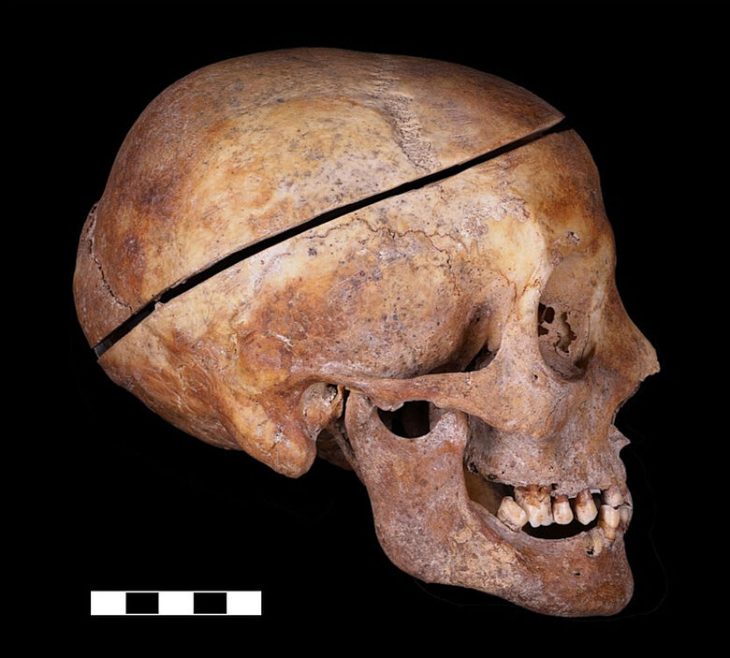
A team of researchers from Kyushu University and the University of Montana has found evidence suggesting that the Hirota community, residing on Tanegashima Island in southern Japan from the late Yayoi era to the Kofun era (3rd to 7th century CE), practiced cranial modification.
Researchers have unveiled new insights into the ancient practice of intentional cranial modification. This phenomenon, observed in various ancient civilizations globally, was also found among the Hirota people.
These inhabitants of Tanegashima, a southern Japanese island, practiced cranial modification between the 3rd and 7th centuries CE, according to a report recently published in PLOS ONE. Interestingly, the research shows no notable differences between the genders, suggesting that both men and women engaged in this practice.
Cranial modification is a form of body alteration where the head of a person is pressed or bound, usually at an early age, to permanently deform the skull. The practice predates written history, and researchers theorize that it was performed to signify group affiliation or demonstrate social status.
“One location in Japan that has long been associated with cranial deformation is the Hirota site on the Japanese island of Tanegashima, in Kagoshima Prefecture. This is a large-scale burial site of the Hirota people who lived there during the end of the Yayoi Period, around the 3rd century CE, to the Kofun Period, between the 5th and 7th century CE.” explains Noriko Seguchi of Kyushu University’s Faculty of Social and Cultural Studies who led the study.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
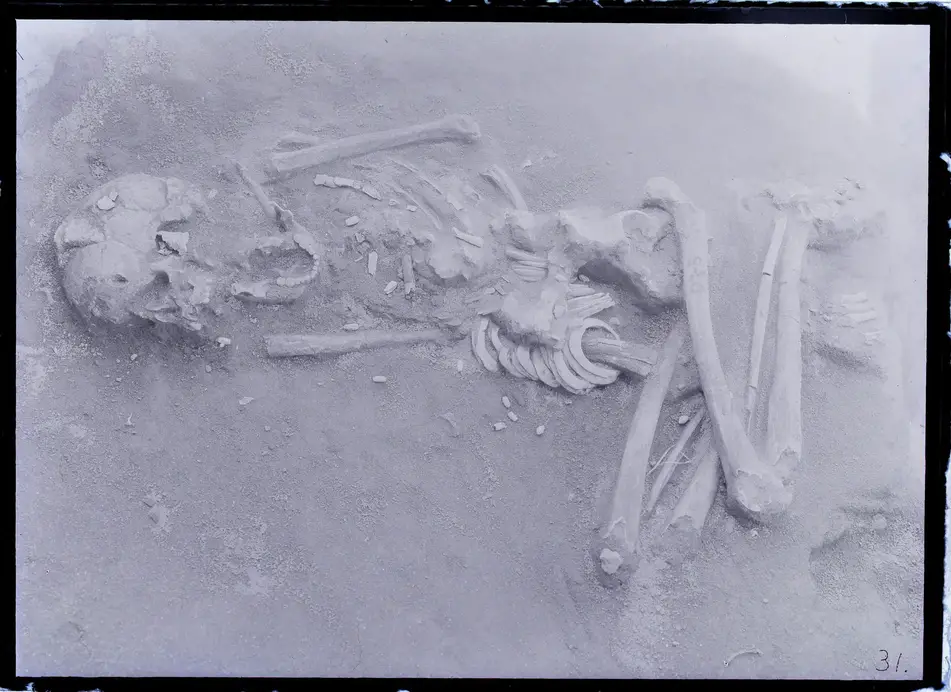
“This site was excavated from 1957 to 1959 and again from 2005 to 2006. From the initial excavation, we found remains with cranial deformations characterized by a short head and a flattened back of the skull, specifically the occipital bone and posterior parts of the parietal bones.”
