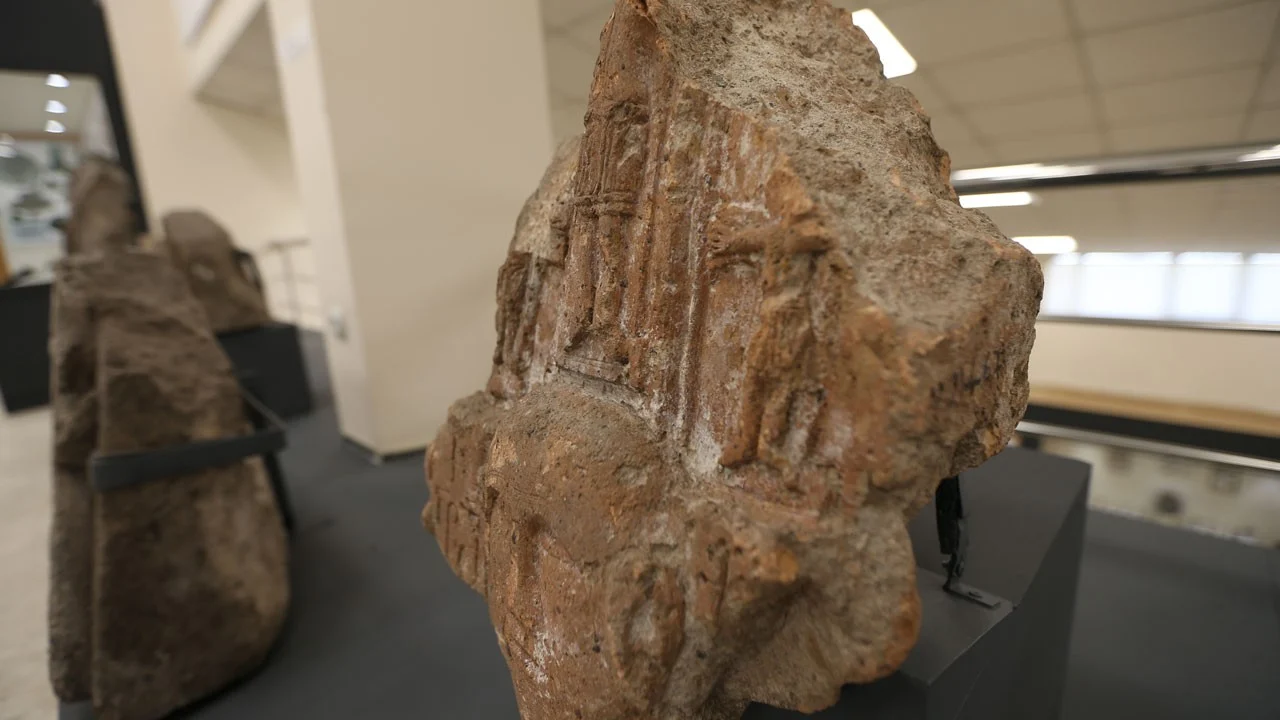
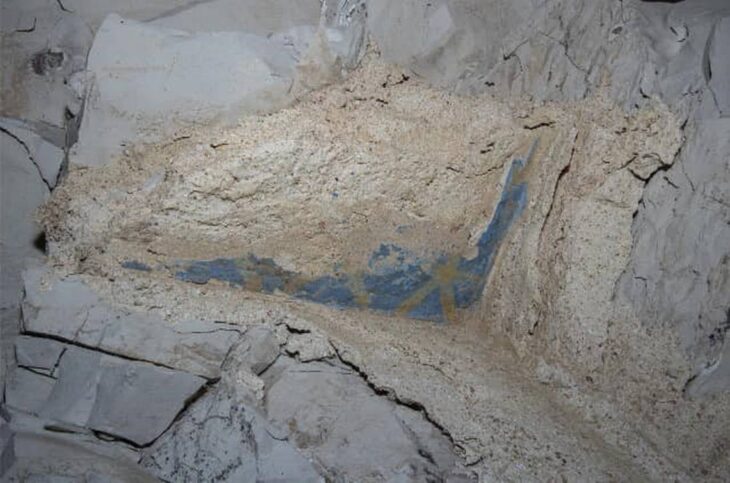
A significant archaeological artifact depicting Jesus Christ has been put on public display for the first time at the Kars Archaeology and Ethnography Museum. The stone relief, originally excavated in 1892 from the ancient Ani Ruins, had been preserved in the museum’s storage for over a century before finally being exhibited.
