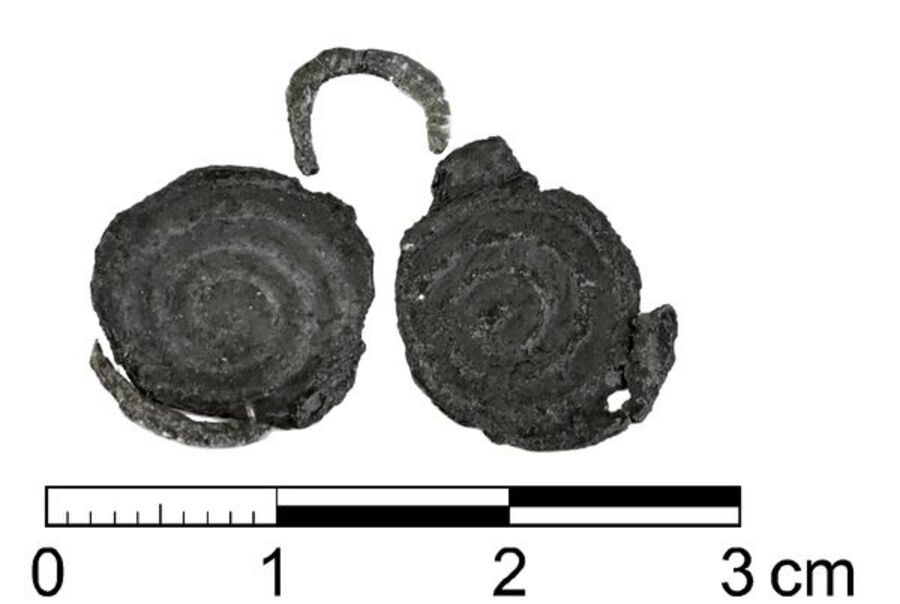
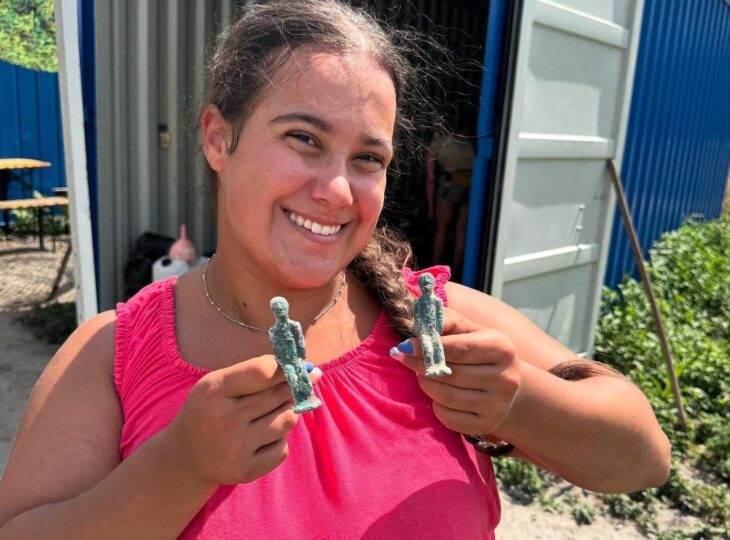
Researchers have uncovered the oldest confirmed evidence of metal ore mining and metallurgy in Poland through the study of lead artifacts from the Early Iron Age (800–500 BCE) sourced from the Olkusz deposits.
Researchers from the Jagiellonian University (JU) Institute of Archaeology have co-authored a groundbreaking paper published in the latest edition of the journal Archaeometry. The study focuses on lead trinkets from the Early Iron Age (800–500 BCE) and employs isotopic provenance methods to demonstrate that these artifacts were crafted from lead sulfide sourced from the Olkusz deposits. This discovery marks the oldest confirmed evidence of metal ore mining and metallurgy in Poland.
The geographical distribution of material culture has long been a focal point in archaeology, helping to illuminate the communication networks of ancient societies. While traditional methods such as classification and typology have been widely used, archaeometric techniques are increasingly supplementing these approaches. These modern methods allow researchers to trace the origins of raw materials rather than just the production sites, thereby reconstructing long-distance trade routes. Geochemical methods, particularly those analyzing copper provenance, utilize unique ‘fingerprints’ based on trace elements and lead isotope ratios that vary across geological deposits.
