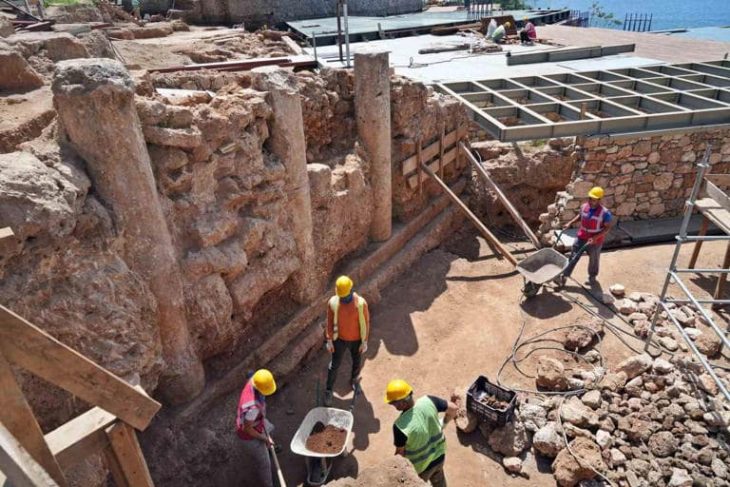
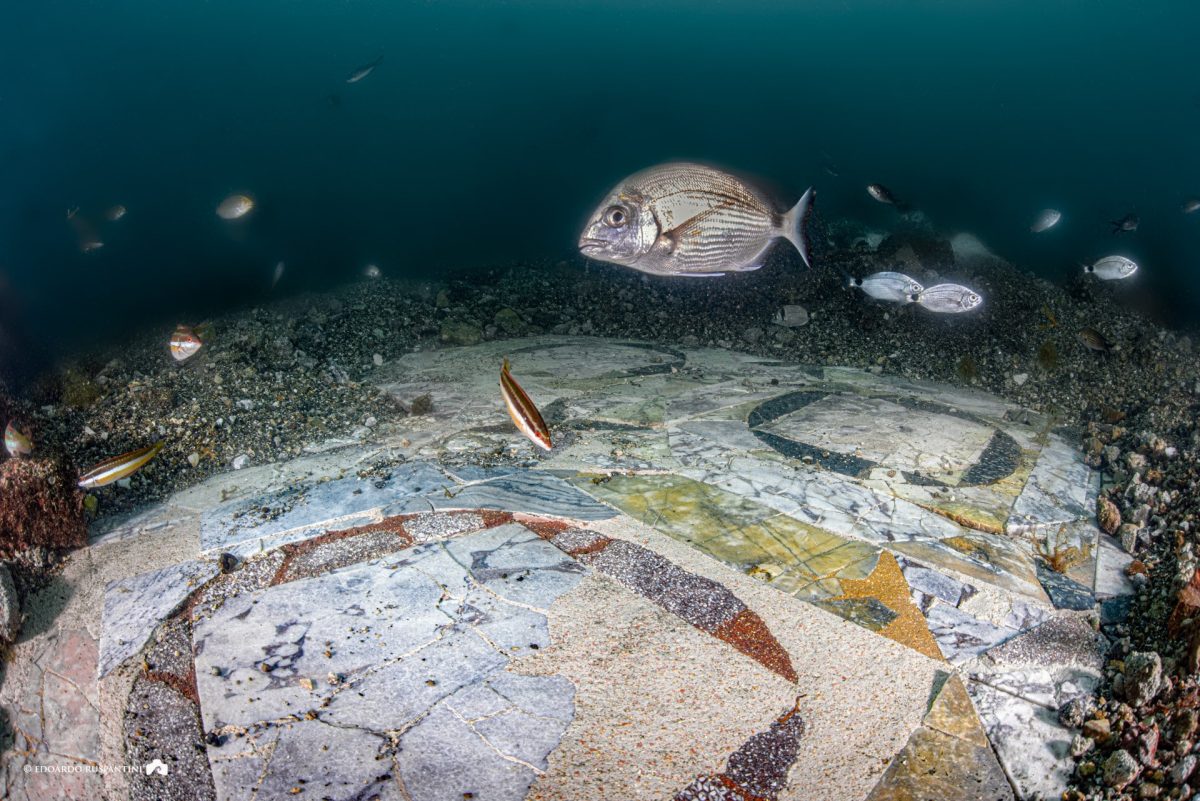In Bacoli, Italy, an underwater restoration project has uncovered the marvelous marble floor of a submerged Roman villa. This remarkable find is part of an ongoing excavation by CSR Restauro Beni Culturali and Naumacos Underwater Archaeology and Technology at the Submerged Archaeological Park of Baiae, which aims to illuminate the most historically significant underwater region of the Roman Empire.
In a Facebook post, the Parco Archeologico Campi Flegrei announced the discovery of the stunning marble floor near the submerged city of Baiae, located next to present-day Naples.
