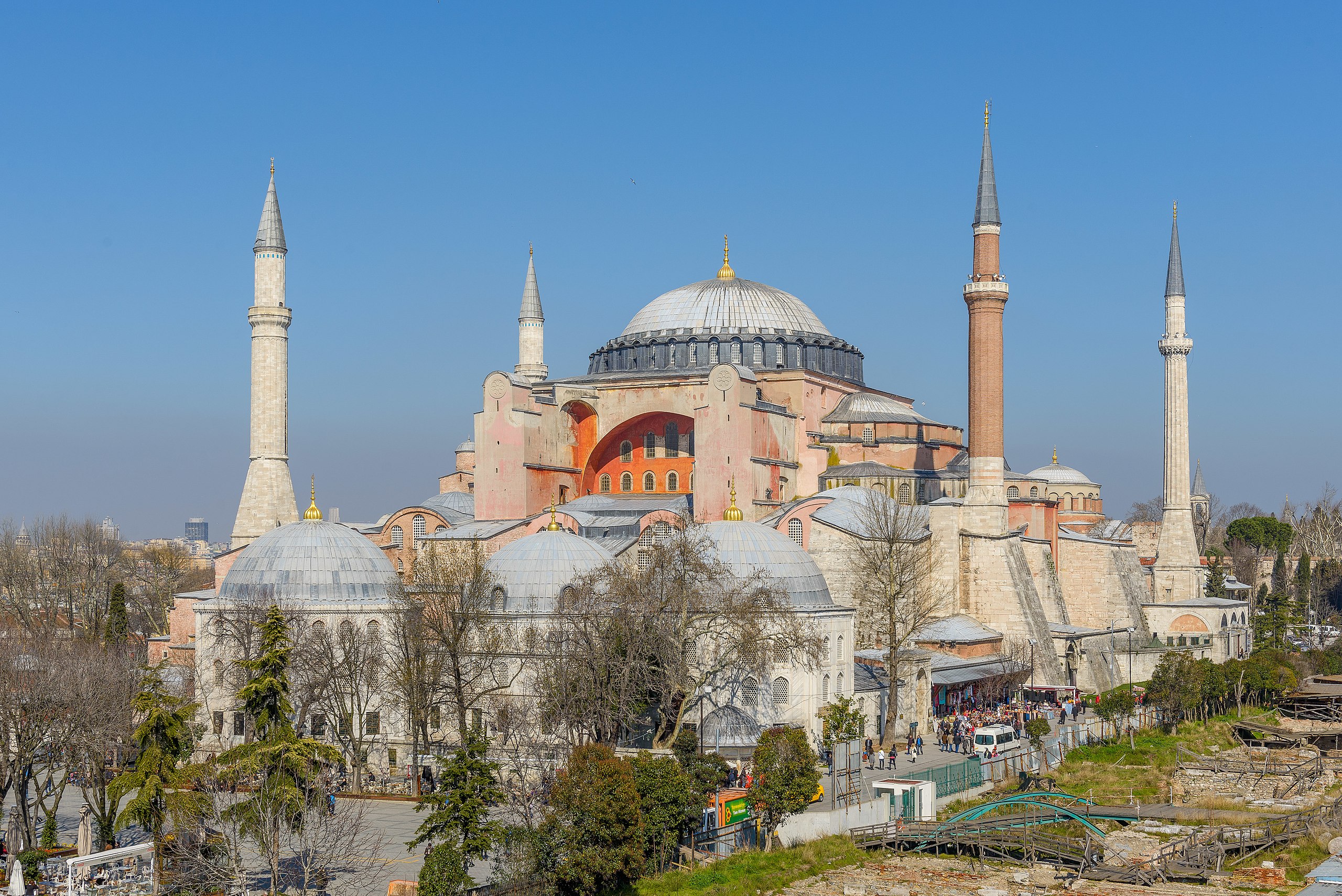
Beneath the grandeur of Hagia Sophia’s golden domes and sacred mosaics lies a ticking time bomb. With over 1,500 years of history embedded in its stone walls, the iconic Istanbul landmark — once the world’s largest cathedral — now stands at a dangerous crossroads.
“It’s only a matter of time unless urgent action is taken,” warns esteemed historian İlber Ortaylı. “The building’s foundation is unstable, its corridors hollow, and it’s absorbing more strain than it can handle.”
As one of the oldest and most significant architectural marvels in human history, Hagia Sophia is not just a symbol of empire and faith, but a monument of universal heritage. Yet, experts across disciplines — historians, archaeologists, tour guides, and cultural watchdogs — are sounding the alarm: this treasured monument could face irreversible damage or even collapse unless preservation efforts intensify and access is more carefully controlled.
