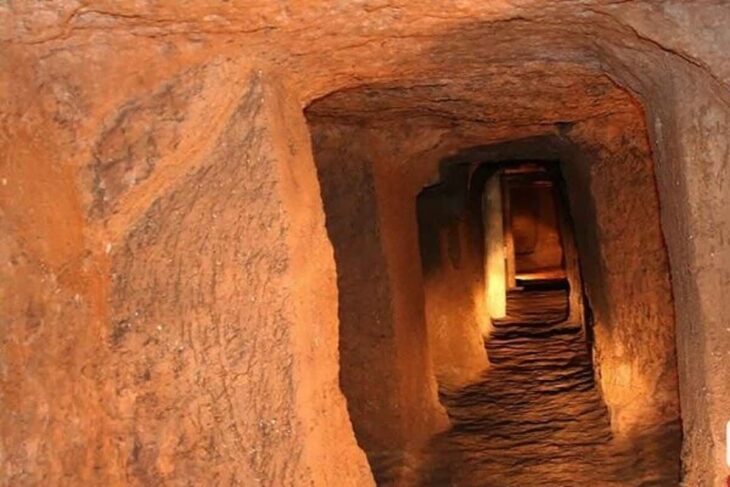
A social complex (Külliye) and new artifacts from the Western Gokturk period were discovered in Kazakhstan. Among these items, a belt buckle depicting the face of a Gokturk Khagan was found for the first time in history.
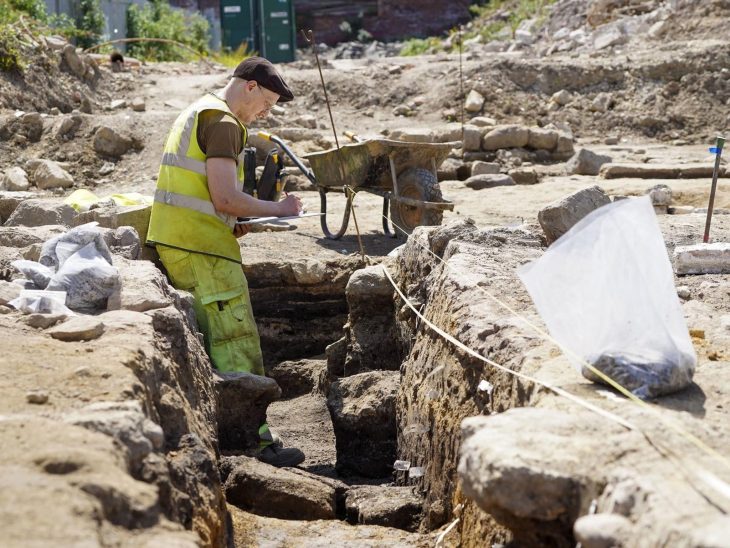
Kazakh archaeologist Professor Zainolla Samashev, who carried out the excavations and identified the findings, told TRT Haber (Turkish Radio and Television Corporation: the national public broadcaster of Turkey) the details for the first time.
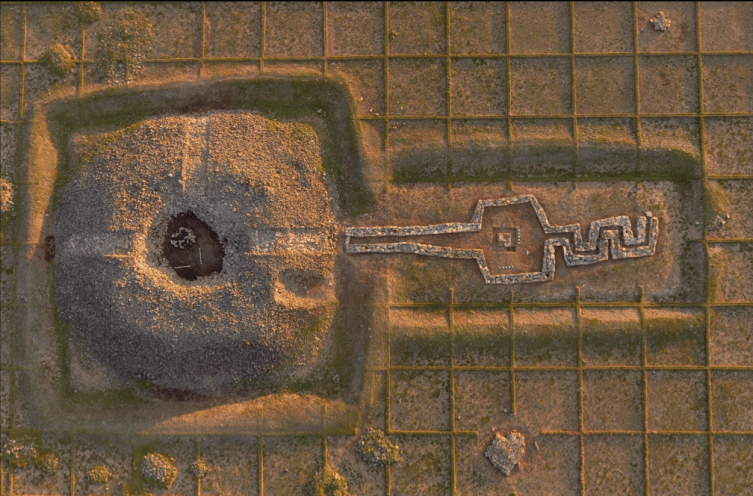
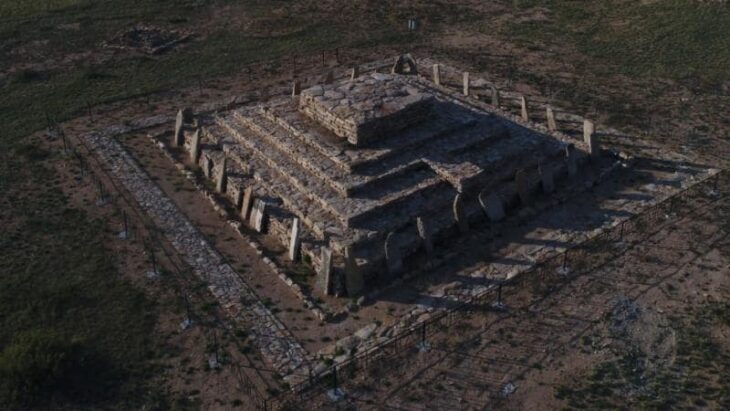
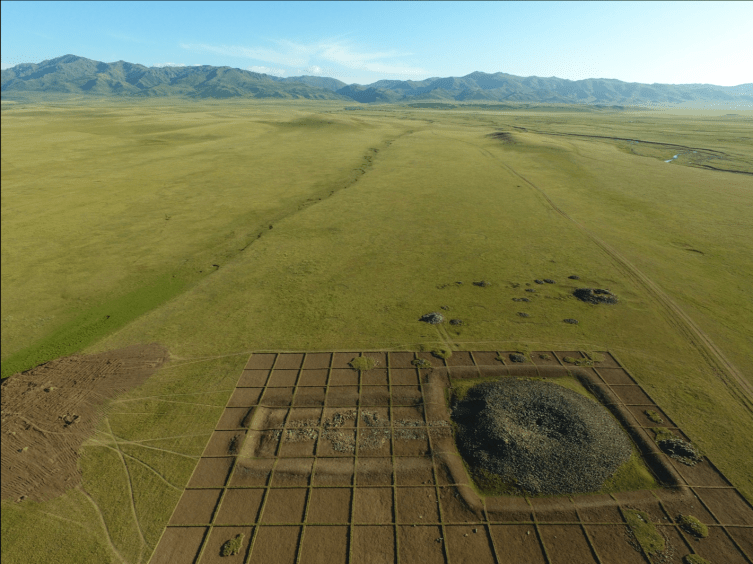
The works were discovered in the Kurgan area of the Eleke Sazy Khagan social complex.
Eleke Sazy is a valley in the Tarbagatay district of Kazakhstan’s Eastern Kazakhstan region. As a result of the archaeological surveys conducted between 2016 and 