Researchers from Cairo University and the Technical University of Munich (TUM) have made a groundbreaking discovery within the Pyramid of Menkaure, the smallest of the three Great Pyramids of Giza. Using a combination of non-destructive testing (NDT) techniques, the team identified two hidden air-filled anomalies beneath the eastern facade of the pyramid—an area long suspected to conceal a second entrance.
The finding, published in NDT & E International as part of the ScanPyramids project, marks the first time structural voids have been confirmed behind the eastern granite casing of the Menkaure Pyramid. These results may finally validate a hypothesis first proposed in 2019 by Dutch researcher Stijn van den Hoven, who noticed striking similarities between the highly polished granite blocks on the pyramid’s eastern side and those framing its known northern entrance.
Advanced Technologies Reveal the Unseen
To investigate the long-standing theory of a hidden access point, the research team used three cutting-edge, non-invasive imaging techniques:
Electrical Resistivity Tomography (ERT) – detects subsurface resistivity variations that can reveal cavities or materials of differing density.
Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) – measures electromagnetic reflections to identify changes in underground structures.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Ultrasonic Testing (UST) – analyzes sound wave travel to detect internal boundaries and voids within solid materials.
Each method contributes unique insights. When combined, they allow for an unparalleled view beneath the pyramid’s outer casing without causing damage. The researchers also used Image Fusion (IF), a data-integration process that merges multiple imaging results to create a single, high-resolution composite. This advanced approach was key to confirming the anomalies’ presence and position with precision.
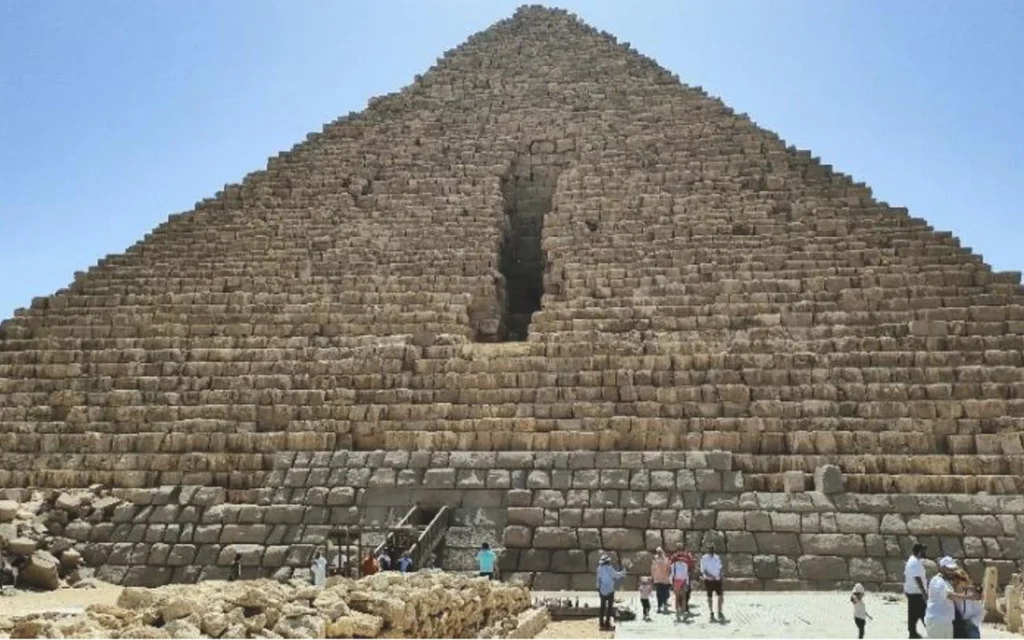

Discovery of Two Distinct Anomalies
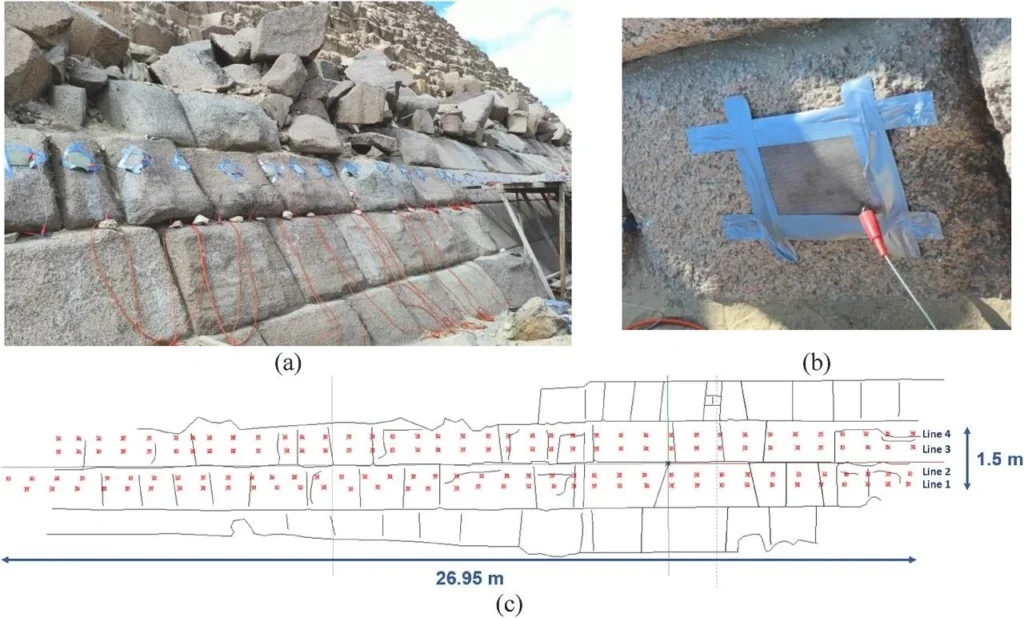
The integrated dataset revealed two distinct air-filled cavities located directly behind the smooth granite blocks of the pyramid’s eastern side. These are now labeled Anomaly A1 and Anomaly A2:
Anomaly A1: Positioned approximately 1.35 meters below the surface, measuring about 1.5 meters wide and 1 meter high.
