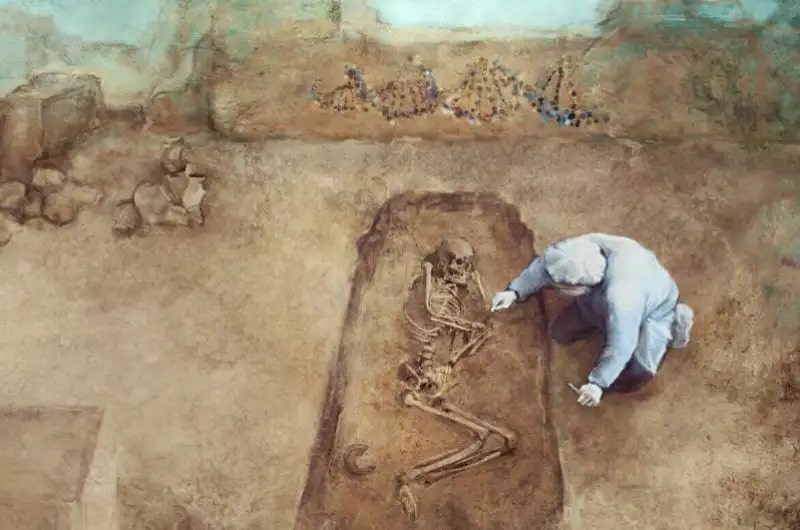
A combined study of genetics and skeletal remains shows that the switch from primarily hunting, gathering and foraging to farming about 12,000 years ago in Europe may have had negative health effects as indicated by shorter than expected heights in the earliest farmers, according to an international team of researchers.
“Recent studies tried to characterize the contribution of DNA to height,” said Stephanie Marciniak, assistant research professor, Penn State. “We started thinking about the longstanding questions around the shift from hunting, gathering and foraging to sedentary farming and decided to look at the health effect with height as a proxy.”
Working with George H. Perry, associate professor of anthropology and biology, Penn State, and more than 40 international researchers, Marciniak looked at the heights of individuals who lived before the Neolithic, and in the Neolithic, Copper, Bronze and Iron ages. The researchers measured the long bones of skeletal remains that were also being sampled or had already been sampled for ancient DNA testing by other researchers.
The researchers created a model that used adult height, indicators of stress seen in the bones and ancient DNA. They also looked at genetic indications of ancestry. The researchers reported their results in a recent issue of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
“Our approach is unique in that we used height measurements and ancient DNA taken from the same individuals,” said Marciniak.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The switch from a hunting, gathering and foraging lifestyle to a settled agricultural lifestyle did not occur across Europe simultaneously, but in different places at different times.
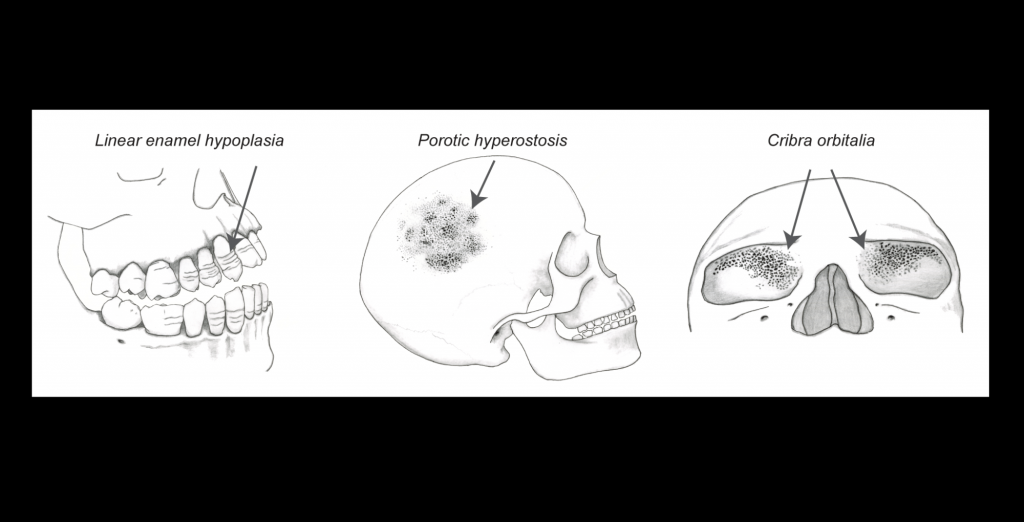
The researchers studied 167 individuals who lived from 38,000 to 2,400 years ago. This included preagricultural individuals, the earliest farmers, and subsequent farmers. They found that individuals from the Neolithic, taking into account their genetically indicated potential heights, were an average of 1.5 inches shorter than previous individuals and 0.87 inches shorter than subsequent individuals. They also found that heights steadily increased through the Copper — 0.77 inches, the Bronze — 1.06 inches, and the Iron — 1.29 inches with respect to Neolithic heights.
“Right now, what we know is that 80% of height is from genetic makeup and 20% is from the environment,” said Marciniak. “Researchers haven’t yet identified all the genetic variants associated with for height.”
The switch from hunting, gathering and foraging to agriculture did not always result in a height loss, although it did in some parts of Europe, according to Marciniak.
Marciniak and her team also looked at genetic ancestry in their study.
“There was movement of people, generally from east to west, ” she said. “We wanted to account for that migration that perhaps brought different proportions of height-associated genetic variants.”
When the team incorporated ancestral information, they found that for the Neolithic, the height decrease is reduced a bit so that it is not as extreme.
“This research requires more study with larger datasets,” said Marciniak. “Our work represents a snapshot of something that is very dynamic and very nuanced. We need to do more to see what is the cause of the decrease in achieved height versus predicted genetic height during the shift to farming.”
The researchers said they believe that their approach is adaptable to studies of past human health and could be applied in other contexts.
The Wenner-Gren Foundation, National Institutes of Health, Czech Science Foundation, Croatian Science Fund, Ministry of Culture of the Czech Republic, a Marie Sklodowska-Curie grant, and the Hungarian Research, Development and Innovation Office supported this work.
Cover Photo: Drawing of a scientist working with human skeletal remains and ancient DNA. Credit: Marija Stojkovic
