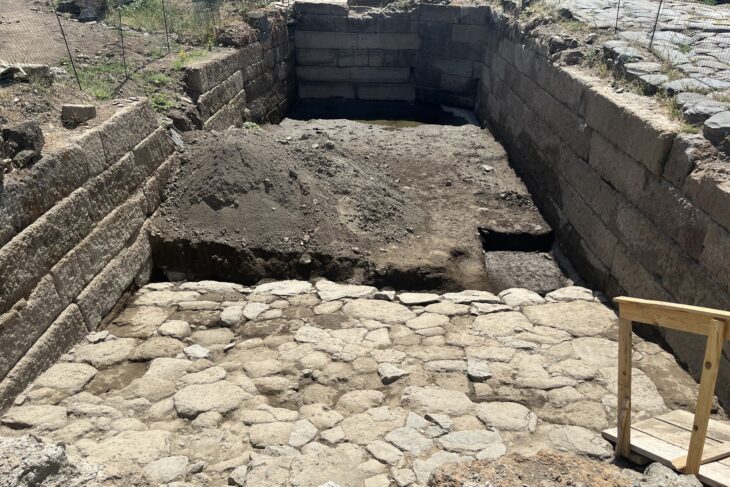
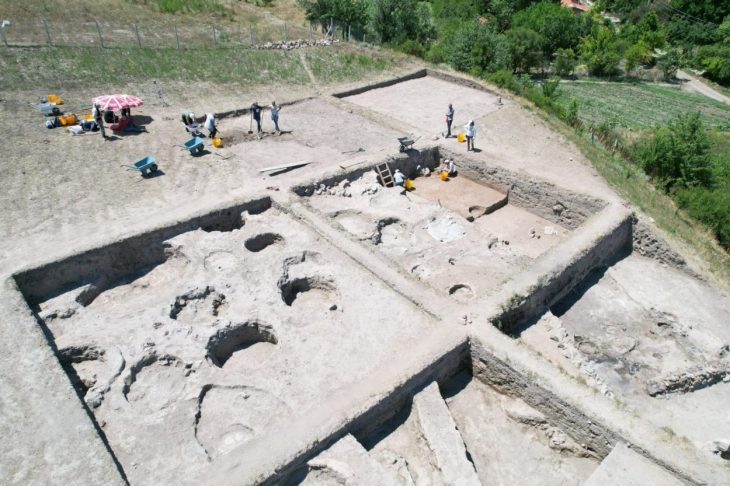
The Ani Ruins, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, are renowned for having hosted 23 different civilizations throughout history. Spanning across a vast area, Ani features a remarkable collection of architectural remains, including fortifications, mosques, cathedrals, palaces, churches, monasteries, baths, bridges, and partially destroyed covered passages. About 25 major structures still stand, providing a vivid glimpse into the city’s rich past. Archaeological excavations in Ani have been ongoing for over a century, continuously uncovering artifacts that shed light on the cultural and religious history of the region.
