A decade-long investigation conducted by the Korea Heritage Service has uncovered a crucial palace site of the Silla Kingdom (57 BC-935 AD), revealing findings that could potentially reshape the historical narrative of this ancient kingdom.
The Silla Kingdom, one of the oldest kingdoms in Korea, was established in 57 BC and lasted until 935 AD. As part of the Three Kingdoms period, Silla made significant advancements in art, architecture, and metalworking. In 668, Silla allied with the Tang Dynasty to conquer Baekje and Goguryeo, unifying much of the Korean Peninsula.
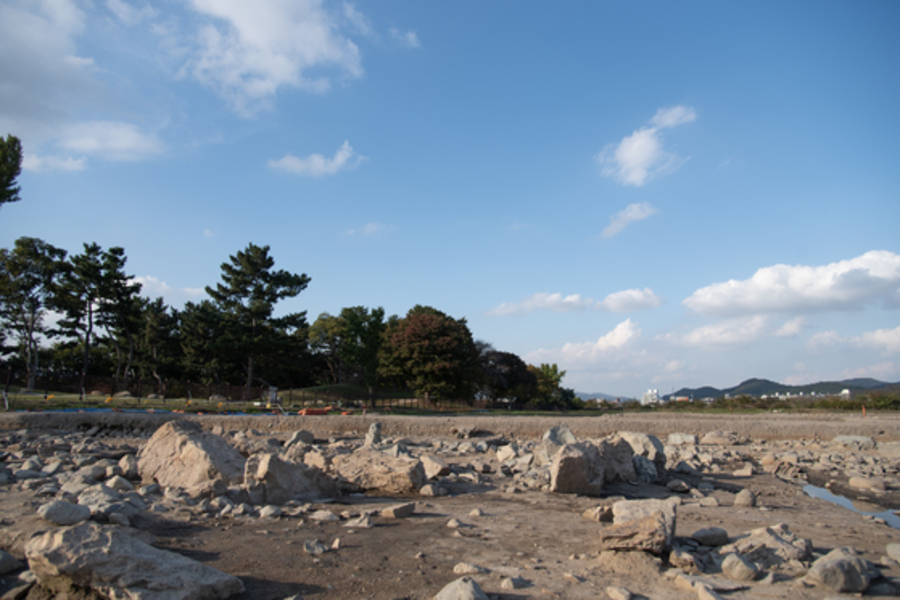
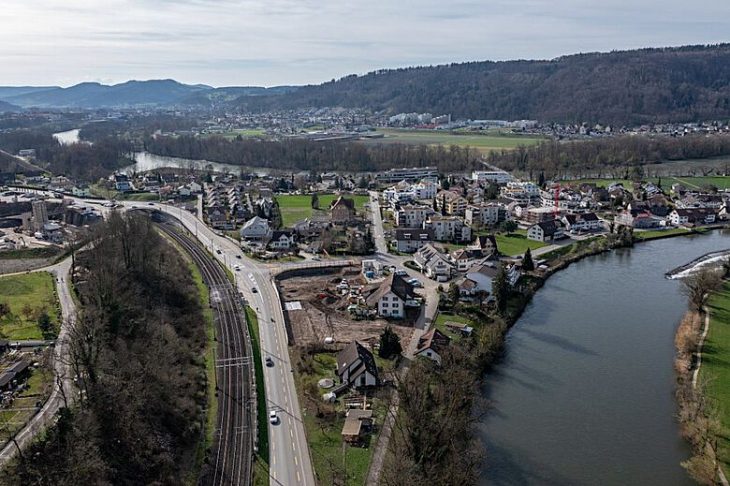
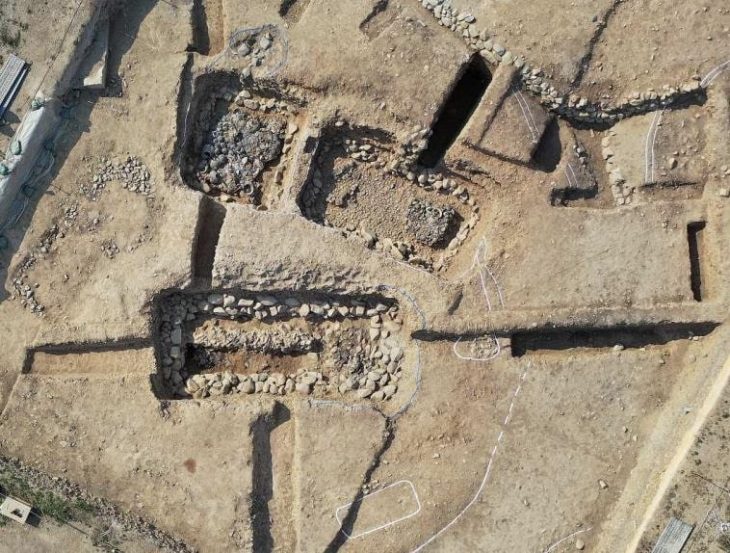
On Thursday, the South Korean Heritage agency said that according to new findings, Donggung, the palace of the crown prince of Silla, is located east of the pond called Wolji, not west of it as previously thought.
