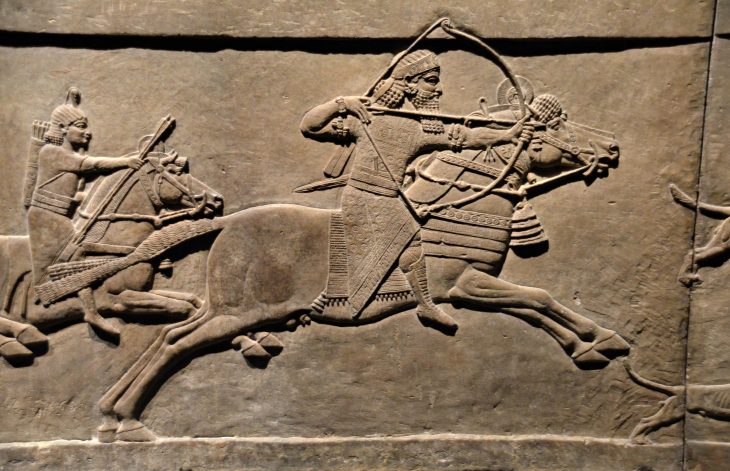
An archaeological excavation in Creuzier-le-Neuf, a small town located six miles north of Vichy, has unveiled a remarkable Celtic necropolis, revealing a trove of exceptional metal artifacts, including two swords still encased in their original scabbards. These findings, which date back to the middle La Tène period (4th – 2nd century B.C.), provide invaluable insights into the funerary practices and social hierarchies of the Iron Age, particularly among the elite of the time.
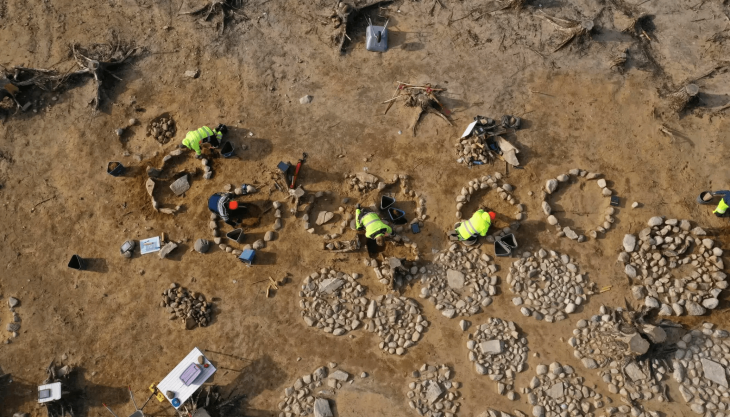
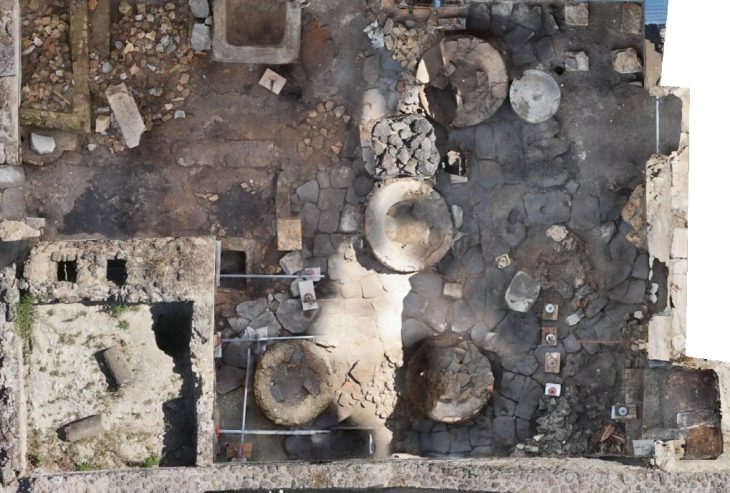
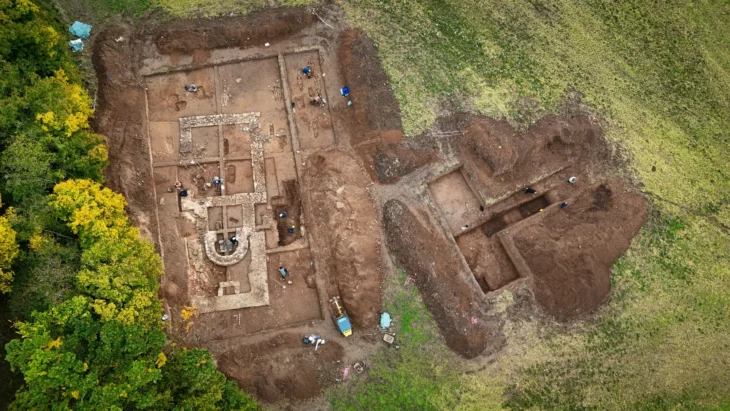
The necropolis was discovered during a preventative archaeology excavation in 2022, but the announcement of the findings comes after years of meticulous conservation work. The site, which covers approximately 650 square meters, is configured as a quadrangular enclosure surrounded by a wide ditch. Within this perimeter, archaeologists have recorded more than 100 graves, primarily oriented in a north-south direction. This layout suggests a significant level of organization and ritualistic planning, indicative of the social structures that existed among the Arverni, Aedui, and Bituriges peoples.