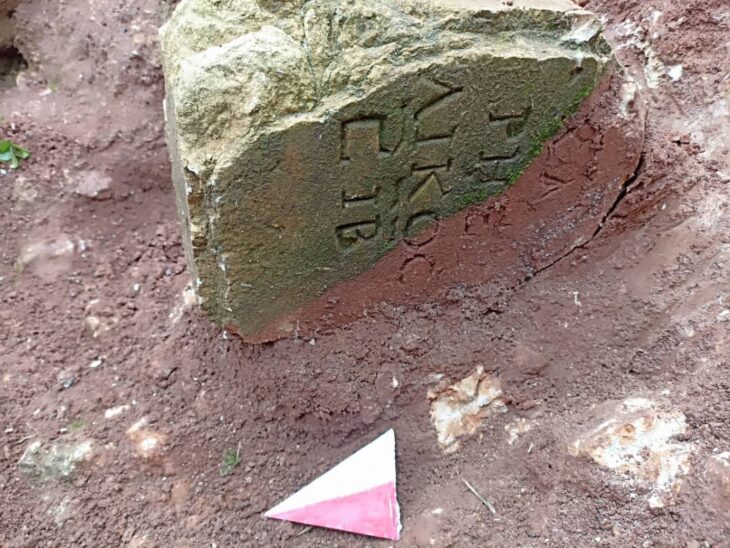
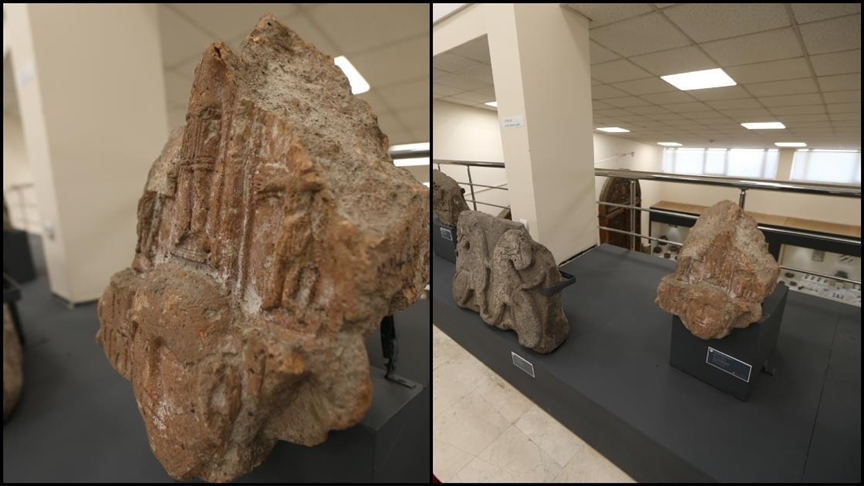
The newly displayed relief was uncovered by Russian archaeologist Nikolai Yarkovlevich Marr during his 1892 excavation. According to Hakim Aslan, Acting Director of the Kars Archaeology and Ethnography Museum, the relief is part of the “Ani’s Story” exhibition, which showcases 244 artifacts, including 196 items on display for the first time.
Describing the artifact, Aslan explained: “At the center and bottom of the relief, there is a portrait of a saint. Above it, Jesus Christ is depicted standing on a throne in a frontal position. On either side, two soldiers present offerings to Jesus. This stone relief is considered one of the most important pieces in our museum collection.”
While the relief was discovered 133 years ago, its creation likely dates back much further. Experts suggest it originates from the 11th to 12th century, during the height of the Armenian Kingdom of Ani, making it approximately 850 to 950 years old. This period saw the flourishing of stone architecture and detailed figurative reliefs in Ani’s churches and monasteries, highlighting the city’s religious and cultural significance.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

The Ani Ruins themselves hold immense historical and archaeological value. Located near the modern border of Türkiye and Armenia, Ani was once a bustling medieval city, often referred to as the “City of 1001 Churches” due to its numerous religious structures. Its strategic location along trade routes made it a center of commerce and culture. Over time, Ani experienced earthquakes, invasions, and political decline, but many structures still survive, offering a window into medieval urban life.
The display of the Jesus Christ relief is part of the Ministry of Culture and Tourism’s “100+2 Temporary Museum Exhibitions Project”, which aims to bring rarely seen artifacts into public view. According to Aslan, “The exhibition allows visitors to connect with Ani’s rich history and see items that have remained in storage for decades.”
The Ani exhibition and the Jesus Christ relief highlight the region’s deep religious, historical, and artistic heritage. Visitors can now witness firsthand the intricate craftsmanship of medieval Armenian stonework and the city’s long-standing significance in Anatolian history.
With Ani continuing to be a focus of archaeological study, the museum hopes to expand its collection of exhibited items, offering both scholars and the general public a chance to explore one of the most remarkable ancient cities in the world.
Cover Image Credit: Anadolu Agency (AA)