the oldest finds were primarily weaponry, including crossbow bolts and arrowheads. Later discoveries include lead balls for light cannons and pistols, some of which were even manufactured within the fortress walls and potentially fired.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
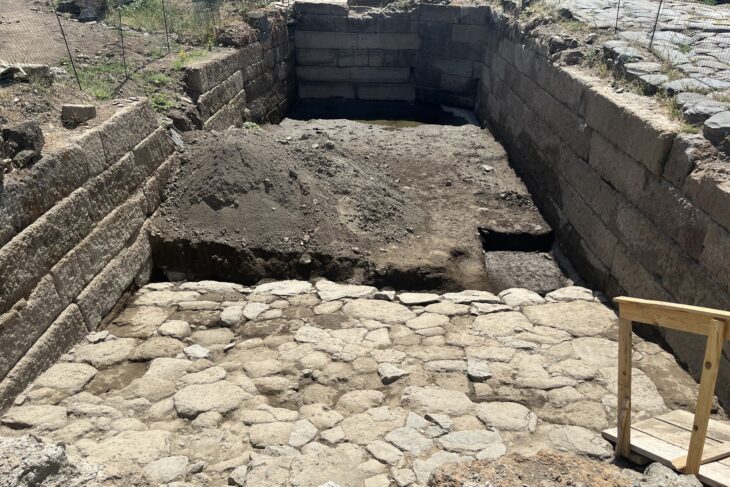
Beyond weaponry, the archaeologists also uncovered remnants of daily life. The foundations of a 16th-century tower, boasting remarkably thick 13-foot walls, revealed a cellar containing beer barrel taps, a sand sprinkler used to absorb excess ink, and a particularly noteworthy find: an intact limestone sundial, albeit missing its pointer.
The “testicle dagger,” with its distinctive hilt featuring two rounded, testicle-like decorations, is believed by experts to have been worn in a manner befitting its suggestive shape. While it may have been a somewhat flamboyant accessory for a warrior of the Tudor era, potentially offering a better grip for delivering forceful blows through armor, the broader context of the findings paints a picture of a thriving, albeit often besieged, community.
“We did not think there would be as much left as there was,” commented Anders Altner, an archaeologist at the State Historical Museum. The excavations revealed sophisticated construction techniques, with parts of the fortification built from stone and brick, while others utilized earthworks and timber. The remarkably well-preserved basement room, complete with its staircase, floor, and sections of walls and roof, was a particularly exciting discovery.

Originally established as a border fortress during the reign of King Birger Magnusson, the site remained in use, thanks to the presence of two forts, until the 19th century. The unearthed remains of houses, walls, and earthworks offer a tangible connection to the lives of people spanning several centuries. Analysis of ceramics indicates both local production and imports, while the wood used in a bridge has been dated to the 1460s, and timber from some buildings to around 1570.
The collection of artifacts unearthed during the decade-long excavations, including the intriguing “testicle dagger,” is currently on display at the Historical Museum in Stockholm as part of its Current Archaeology exhibition, which runs through January 2026. This exhibition offers a unique opportunity to witness the tangible remnants of a pivotal historical site and the lives of those who once inhabited and defended Gullberg Fortress.
Cover Image Credit: Arkeologerna/SHM