Previously, it was believed that Donggung was situated west of Wolji, an artificial pond formerly known as Anapji. However, the Korea Heritage Service announced last week that new findings indicate Donggung is actually located to the east of the pond. This conclusion is backed by substantial evidence collected on-site in Gyeongju, the city in North Gyeongsang Province that served as the capital of the Silla Kingdom.
Korea Heritage Service (KHS) chief Choi Eung-chon stated at a press conference on Thursday that the ground on the west side of the pond is slightly more elevated than on the east side, with remnants of structures on the west side standing a bit taller. He explained that this suggests the king occupied the western area, while his son resided in the eastern space. The two separate spaces, Choi added, were disconnected and the east side had an independent pond.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

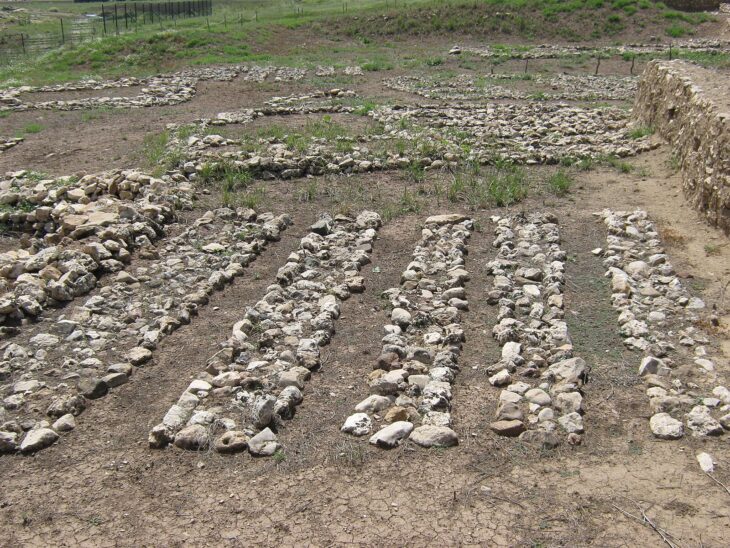
According to officials from the Gyeongju National Research Institute of Cultural Heritage, which is operated by the Korea Heritage Service (KHS), Drainage systems for the two spaces were different as well,. Choi Eung-chon said the discovery of a large building site on the eastern side of Wolji, which included the remains of a flush-style toilet system believed to date back to the Unified Silla period (668-935). Choi emphasized that this finding has resolved a long-standing debate and rewritten the history of the Silla Kingdom.
A representative from the think tank noted that the drainage systems not only reflect the lifestyle of the Silla people but also demonstrate the engineering skills of the time, contributing to a deeper understanding of this ancient kingdom, which is central to Korean history.
“This is an early example of a sophisticated plumbing system, reinforcing the idea that this was a royal facility,” said Kim Gyeong-yeol, senior researcher at the Gyeongju National Research Institute of Cultural Heritage, who has been working on the excavation project since 2014.