2018, more than 300 kurgans dating to the wide period of time from 9th century B.C. to 7th century A.D. were identified. Primarily, the discovery of the memorial cult-complex of the Western Turkic Khaganate attracts particular attention.
Eleke Sazy is a significant discovery from the perspective of pre-Islamic Turkic Art and Archaeology because it is the first and only memorial cult complex of Turkic Khaganate have determined outside of Mongolia until present.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
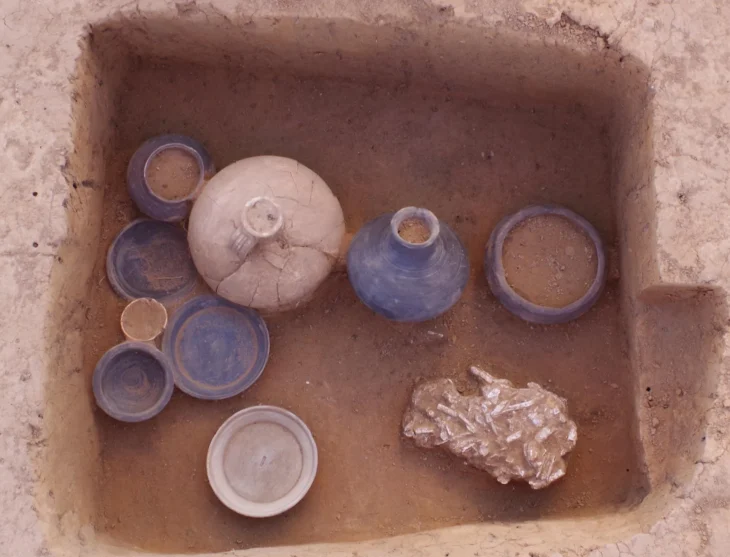
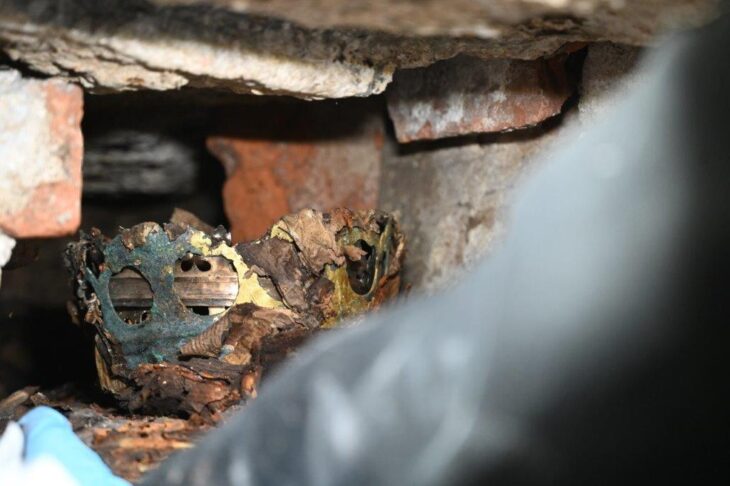
During the excavations in 2021, the personal belongings of Tegin -an ancient Turkish title with the original meaning of “prince”-, who belonged to the Göktürk lineage and was assigned to manage the On-Ok province on behalf of the Turkish Khagan in Suyab, were found in the kurgan area in the Eleke Sazy Khagan complex.
