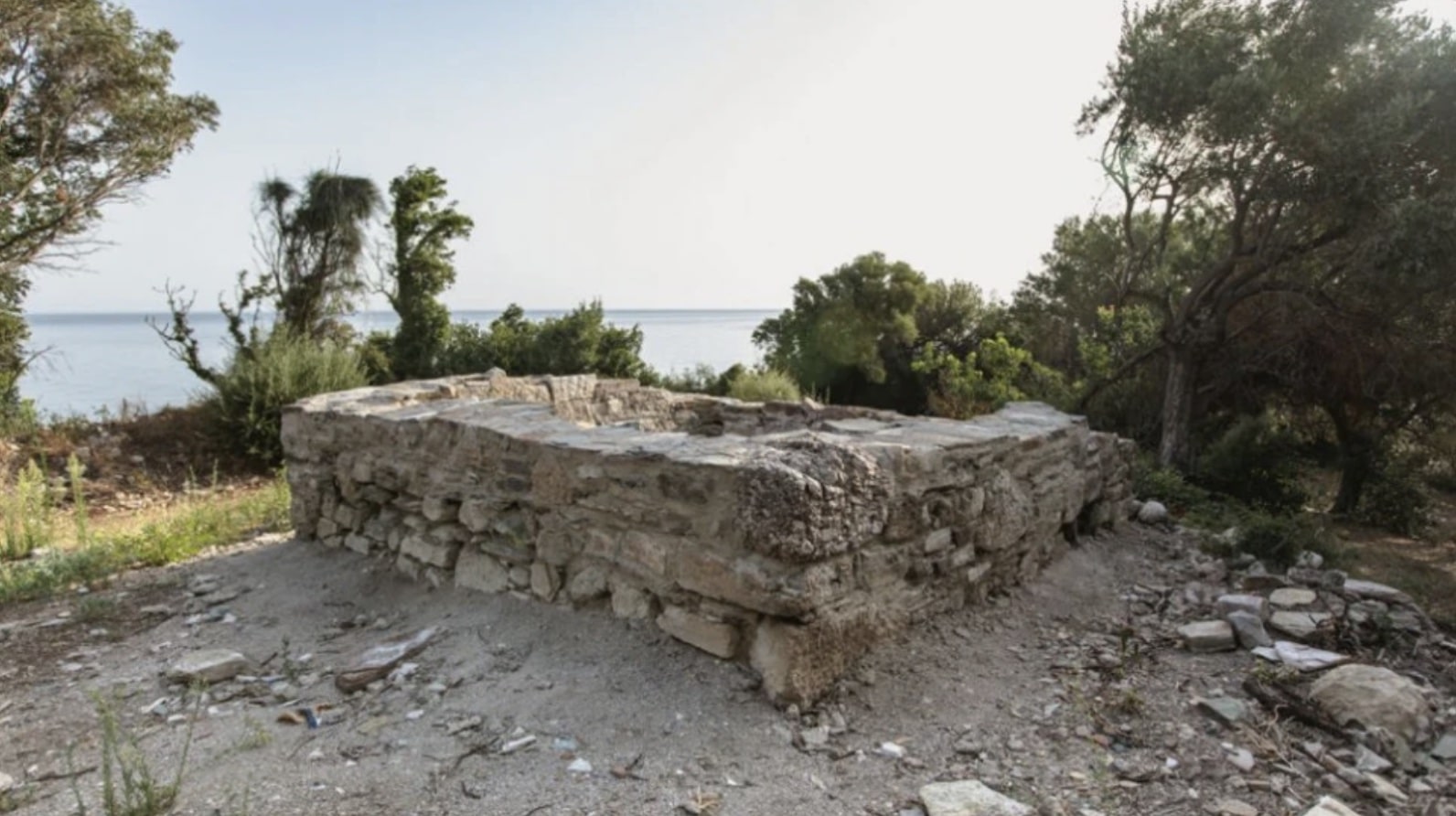
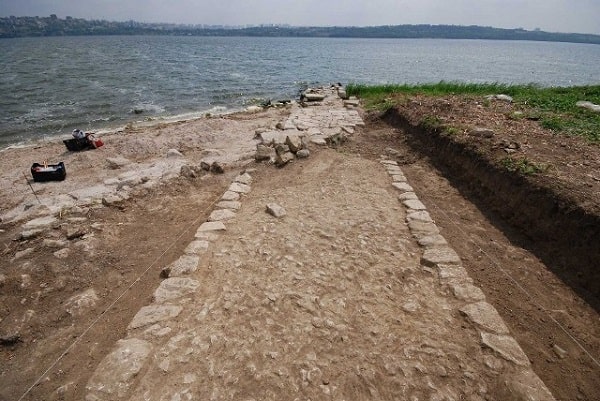
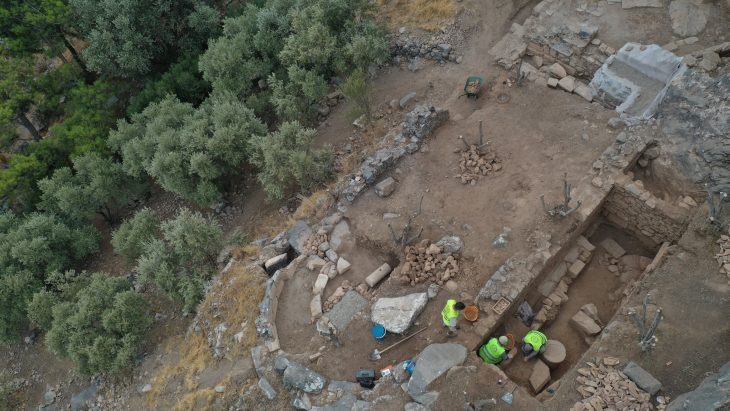
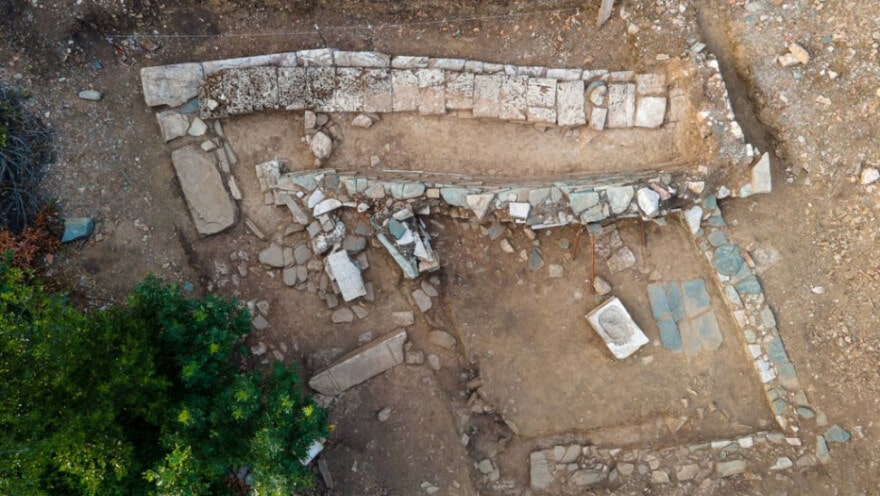
The Hellenic Ministry of Culture and Sport reported on Friday the discovery of ancient Greek and Hellenistic era structures at the archaeological site of Skiathas near Larissa, central Greece.
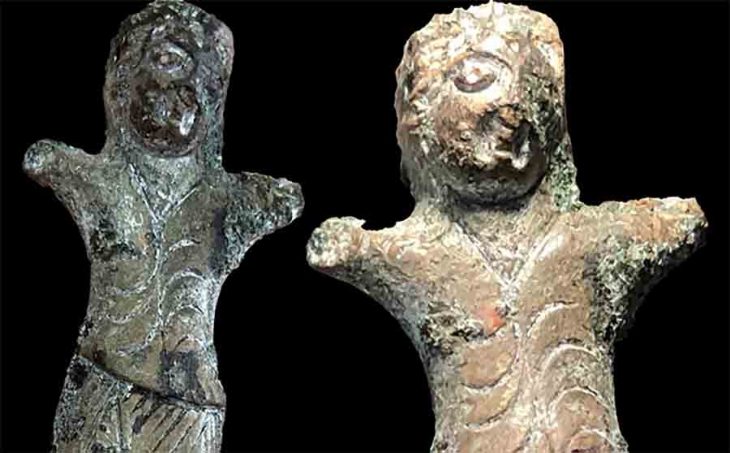
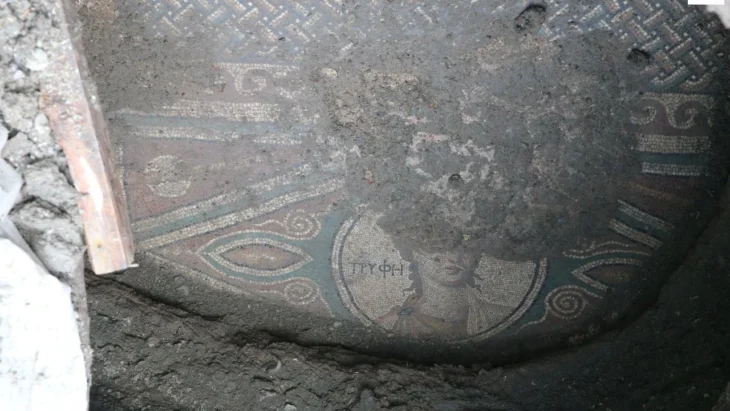
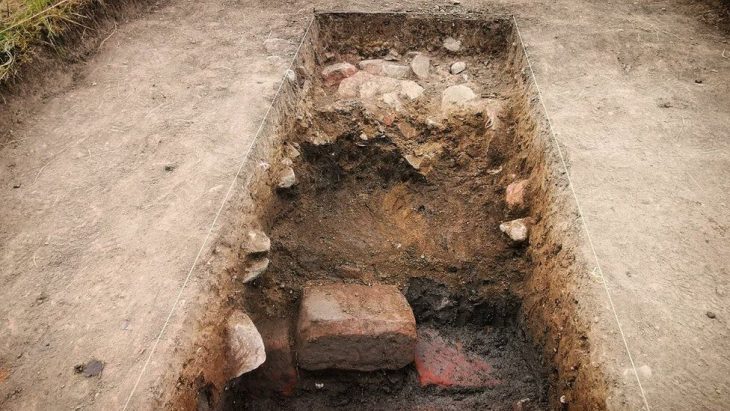