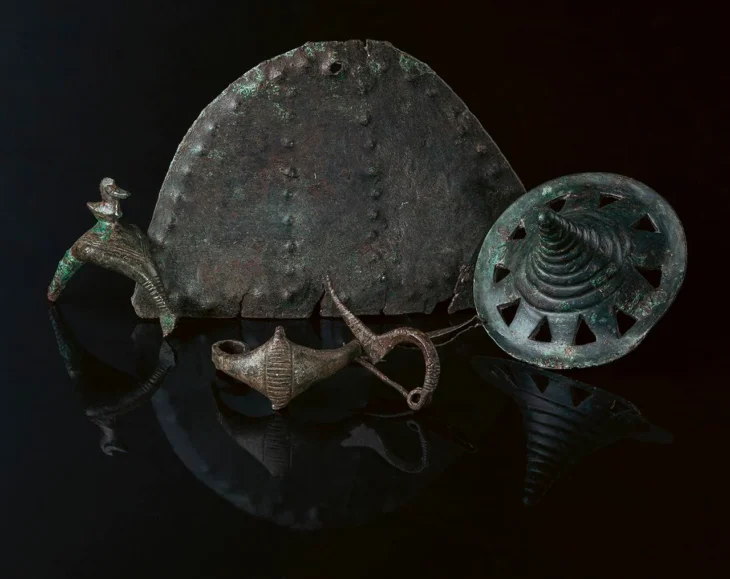
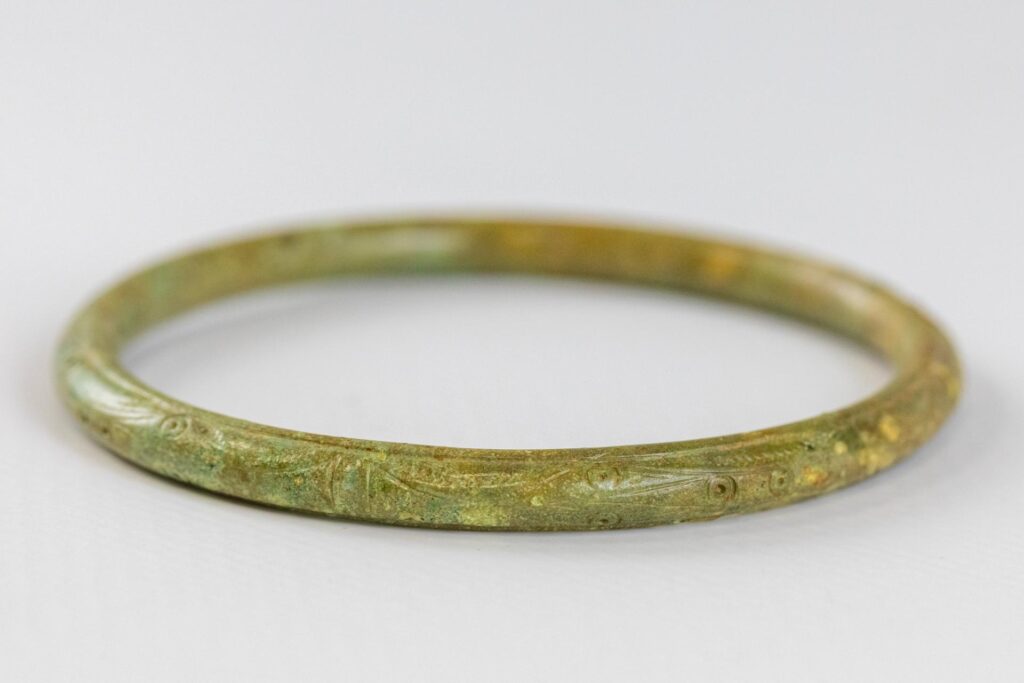
One of the most striking aspects of the excavation is the preservation of metal artifacts, despite the highly acidic soil conditions that have prevented the survival of human remains. Nearly half of the graves contained metal jewelry, predominantly bronze bracelets, which were found both as singles and in pairs. The designs of these bracelets vary widely, ranging from simple coiled rods to intricately crafted pieces adorned with curvilinear and circular motifs. Many of the bracelets feature concealed clasps, showcasing a high level of craftsmanship and technical sophistication.