A Monument of Global Importance Under Pressure
Originally built in 537 AD during the reign of Byzantine Emperor Justinian I, Hagia Sophia has served as a cathedral, mosque, and museum, before returning to mosque status in 2020. Its architectural genius — particularly its massive dome — influenced countless sacred buildings worldwide.
But today, cracks in both the literal and metaphorical structure are showing. According to Ortaylı, no comprehensive structural restoration has taken place since Ottoman genius Mimar Sinan reinforced the monument in the 16th century. Millions of visitors annually put even more pressure on an already fragile structure.
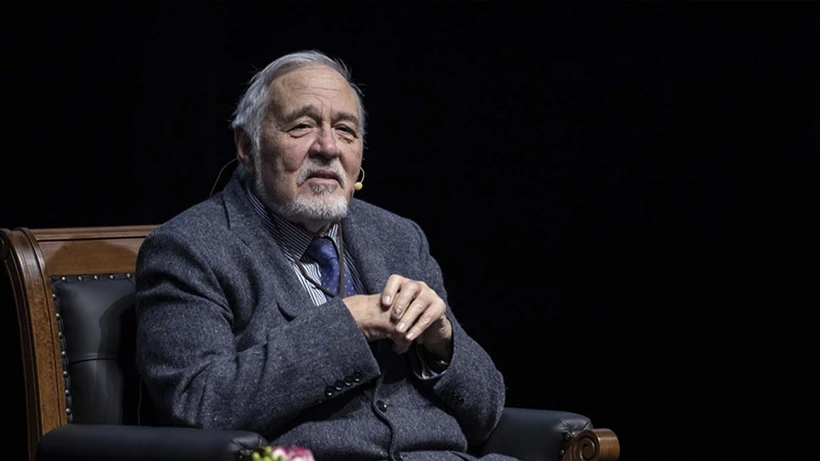

What Lies Beneath: A Weak Foundation and Unstable Future
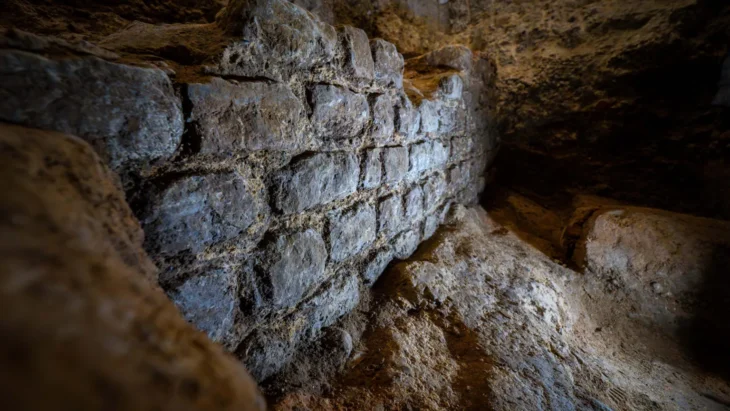
Underneath Hagia Sophia, experts say, is a network of ancient passageways and unstable ground. Earthquakes, vibrations, and crowds have worsened the condition of its columns and dome. Some columns now lean visibly; the marble floors are fractured. During a recent 6.5-magnitude earthquake, the site was hastily closed, exposing fears about its long-term stability.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Tour guides, who witness the building’s deterioration daily, describe the risk starkly: “We’re walking in there with our lives at risk. And the public doesn’t even see half the damage.”
Restricted Access and Cultural Tensions
While the building functions once more as a mosque, not all visitors are granted equal access. Some foreign tourists are denied entry to certain sections unless they are Muslim. This has sparked criticism about religious discrimination and a growing sense that the site is being politicized rather than protected.
“The dome — the most stunning view — can only be properly seen from a section many can’t access,” says a local guide. “This isn’t how global heritage should be treated.”