For the first time in history, a depiction of a Göktürk Khagan was found among these items.
The similarity of the complex in structure and form shows that it may have been built during the 2nd Gokturk State.
“Of course, this center was a complex built in memory of one of the Western Gokturk Khagans. Later, a large mausoleum was built here. Of course, this complex is of great importance for the Turkish world in terms of its architectural style, burial ceremonies, findings, and religious belief cult,” said Prof. Dr. Zainolla Samashev.
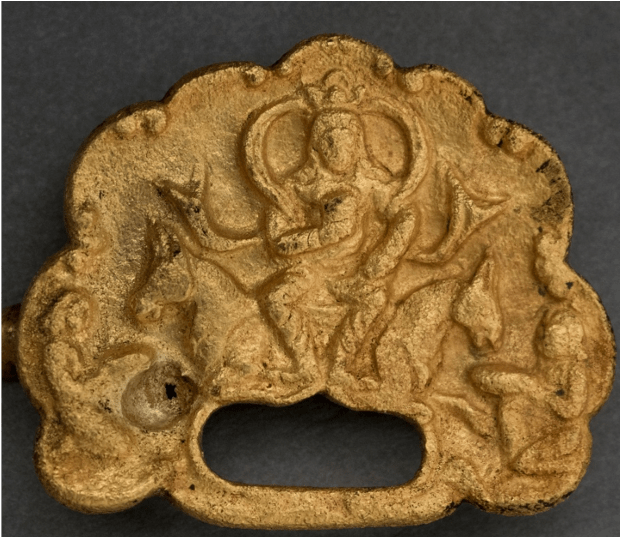

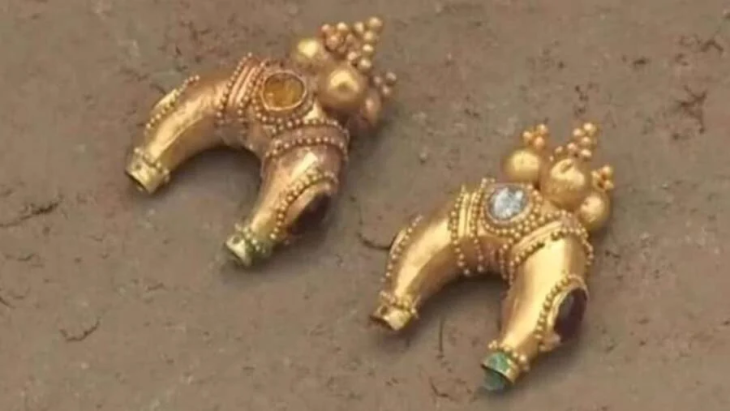
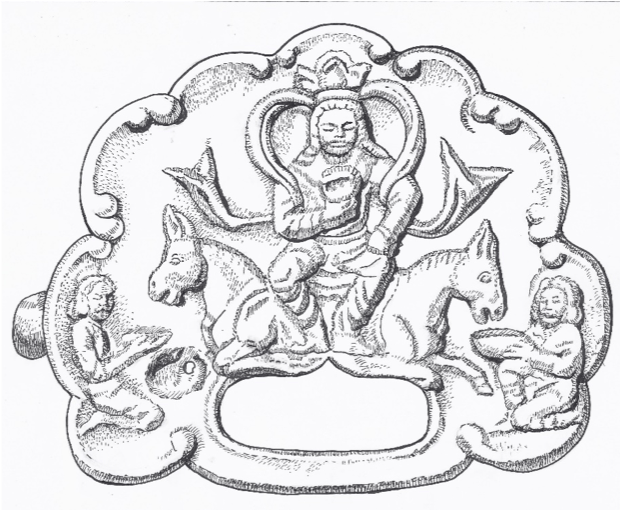
Stating that the findings found in the grave area were the personal belongings of the representatives who attended the Khagan’s burial ceremony, Professor Samashev said, “When we look at the Göktürk burial ceremonies, it was a duty to put personal belongings and weapons in the grave of the deceased. Among the recovered objects was a belt buckle made of gold plates.” made the statement.
