A recent shipwreck was found off the coast of Japan this year and identified as part of a Mongol fleet that sailed to Japan in the latter part of the 13th Century.
The recent discovery has offered a fresh reminder that Japan is awash with underwater archaeological sites in the ocean and its lakes and rivers.
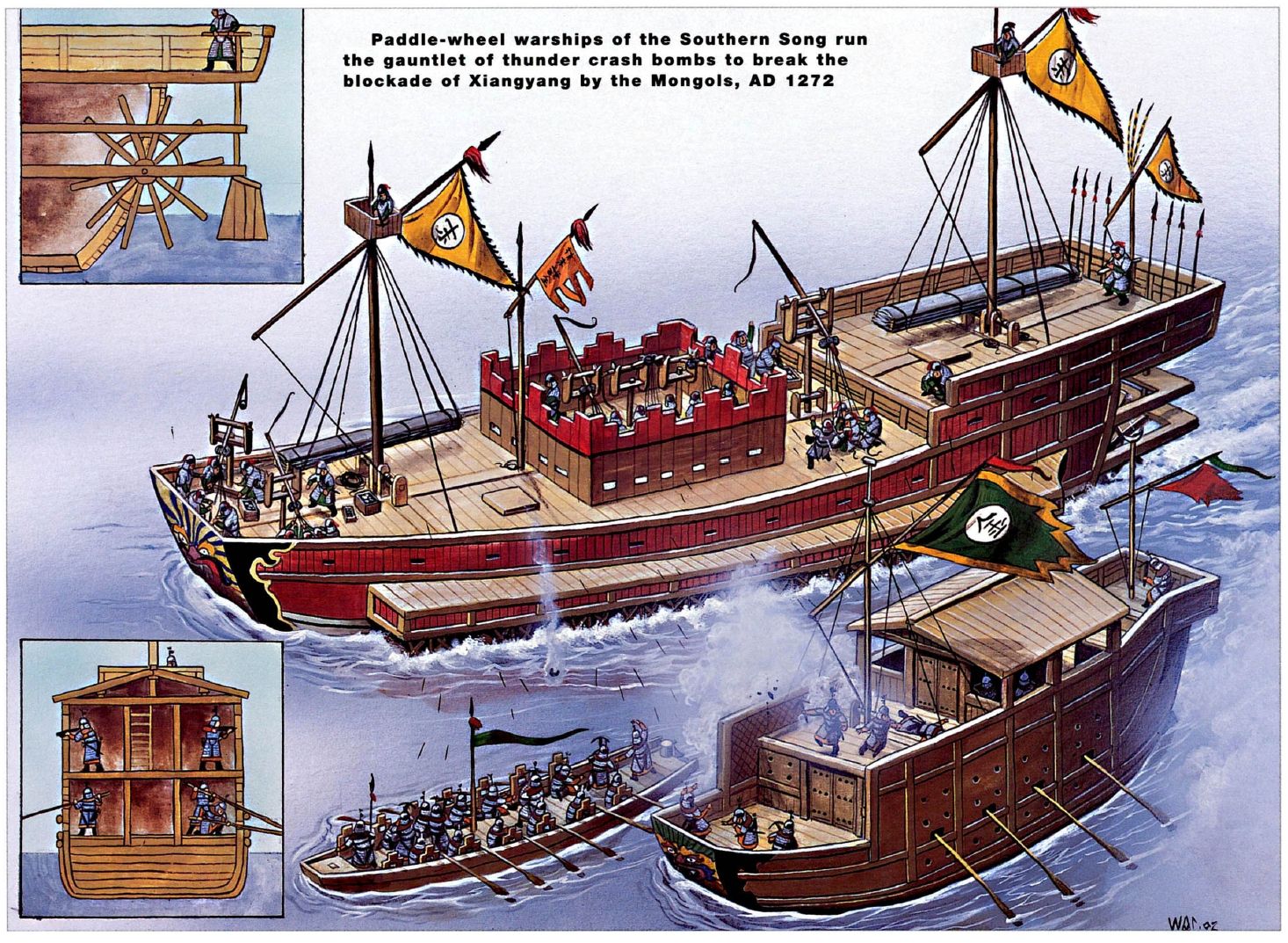
In 1274 and 1281, Kublai Khan, the then-Mongol leader, dispatched two military expeditions to Japan. In Japan, these are known as the “Mongol Invasions.” The Mongol army sailed to Japan in 1281 with up to 4,000 ships and 140,000 soldiers, making it the largest sea invasion force assembled until Operation Overlord 670 years later.