Anomaly A2: Begins at a depth of 1.13 meters, measuring around 0.9 meters by 0.7 meters.
Both anomalies lie beneath the polished granite section, an area about four meters tall and six meters wide—dimensions identical to the smoothed northern entrance zone. The data strongly suggest that these voids are not natural fissures or cracks but deliberate architectural features.
According to Professor Christian U. Grosse of TUM, a co-leader of the project, the combined results “bring us a big step closer to confirming the existence of another entrance” to the pyramid. He noted that this integrated methodology represents “a new era of archaeological investigation—one that preserves heritage while revealing its hidden architecture.”
Interpreting the Purpose of the Voids
Through additional numerical simulations, the researchers tested different scenarios to interpret what could create such anomalies. The modeling results suggest that both A1 and A2 are likely air-filled voids extending into the limestone core of the pyramid. The data for A1 in particular matches a configuration where a trapezoidal granite block is positioned above a hollow space—possibly the beginning of a sealed corridor or chamber.
However, the full extent and function of the cavities remain uncertain. Due to the limited penetration depth of the employed technologies, researchers cannot yet determine how far these anomalies extend into the pyramid’s core. The team has recommended further studies using complementary methods such as muon tomography, infrared thermography, or micro-gravimetry to obtain deeper insights.

Building on Past Successes
This discovery follows ScanPyramids’ celebrated 2023 revelation of a hidden corridor inside the Great Pyramid of Khufu (Cheops), detected using similar technologies. That find demonstrated how combining multiple NDT methods can produce accurate three-dimensional reconstructions of previously unknown structures without excavation.
By applying the same multimodal imaging strategy to the Menkaure Pyramid, the researchers are extending that success. Their findings suggest that the eastern facade—previously overlooked by archaeologists—may conceal key insights into the construction methods and ceremonial design choices of ancient Egyptian builders more than 4,000 years ago.
Technological Innovation Meets Ancient Engineering
The study highlights how modern engineering and data science can illuminate ancient mysteries. The research involved over a dozen experts in geophysics, civil engineering, and Egyptology, including figures such as Zahi Hawass, Hany Helal, and Mehdi Tayoubi, underlining the international scope of the ScanPyramids collaboration.
To ensure accuracy, the team also conducted simulation experiments using open-source modeling tools like pyGIMLi, gprMax, and Salvus. These models helped differentiate between potential explanations—such as denser granite layers versus true air-filled cavities—by comparing synthetic data with real field measurements. The results consistently supported the interpretation of intentional voids.
The Road Ahead
While the newly discovered cavities do not yet confirm the presence of an undiscovered passage or burial chamber, they represent the most compelling evidence to date for a possible second entrance to the Menkaure Pyramid. If verified, this would fundamentally reshape understanding of the pyramid’s design and ritual symbolism.
For now, the ScanPyramids team continues its mission to explore Egypt’s ancient monuments using safe, non-destructive technologies. As Professor Grosse emphasized, “We are not just preserving the pyramids—we are learning from them in ways never before possible.”
Technical University of Munich
Khalid Helal, Polina Pugacheva, Hussien Allam, Mohamed Fath-Elbab, Mohamed Sholqamy, Olga Popovych, Simon Schmid, Benedikt Maier, Amr Galal, Alejandro Ramirez, Johannes Rupfle, Khalid Taie, Menna Ali, Clarimma Sessa, Thomas Schumacher, Mehdi Tayoubi, Christian U. Grosse, Hany Helal, Mohamed Elkarmoty: Detection of two anomalies behind the Eastern face of the Menkaure Pyramid using a combination of non-destructive testing techniques. NDT&E International (2025). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ndteint.2025.103331
Cover Image Credit: Cairo, Gizeh, Pyramid of Menkaure, Egypt, Oct 2005 – Wikipedia