During the Bronze Age and Early Iron Age, Europe witnessed significant advancements in trade relations, driven by the demand for valuable metals like copper, tin, and lead. The paper titled “The First Isotopic Evidence of Early Iron Age Lead Ore Exploitation in the Silesian-Krakow Upland, Poland: A Provenance Study of Lusatian Culture Lead Ornaments” presents new findings on the use of galena ores (lead sulfide) from Silesia and the Kraków-Częstochowa Upland, known as the Olkusz ore deposits.
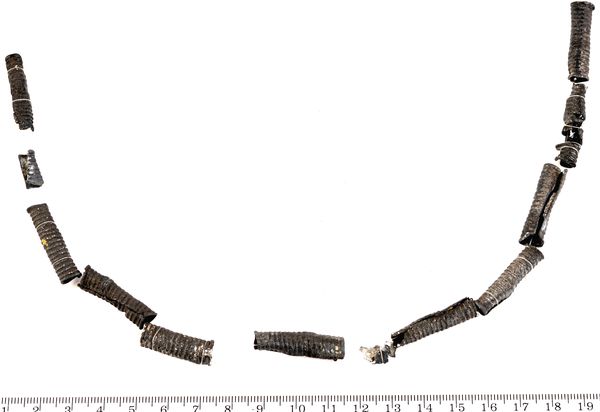

The researchers analyzed eleven lead trinkets from late Lusatian culture cemeteries using lead isotope analysis, confirming that most were made from local ore. This indicates that the Olkusz lead deposits were exploited much earlier than previously believed, now dated to 1,000 years earlier.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Dr. Karol Dzięgielewski from the JU Institute of Archaeology noted that historical records and geochemical data had previously confirmed the use of these deposits during the Middle Ages and Roman period. The recent findings extend the timeline of local deposit exploitation to the 1st millennium BCE, marking the earliest evidence of metal smelting from ores in Polish lands. Despite the extensive knowledge of metalworking in the region, the extraction of metals from ores had not been confirmed until this study. Throughout the Bronze Age, only imported copper, tin, and lead were utilized in what is now Poland.
He further noted, “Our research indicates that lead extraction from Olkusz galena deposits can be traced back to the 1st millennium BCE, suggesting that mining and smelting of metal ores in Poland began around the 8th or 7th century BCE, starting with lead rather than copper.”
The research team plans to continue their investigations by comparing archaeological and geochemical tools to reconstruct the distribution patterns of raw materials for metallurgical production, particularly copper alloys, from the Bronze Age (circa 2000 BCE) to the end of the Early Iron Age (circa 450 BCE).
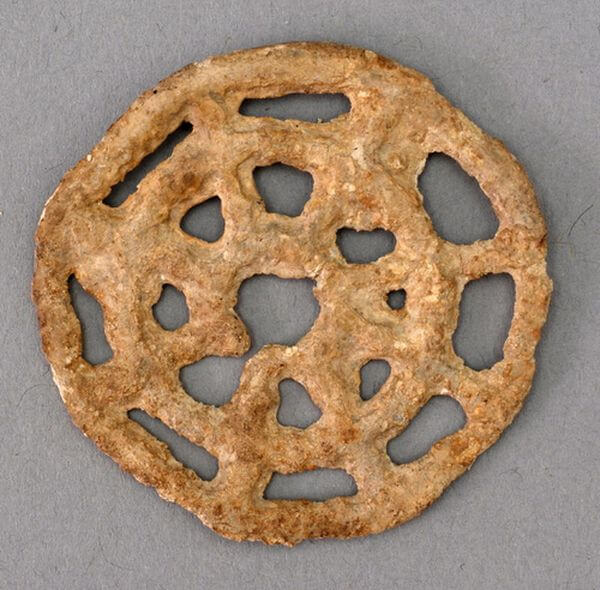

They aim to enhance the database of isotopic signatures (lead and tin) related to artifacts from this period. For iron artifacts, they will analyze the chemical composition of slag and employ innovative techniques involving osmium and strontium isotopes, referencing a comprehensive collection of geochemical data on prehistoric metal ore deposits across Europe.
The main authors of the study include Dr. Ewelina Miśta-Jakubowska, Dr. Karol Dzięgielewski, and Renata Czech-Błońska from the JU Institute of Archaeology, with contributions from scientists at AGH University of Science and Technology in Kraków, the National Centre for Nuclear Research in Otwock, and the University of Warsaw.
Cover Image Credit:Lead pendant from the Early Iron Age (800–500 BCE) discovered in a cemetery in Jankowice, Lesser Poland Voivodeship Credit: R. Czech-Błońska