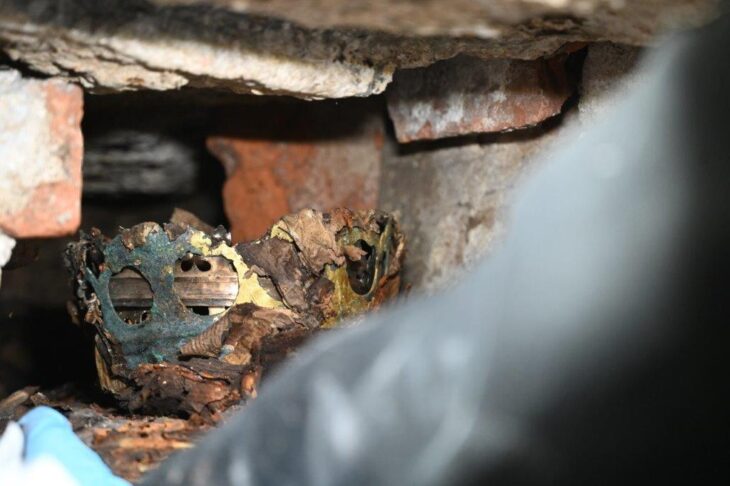
Archaeological research at the Manot Cave in what is now the Galilee in northern Israel has uncovered evidence of ritualistic gatherings dating back 35,000 years. This important discovery is shedding new light on the earliest inhabitants of the Asian continent.
Manot Cave was used for thousands of years as a living space for Neanderthals and humans at different times. In 2015, researchers from Case Western Reserve helped identify a 55,000-year-old skull that provided physical evidence of interbreeding between Neanderthal and homo sapiens, with characteristics of each clearly visible in the skull fragment.
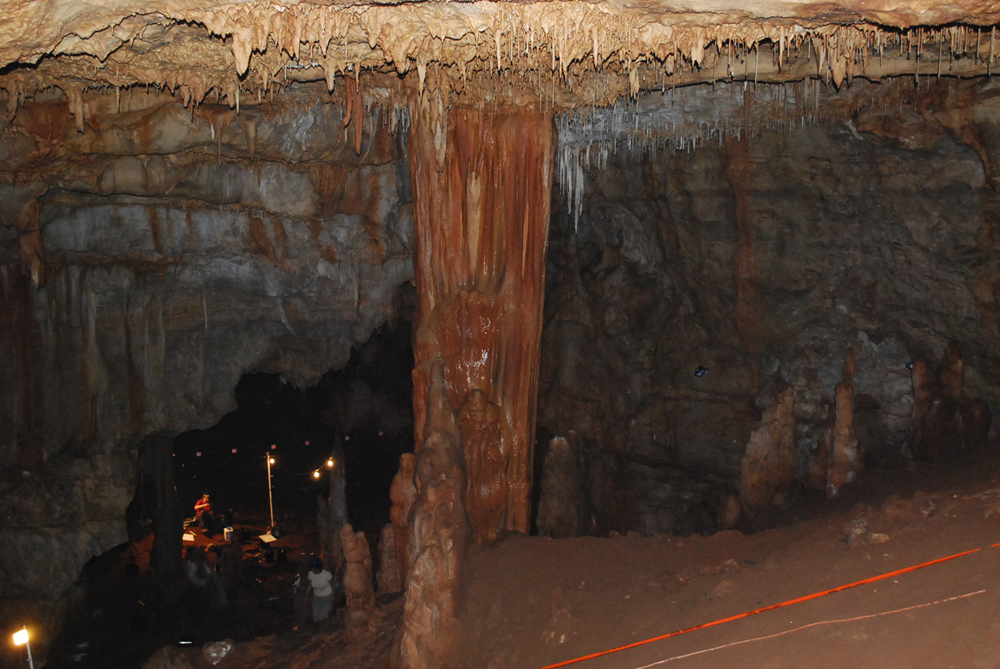
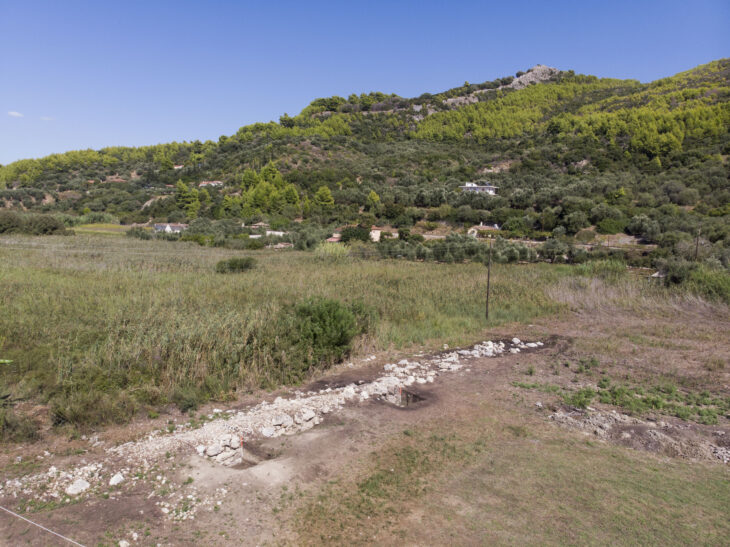
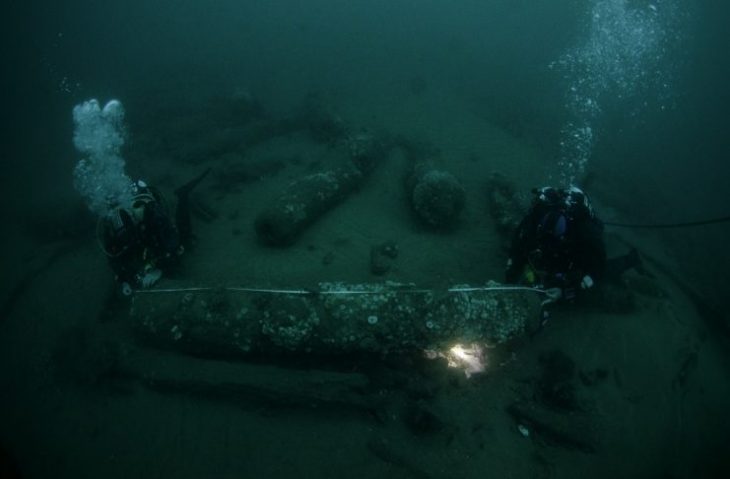
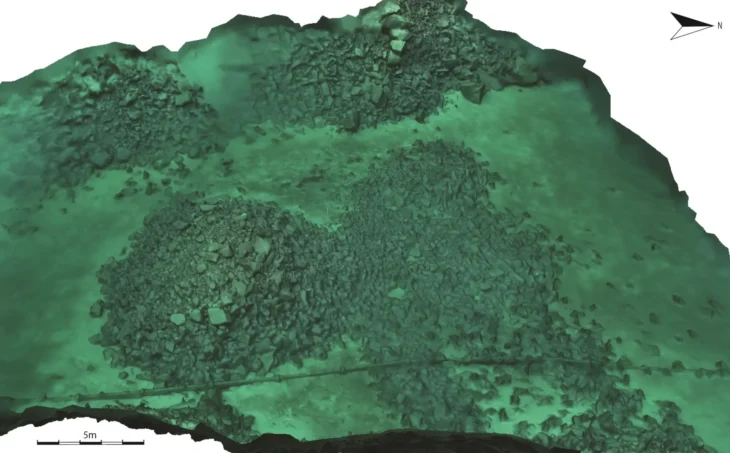
Manot Cave may have once been a ritualistic gathering site for early humans some 35,000 years ago, likely making it the earliest ritual site in Southwest Asia.
An important development in anthropological research, this discovery was just published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences journal. Under the direction of three Israeli researchers, the project included international partners, including a team from the School of Dental Medicine (CWRU) at Case Western Reserve University, which has been working at the location for more than ten years.
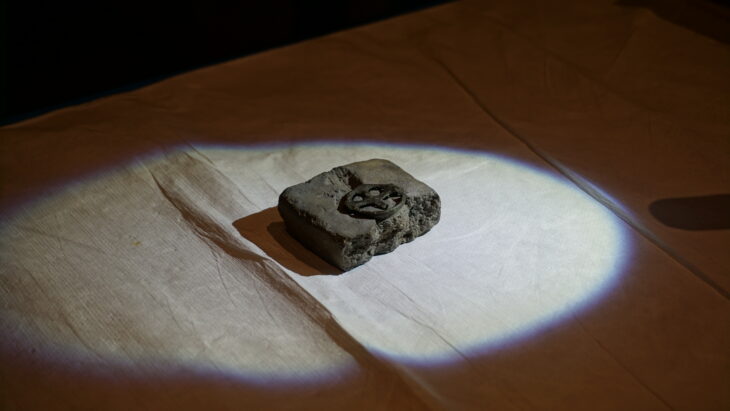
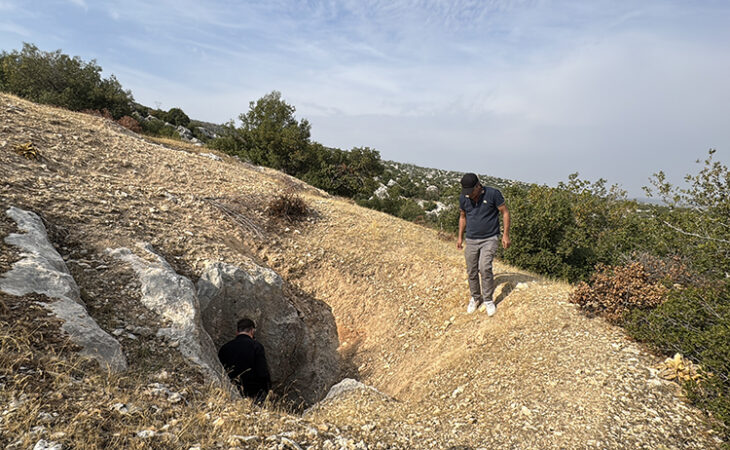
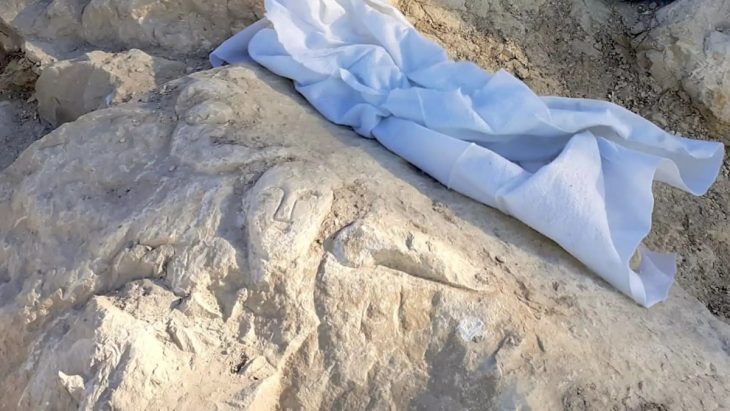