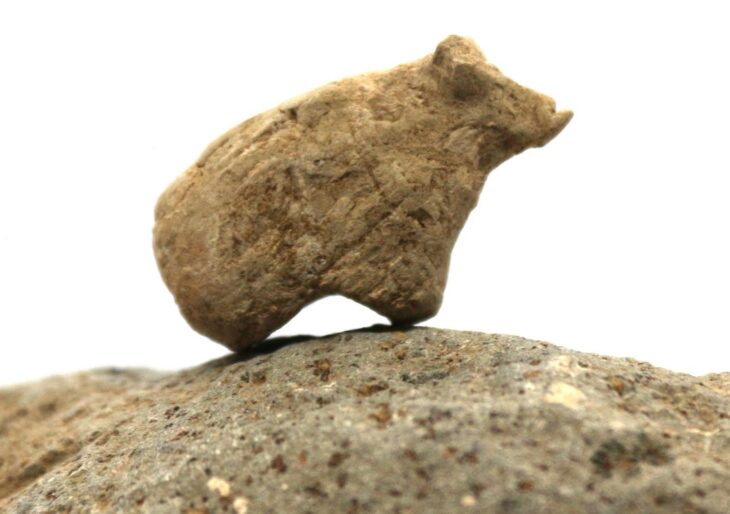
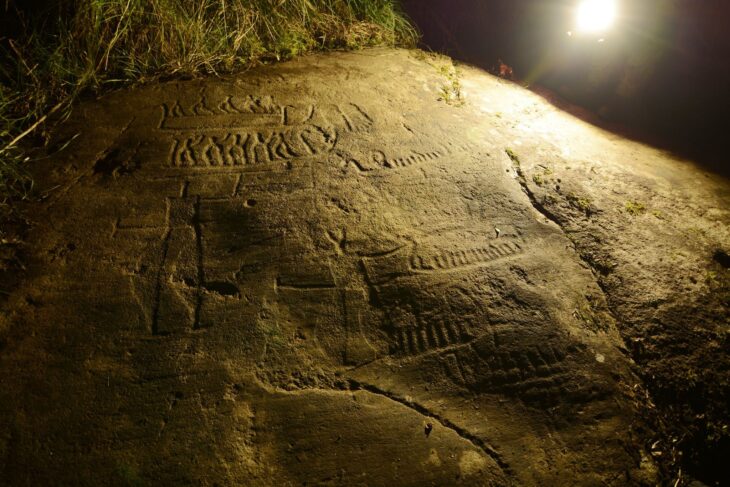
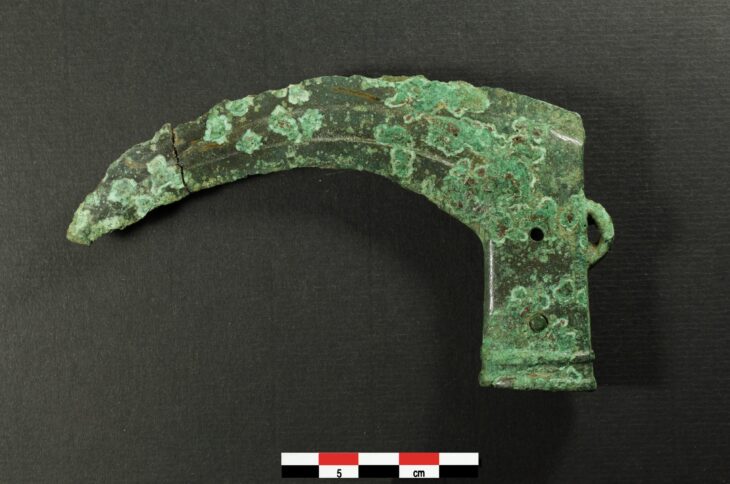
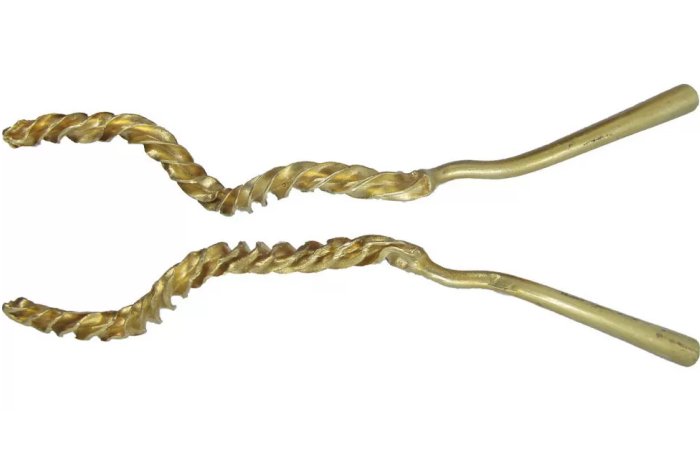
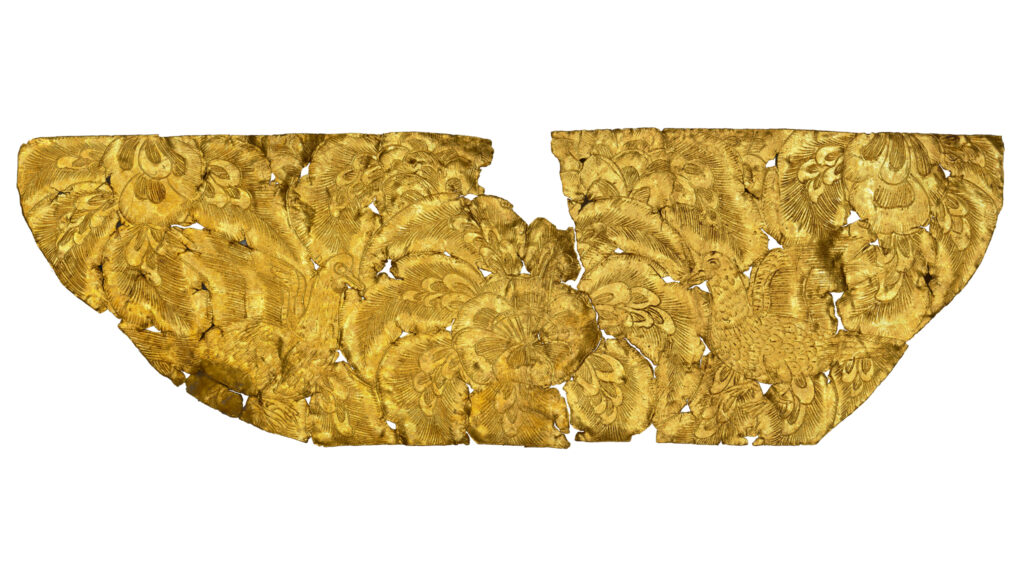
Over the past decade, numerous artifacts have been unearthed near Donggung. In 2017, archaeologists discovered a perfectly cube-shaped ivory die, while in 2022, an exquisite piece of pure gold foil featuring intricate microscopic carvings was found. This remarkable artifact, measuring 3.6 by 1.17 centimeters (1.4 by 0.46 inches), was located within an extensive excavation site covering 18,100 square meters (4.47 acres). Experts determined that this paper-thin piece of gold served as a canvas, engraved with two birds and imaginary flowers known as danhwa. The birds were carved to a thickness of just 0.05 millimeters (0.002 inches), which is finer than a human hair, highlighting the advanced metalworking skills of Silla artisans.