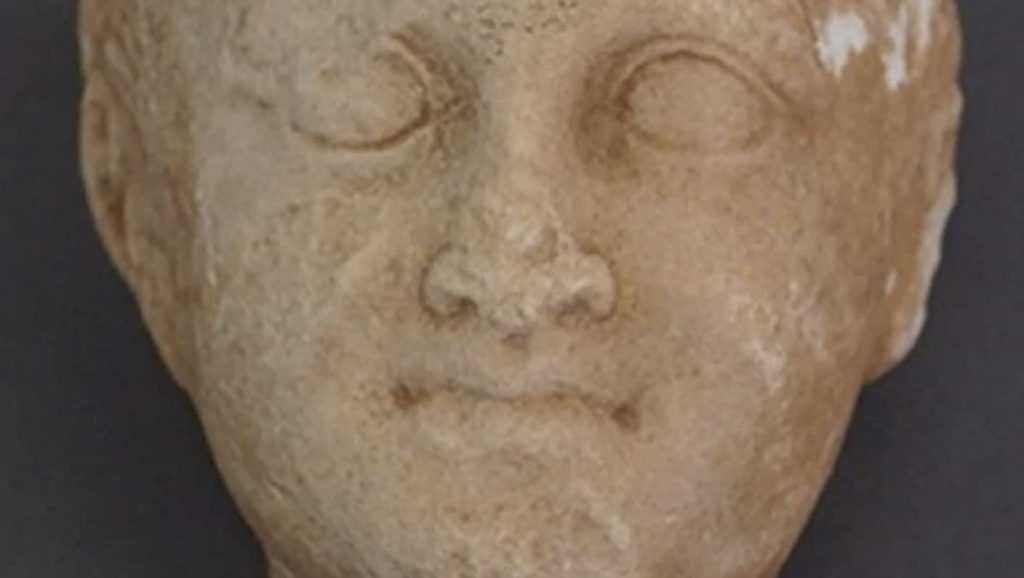
According to the announcement, excavation data so far show that it was a Hellenistic period (3rd-2nd century BC) sanctuary made of alabaster and local stone. Architectural elements were found, such as part of the entablature and five Doric capitals. In addition, a statue base, a column section, a marble bank foot, and two marble child heads, a girl and a boy, were found inside.