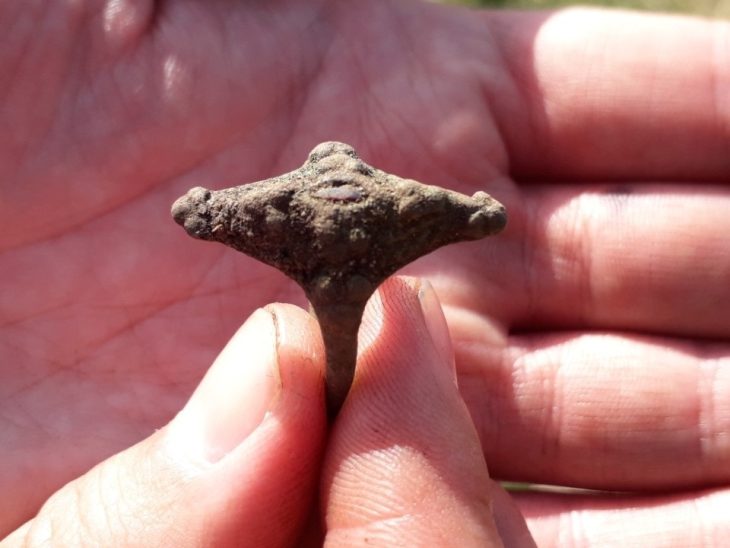
In addition to the bracelets, the excavation revealed 18 fibulae—brooches used to fasten garments—mostly made of iron or copper alloys. Although these fibulae were heavily corroded upon recovery, specialists at the Municipal Center for Restoration and Archaeological Studies (CREAM) in Vienne successfully restored them, revealing their decorative potential. One particularly notable fibula features a design similar to that of the bracelets, suggesting a stylistic coherence among the artifacts.
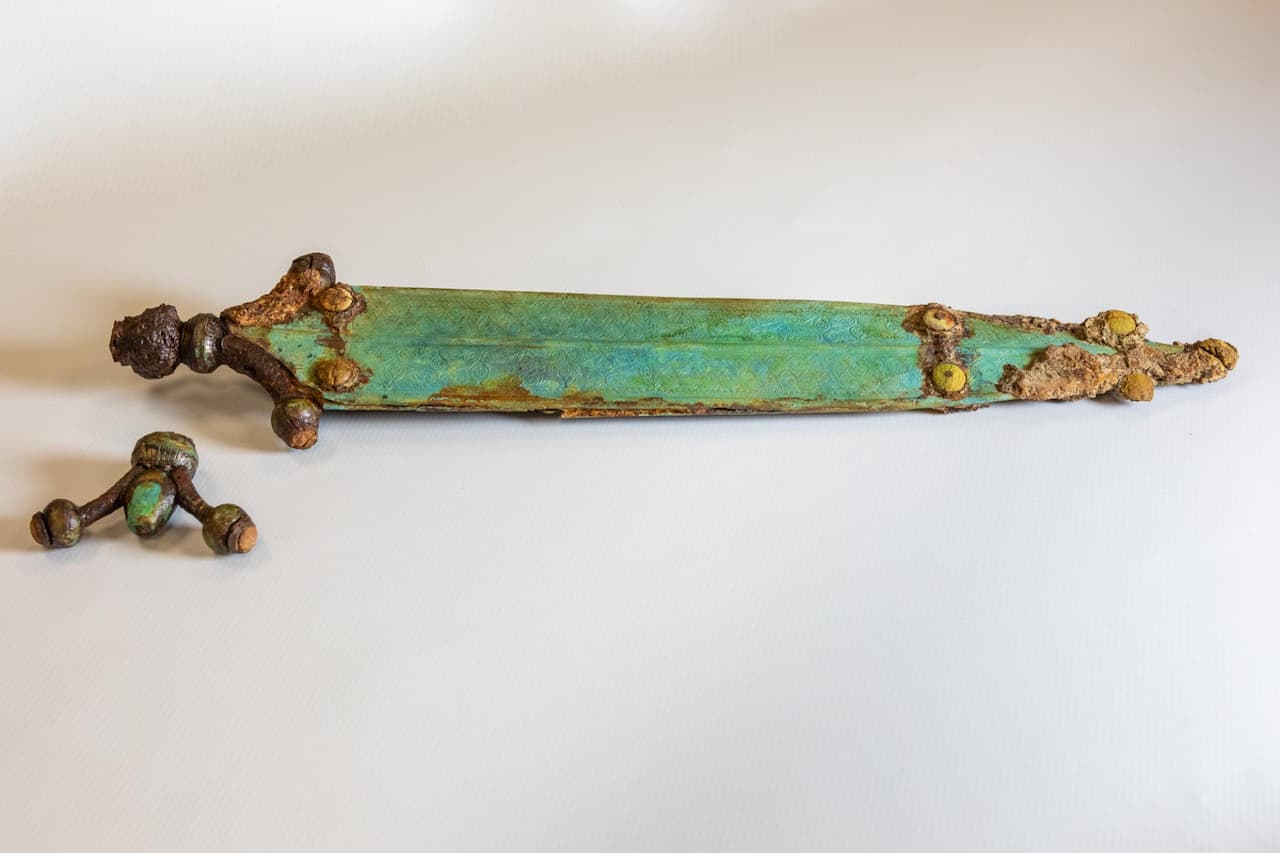
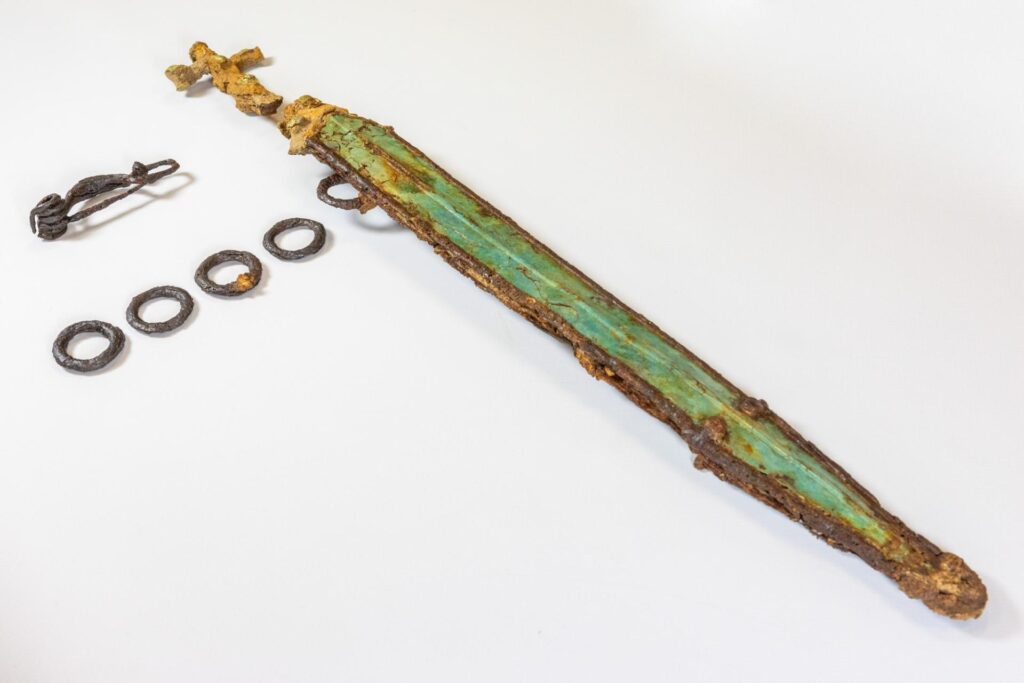
However, the most remarkable discoveries are the two swords found in separate graves. The first sword, unearthed from grave 782, is an exceptional weapon that stands out due to its ornate scabbard, which allowed it to be worn at the waist. The scabbard is richly decorated with scrollwork and cabochons, some of which feature swastika motifs and possibly fragments