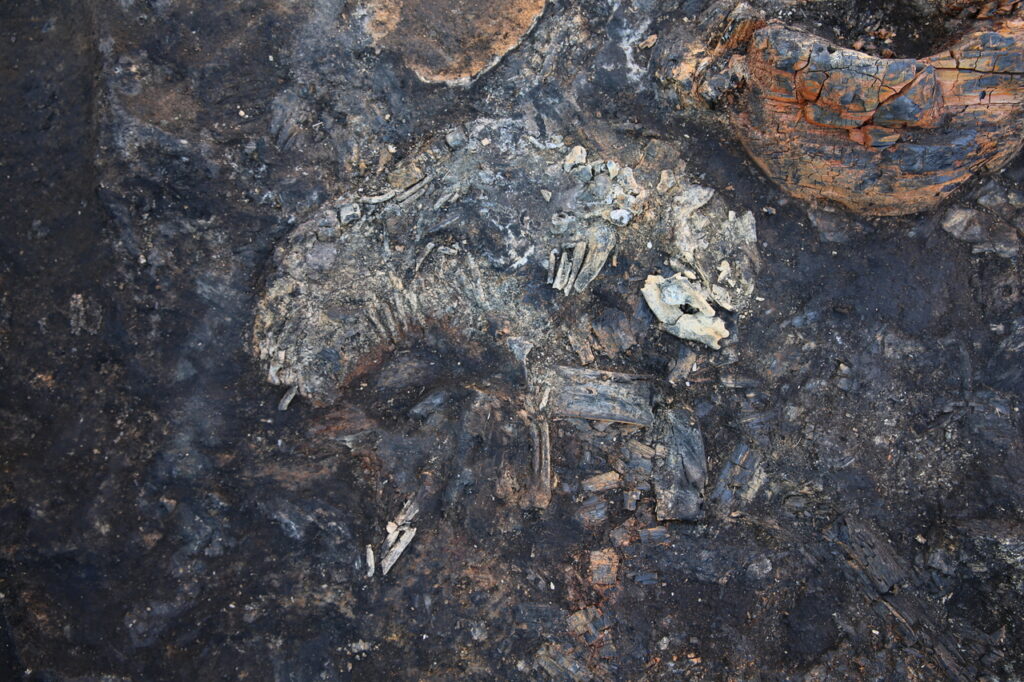

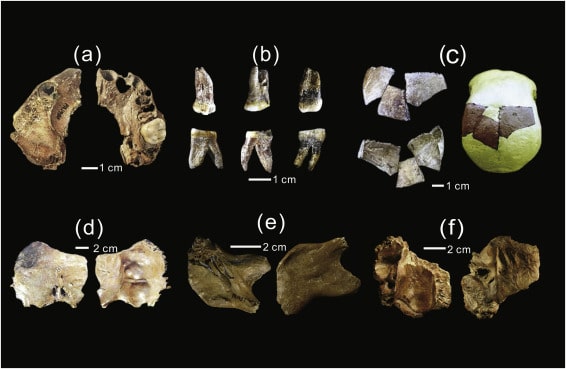
Among the discoveries near Donggung are various artifacts, including the remains of two dogs, a crystal necklace housed in a wooden lacquered container, a sword, and fossils of shark teeth. The remains of one dog were found in October of last year, and at that time, the Korea Heritage Service (KHS) determined that the dog was likely part of a human sacrifice ritual associated with the construction of the fortress, as human remains—bones of individuals believed to be in their 50s—were also uncovered at the site. Scholars suggest this may be evidence of human sacrifice, known as inshingoinghui, where individuals were offered to the gods to ensure the stability of a structure or fortification.
The KHS noted that the dogs were found in close proximity to one another and arranged symmetrically. All the artifacts recovered appeared to have been burned, and most are believed to date back to the third century, providing valuable insights into the rituals and practices of the Silla Kingdom.
According to Choi, the crystal necklace discovered in the wooden container is in fair condition and will aid the Korea Heritage Service in better understanding the types of ceremonies that occurred during the early years of the Silla Kingdom, up to the fourth century. He noted that the lacquered wooden container indicates a luxurious sacrifice, given the rarity of lacquer during that period.
Despite the significant discoveries made during the excavation, the exact location of Silla’s original royal palace remains a mystery. While it is evident that the kingdom expanded Wolseong after unification, the precise site of the pre-seventh-century royal residence is still unknown. According to the Korea Heritage Service, this excavation project is expected to continue for at least another 50 years. Notably, Wolseong is listed as a UNESCO World Heritage site, yet much of the area has been left largely unexplored in relation to its historical significance.
Cover Image Credit: A photo of the excavation site of Gyeongju’s Wolseong, a palace complex of the Silla Dynasty (57 B.C.-A.D. 935). Credit: Korea Heritage Service