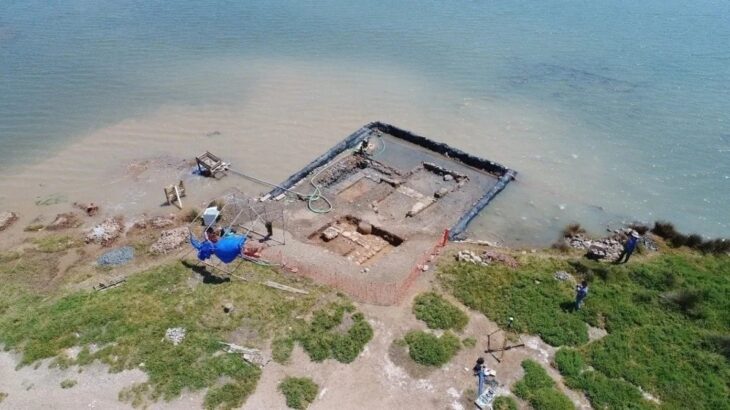
After the weather turned against them, it is said that a portion of Kublai Khan’s second armada sought refuge in Imari Bay, hoping to ride out the storm there. Instead of being saved, the ships met with disaster. Today, the area in Imari Bay where artifacts from these ships are being uncovered has been designated as an underwater cultural historical site. Known as the Takashima Kozaki, due to its proximity to Takashima (Taka Island), it was the first underwater area in Japan to receive this designation.
While surveys had been conducted on and off since the 1980s, a team of researchers led by Yoshifumi Ikeda, an archeology professor at Kokugakuin University, found one of the vessels in 2011 when he was working at the University of the Ryukyus.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
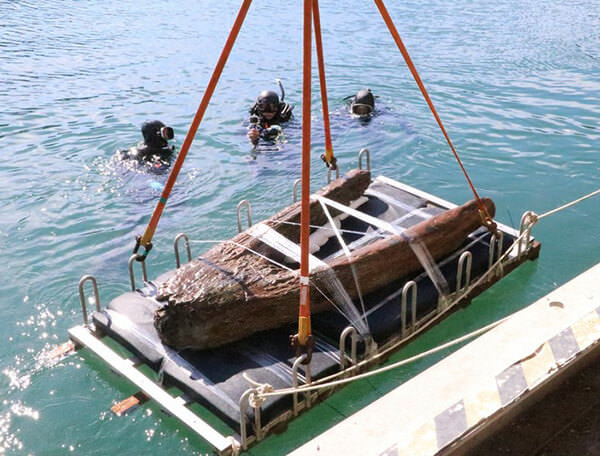

They also caused a stir in the fall of last year when they salvaged a wooden anchor.
Because underwater visibility in the area surrounding Takashima island is “like diving into miso soup,” the team also went through trial and error carrying out acoustic surveys, Ikeda said.
“We take a close look at the seabed topography and stratum and narrow down our search to find ruins,” Ikeda added. “I think we have almost established a way to find ships around Takashima.”
“There are many ruins in Japanese waters that remain undiscovered,” said Jun Kimura, an associate professor at Tokai University, who is well-versed in the history of underwater archaeology and the current landscape around the world.
As there are numerous promising sonar readings that hint of other buried ships from the Mongol armada in the area, the researchers are excited about the opportunities these locations provide for further research and discovery in the years to come.
The researchers also expressed a desire to raise one of the ships at a later time. Despite the technical and financial challenges to making that happen, the Mongol fleet may actually land in Japan after 800 years.
Cover Photo: News.mn