The excavation site is located near the port of Agiokampos in the coastal region of Kato Polydendri in the Municipality of Agia in the Prefecture of Larissa.
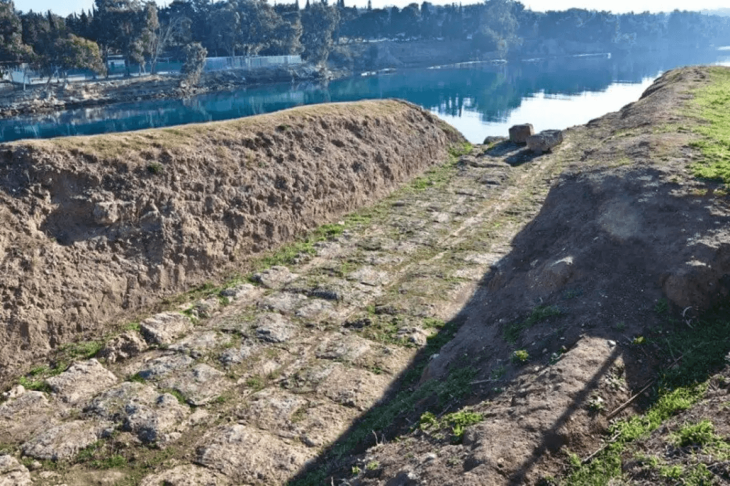
Excavations to find ancient Greek remains have been carried out at the archaeological site’s thickly wooded and very inaccessible acropolis. Parts of the Hellenistic-era edifice, however, were beginning to appear due to severe weather and potential human interference over the years.