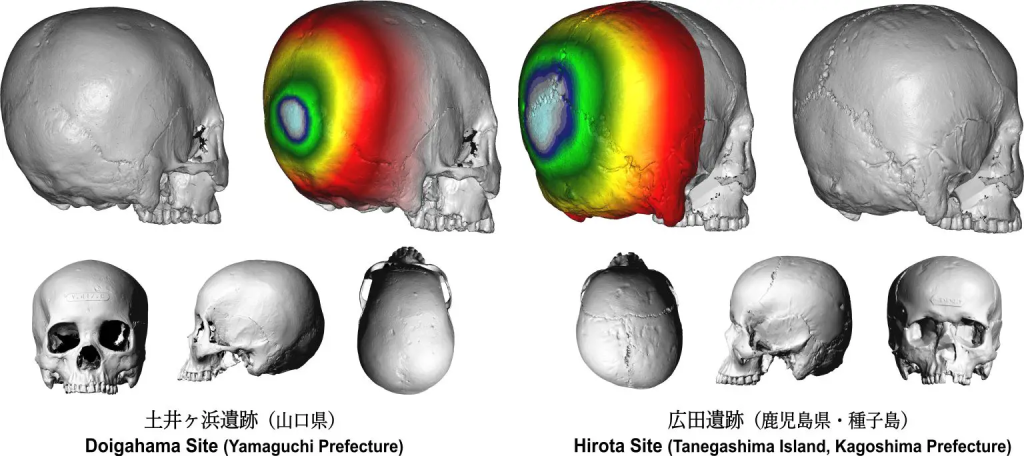
However, while the site provided an ideal opportunity to study the phenomenon, it had remained unclear whether these cranial modifications had been intentional, or were simply the unintended result of other habits.
To conduct the study, the research group employed a hybrid approach, utilizing 2D images to analyze the shape of the skulls’ outlines, as well as 3D scans of their surface. The group also compared crania data from other archeological sites in Japan, such as the Doigahama Yayoi people in Western Yamaguchi, and the Kyushu Island Jomon people, who were the hunter-gatherer predecessors to the Yayoi people. Along with visually assessing skull morphology, the team gathered all this data and statically analyzed the contours and shapes between the skulls.
“Our results revealed distinct cranial morphology and significant statistical variability between the Hirota individuals with the Kyushu Island Jomon and Doigahama Yayoi samples,” continues Seguchi. “The presence of a flattened back of the skull characterized by changes in the occipital bone, along with depressions in parts of the skull that connects the bones together, specifically the sagittal and lambdoidal sutures, strongly suggested intentional cranial modification.”
The motivations behind this practice remain unclear, but the researchers hypothesize that the Hirota people deformed their crania to preserve group identity and potentially facilitate the long-distance trade of shellfish, as supported by archaeological evidence found at the site.
“Our findings significantly contribute to our understanding of the practice of intentional cranial modification in ancient societies,” concludes Seguchi. “We hope that further investigations in the region will offer additional insights into the social and cultural significance of this practice in East Asia and the world.”
DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0289219
Cover Photo: A photograph of the ancient human remains found at the Hirota ruins. A notable characteristic of the remains is the wearing of many shell accessories, indicative of the culture and trade of the region at the time. Photo: The Kyushu University Museum