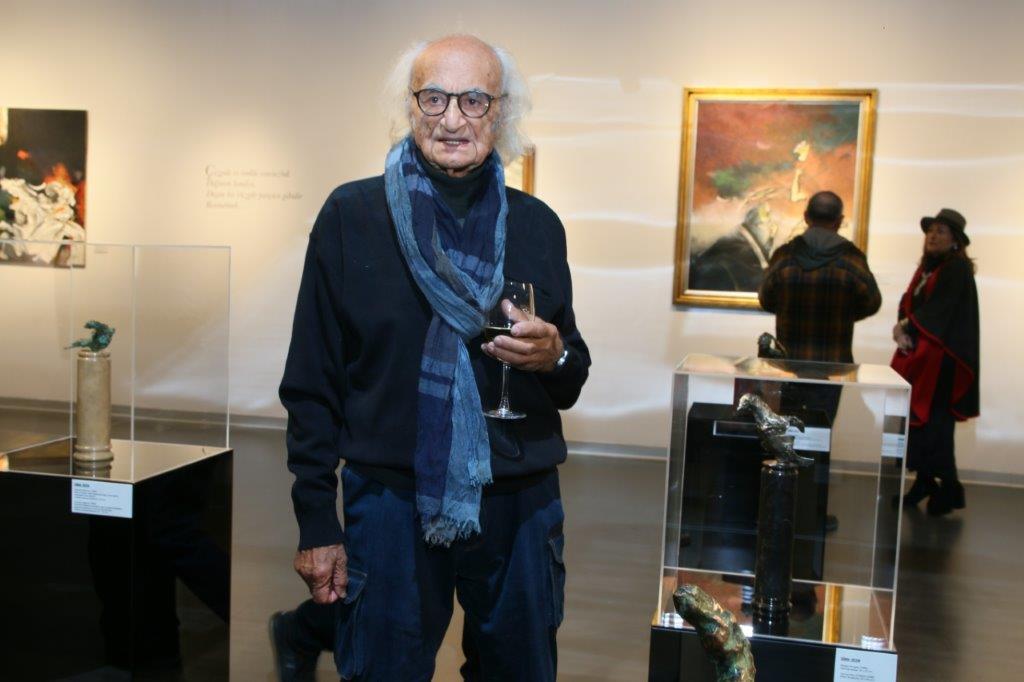

A Legacy Shared by All Civilizations
Art historian and painter Gürol Sözen passionately reminds us that Hagia Sophia was once a beacon of tolerance. “Did no one remember Sultan Mehmed’s approach when he entered Constantinople?” he asks. “This space belongs to everyone. Faith should not divide us here.”
He echoes the words of Sufi mystic Rumi and Seljuk ruler Izzeddin Keykavus, invoking centuries-old wisdom about inclusion and shared responsibility. “We are the caretakers of a legacy left on a golden platter by 12,000 years of Anatolian civilizations,” he says.
A Call for Transparent, Science-Based Preservation
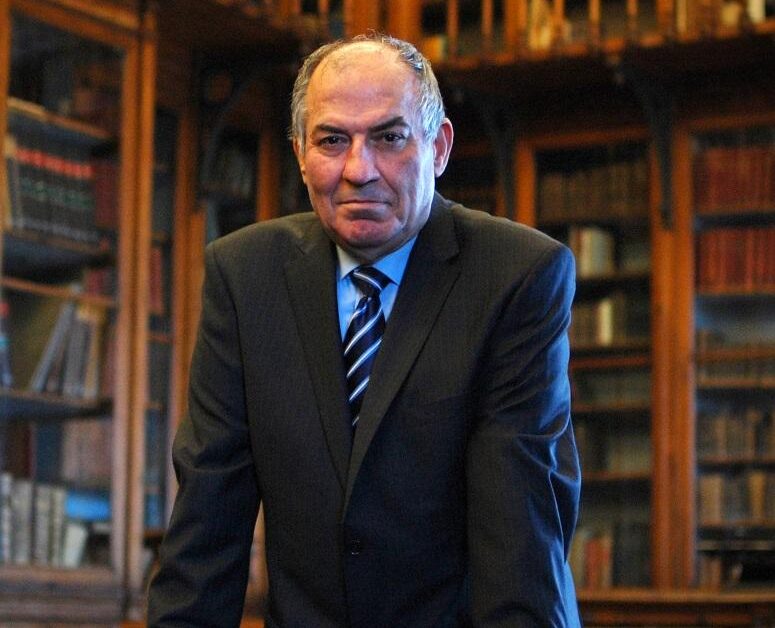
Nezih Başgelen, director of the Cultural and Natural Heritage Monitoring Platform and archaeologist, stresses the need for a new, rational management model. He argues for 24/7 structural monitoring, clear decision-making by restoration experts — not just religious or political authorities — and public transparency.
“The building must be treated like an elderly patient — constantly monitored, carefully handled,” Başgelen notes. “UNESCO status alone is not protection. Only informed action can save Hagia Sophia.”

Conclusion: Time Is Running Out
Hagia Sophia is more than stone, faith, or nation. It is a mirror reflecting the triumphs and failures of humanity itself. The current path, shaped by politics and neglect, may lead to the collapse of a global treasure. The world must ask: Are we willing to lose one of civilization’s last sacred giants — not because of time, but because of indifference?
Note: The expert opinions featured in this article are based on interviews originally published in Cumhuriyet Newspaper and conducted by journalist Öznur Oğraş Çolak.
Cover Image Credit: Hagia Sophia Public Domain