The research is being conducted under the supervision of archaeologist Nektaria Alexiou.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
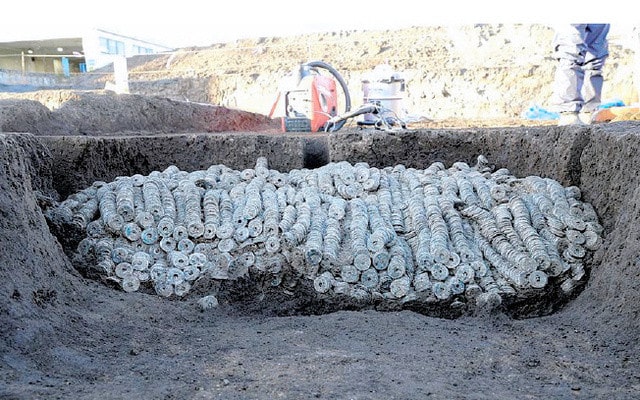
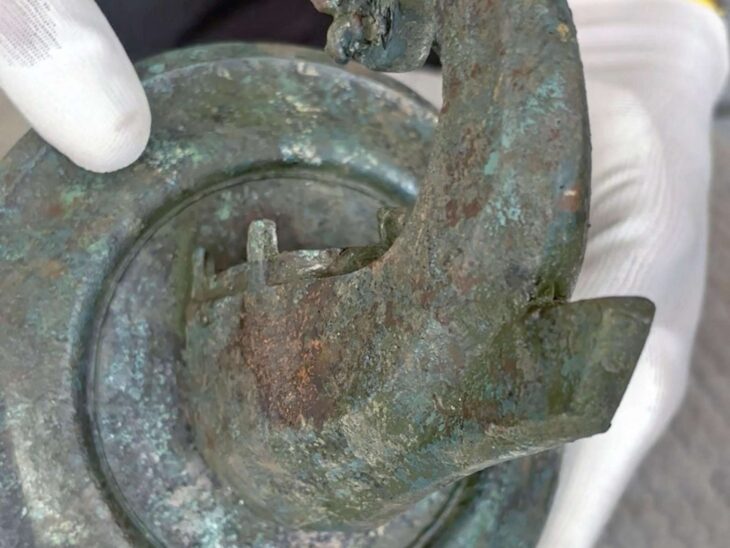
The Larissa digs also turned up transportable Hellenistic-era Greek discoveries such as iron nails, an iron arrowhead, bronze rings, copper bottle pieces, various lead objects, and copper Thessalian and Macedonian coins.

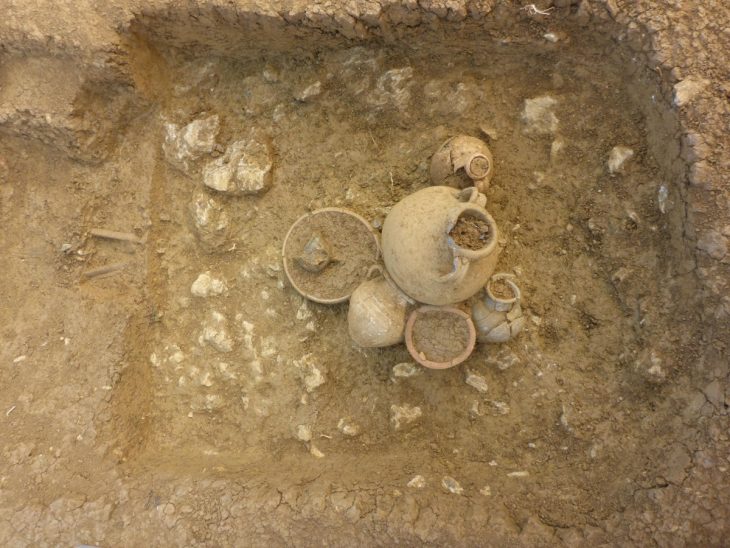
Many clay artifacts, including clay cloth weights, clay lamps, paintings, drinking containers, and remnants of commercial amphorae, were discovered alongside the metal artifacts. Seal tiles containing the names of ceramic workshop owners, as well as a tile with the word “MELIVOIAS,” were discovered among the clay fragments. This has led academics to conclude that the ancient Greek hamlet of Skiathas and the major ancient metropolis of Magnesia Melivoia are linked.
This is the first structure from the walled ancient Greek city to be discovered outside of the city walls. This new structure, as well as a recently found square tower dating mostly from the Byzantine period, are currently being researched.
By continuing their investigations of this coastal area, researchers hope to uncover answers to many key archaeological problems from the Ancient Greek and Hellenistic eras.
Cover Photo: Hellenistic-era structures were found this week in Larissa, Central Greece. Photo: Hellenic Ministry of Culture and Sports