The study found that the cave residents resided nearer to the entrance. The ritual chamber, however, was located approximately eight stories below the cave’s entrance. A carved rock that resembled a turtle shell was found inside the chamber; it seemed to have been placed there on purpose in a niche. The carving was similar to the oldest cave paintings in France.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Stone tools, butchered animal bones, and other artifacts from regular human occupations between 46,000 and 33,000 years ago have been previously excavated at various locations close to the entrance of Manot Cave. That includes the time spent at the back of the cave performing group rituals. Activity in the ritual chamber dates to a time when artifacts in the living areas display influences of Europe’s ancient Aurignacian culture.
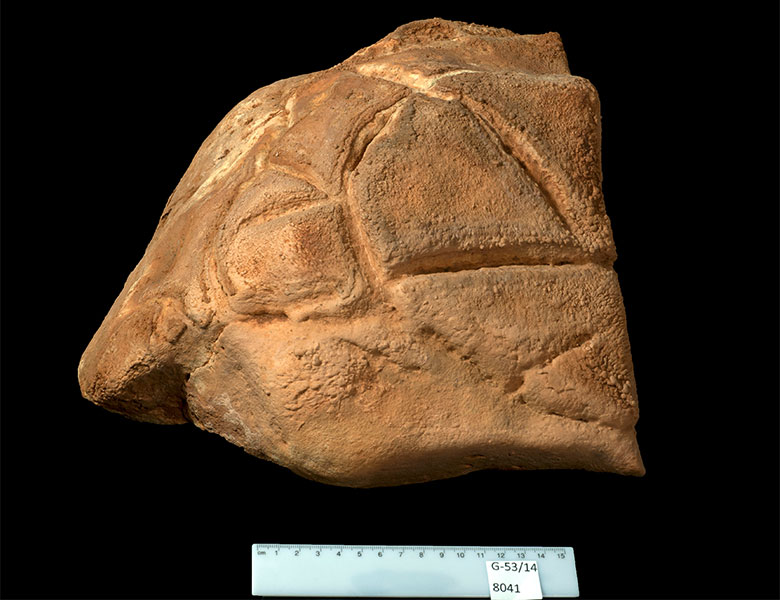

“It may have represented a totem or spiritual figure,” said Omry Barzilai, Head of Material Culture PaleoLab at the University of Haifa and the Israel Antiquities Authority, and team leader, in a press release. “Its special location, far from the daily activities near the cave entrance, suggests that it was an object of worship.”
The cavern has natural acoustics favorable for large gatherings, and evidence of wood ash on nearby stalagmites suggests prehistoric humans carried torches to light the chamber.
Though it is not yet known what rituals took place in this specific chamber, there is evidence that cultures, such as the Mayans, used caves for rituals like human sacrifice.
Manot Cave was discovered in 2008 by workers building condominiums in a mountain resort close to Israel’s border with Lebanon. Case Western Reserve’s School of Dental Medicine got involved in the excavation in 2012. Students from Case Western Reserve’s School of Dental Medicine began assisting archeological teams because of their ability to identify bones from rocks.
“Most people would not suspect that a dental school would be involved in an archaeological excavation,” said Mark Hans, professor and chair of orthodontics at the dental school, in a press release. “But one of the things that are preserved very well in ancient skeletons are teeth because they are harder than bone. There is a whole field of dental anthropology. As an orthodontist, I am interested in human facial growth and development, which, it turns out, is exactly what is needed to identify anthropological specimens.”
Experts from a variety of disciplines have collaborated internationally on the Manot Cave project. One of them, Linda Spurlock, a physical anthropologist from Kent State University, has added a visual element to the findings by sharing her knowledge of reconstructing human faces from skulls.
Case Western Reserve University
O. Barzilai, O. Marder, J. Tejero, A. Ayalon, et al., Early human collective practices and symbolism in the Early Upper Paleolithic of Southwest Asia, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 121 (51) e2404632121, doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2404632121
Cover Image credit: CC BY-SA 3.0