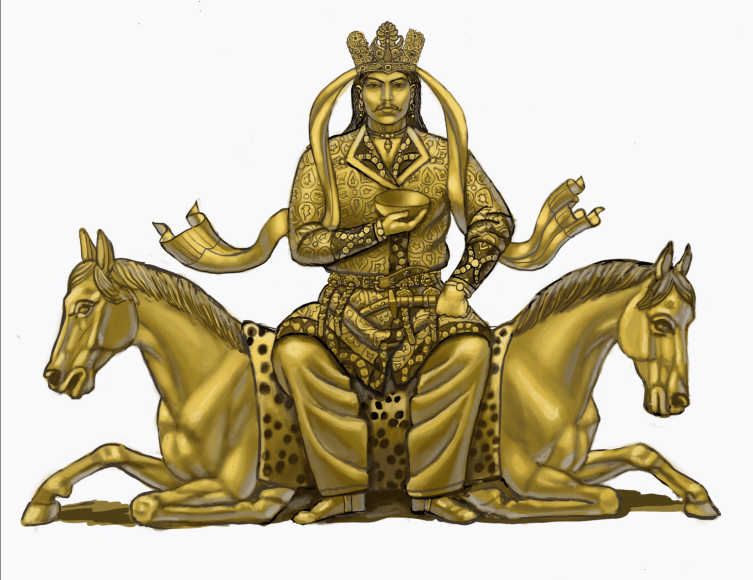
On this buckle, there is a depiction of the Göktürk kagan sitting on his throne, holding a crown on his head and an oath goblet in his hand. Prof. Dr. Samashev emphasized that the discovered ornamentation is a literary heritage attributed to Turkic peoples, highlighting the significance of the depiction in this regard.
The two decorated gold plates, identified as belt buckles, depict a Khagan seated on his throne with attendants serving him. Wearing a golden belt was a sign of dominance in the ancient Turkish states.
Dr. Serhan Çınar says that in the identified images, the Göktürk kagan has long hair and is about 30-35 years old:
“In the composition of the ornament, it is seen that the Khagan is depicted in the traditional Turkish type of sitting cross-legged and has a crown resembling a three-cornered halo on his head. The images in the buckle ornament also clearly show the throne on which the Khagan is seated and the bridesmaids serving him. The flowers surrounding the throne are thought to be lotus flowers, which are often used in Buddhist art.”
Prof. Dr. Zaimollo Samashev states that the belt buckle dates back to the end of the 8th century. Since there is information about who the Khagans were at the end of the 8th century, the owner of the belt likely was one of these Khagans. A second possibility is that the complex where the golden belt buckle was found belonged to a Tudun who was affiliated with the Khagan of Ötüken or Suyab, the center of the Western Göktürk Khaganate and that he gave it as a gift to the ruler’s son as a sign of dominance.
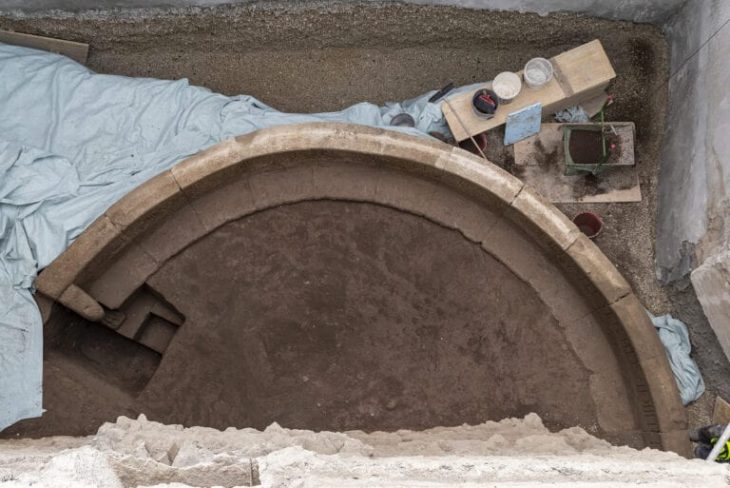
As a result of the archaeological studies and excavations conducted, it has been possible to obtain important information regarding features of the architectural plan of the memorial cult complex of Turkic Khaganate. The memorial cult complex consists of temple, ceremonial pathway and additional structures located in the eastern part. Furthermore, the statue with the all characteristics of a Turkic Khagan made of granite from the same complex is also of great importance.
The granite statue depicting a Gokturk Khagan or Yabgu sitting cross-legged has been placed under protection at the National Museum in Astana.
The two main sections of the tomb complex were surrounded by two separate courtyard walls, but they appear to share a common wall at the junction of the two sections. The grave complex measures approximately 90 x 50.90 meters, according to the boundaries determined by the courtyard walls built from a mixture of clay soil and gravel.