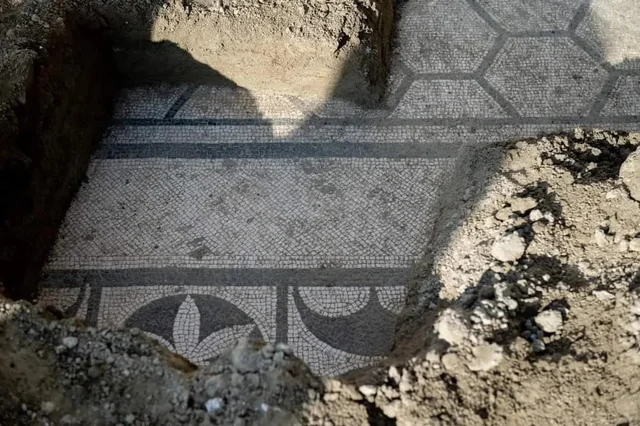
An expansive opus sectile floor, a decorative technique in which precisely cut pieces of stone or marble create intricate geometric patterns, was discovered by archaeologists collaborating with CSR Restauro Beni Culturali and Naumacos Underwater Archaeology and Technology.
In contrast to mosaics, which employ tesserae—small, uniformly sized pieces—opus sectile uses larger, painstakingly shaped pieces that fit together like a puzzle. This makes it possible to create more intricate and detailed designs, which frequently highlight the wealth and sophistication of the building’s owner. Opus sectile was frequently used to display wealth and artistic sophistication in high-status structures like villas, palaces, and public baths.
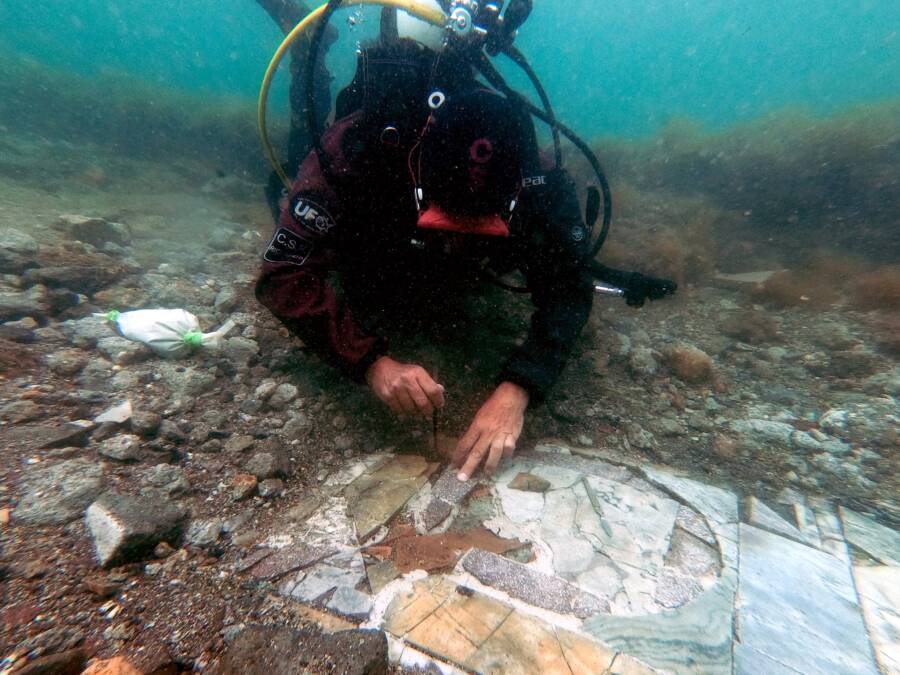

The floor, located in the submerged city of Baiae, spans approximately 2,700 square feet (250 square meters) and dates back to the final days of the Roman Empire. Surprisingly, the floor was built with used marble, probably to cut costs, a reflection of the financial strains that even the wealthiest people were facing at the time.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
“It is the magic of Baia Sommersa, a marble floor from an ancient Roman villa,” said Bacoli’s mayor, Josi Gerardo Della Ragione. “The floor in opus sectile, with its elaborate geometric motifs and extraordinary craftsmanship, offers a fascinating window into the life and art of ancient Rome. This discovery allows visitors to immerse themselves in history, exploring the hidden wonders beneath the surface of the sea.”
Although the restoration project is still ongoing, archaeologists described it as a “very demanding job” and said they hope to continue providing the public with updates on new developments in the coming weeks.

The submerged city of Baiae, also known as Baia, was an ancient Roman town located on the northwest shore of the Gulf of Naples. Baiae was renowned in antiquity as an opulent seaside retreat for Roman nobility, renowned for its opulent villas, thermal springs, and hedonistic ambiance.
However, over time, portions of Baiae sank below sea level as a result of bradyseism, which is the slow, alternating uplift and sinking of the Earth’s surface, and volcanic activity. The city was partially submerged as a result of this geological phenomenon.
Parco Archeologico Campi Flegrei
Cover Photo: The recently restored portion of the marble floor of the protiro villa in the submerged park of Baia. Photo: Edoardo Ruspantini