of glass paste. X-ray analysis of the sword revealed intricate inlays on the blade, including a circle and a crescent moon separated by a line, indicating that it was crafted in the early 4th century B.C.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

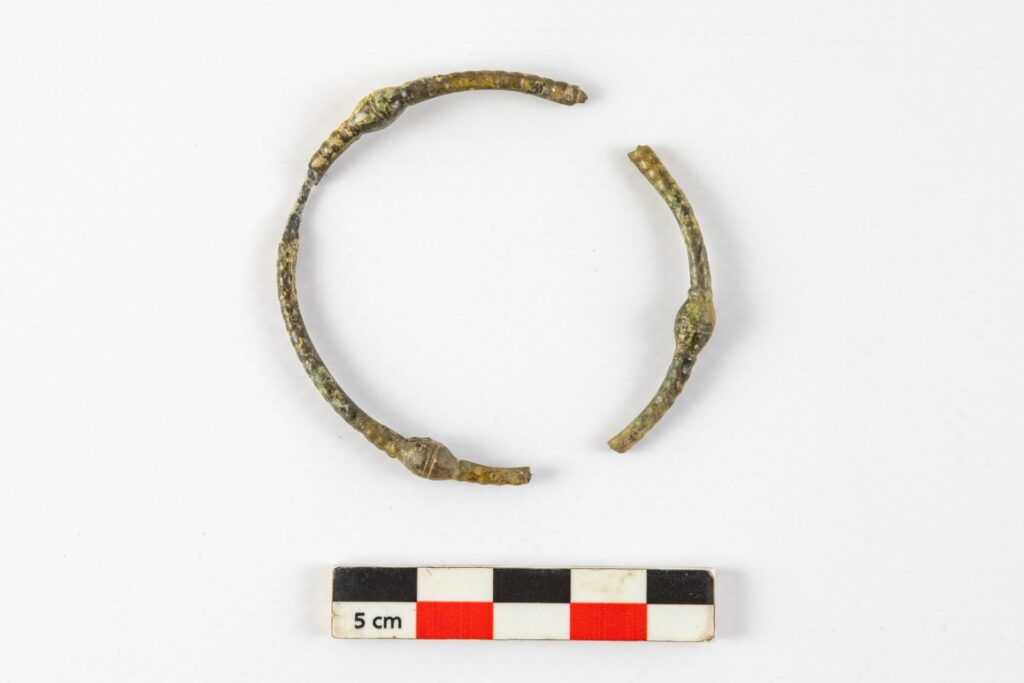
The second sword, discovered in grave 990, is accompanied by suspension rings that also allowed it to be worn at the waist. While it is less ornate than the first, it features a pair of discreet eyespots at the top of the scabbard and retains shreds of fabric caught in the oxidation, which may belong to the deceased’s clothing or a protective cover. The typology and dimensions of this sword suggest it was also made during the 4th century B.C.
The excavation was conducted under the scientific direction of Benjamin Oury and the supervision of Vincent Georges, both members of the National Institute for Preventive Archaeological Research (Inrap). Their work, part of a development project led by Vichy Communauté and overseen by the Regional Archaeology Service, highlights the significance of the Creuzier-le-Neuf site in understanding the social dynamics and ritual practices of pre-Roman Gaul.
The findings from this necropolis not only contribute to the knowledge of Celtic craftsmanship but also underscore the complexity of funerary traditions during this pivotal period in European history. As conservation efforts continue, the archaeological team hopes to further unravel the mysteries of the past, providing a deeper understanding of the lives, beliefs, and customs of those who once inhabited this region.

The exceptional quality of the artifacts discovered at Creuzier-le-Neuf promises to enrich our understanding of Iron Age societies and their cultural legacies.
National Institute for Preventive Archaeological Research (Inrap)
Cover Image Credit: Fully decorated short sword with antennae handles discovered in burial 782. Flore Giraud, Inrap