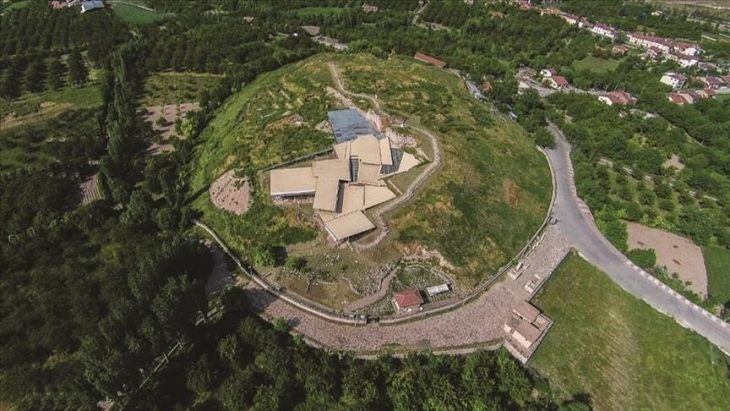
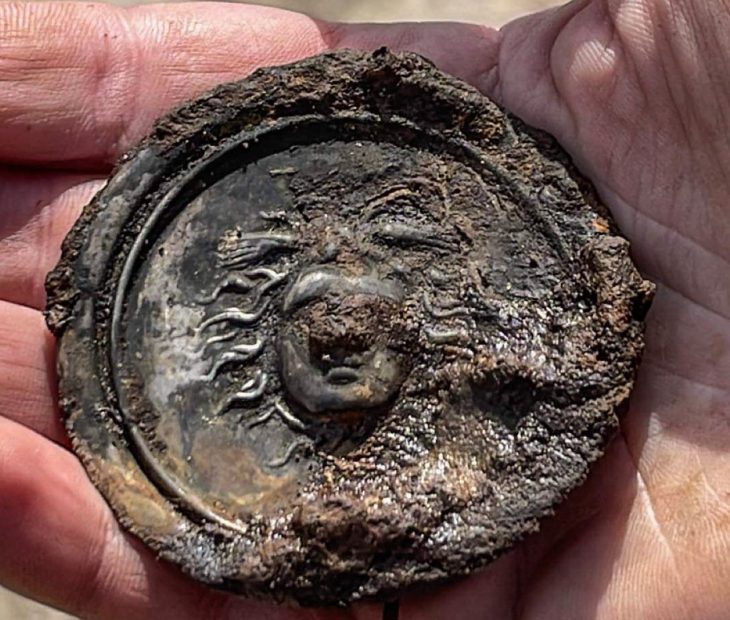
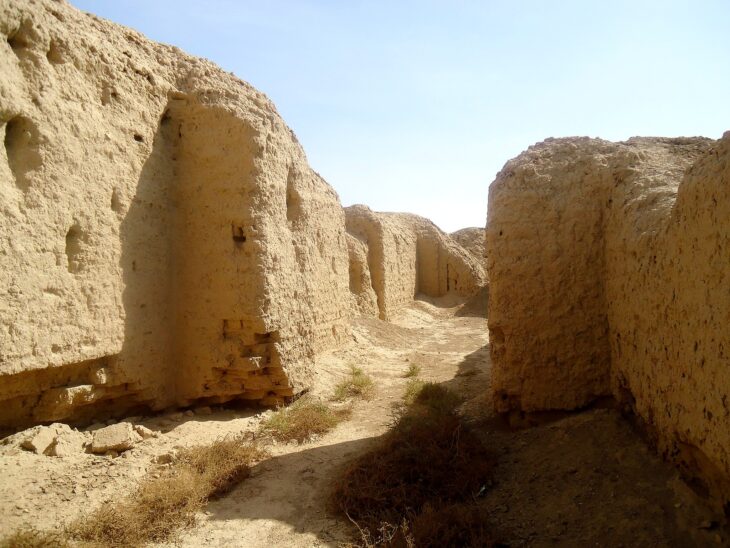
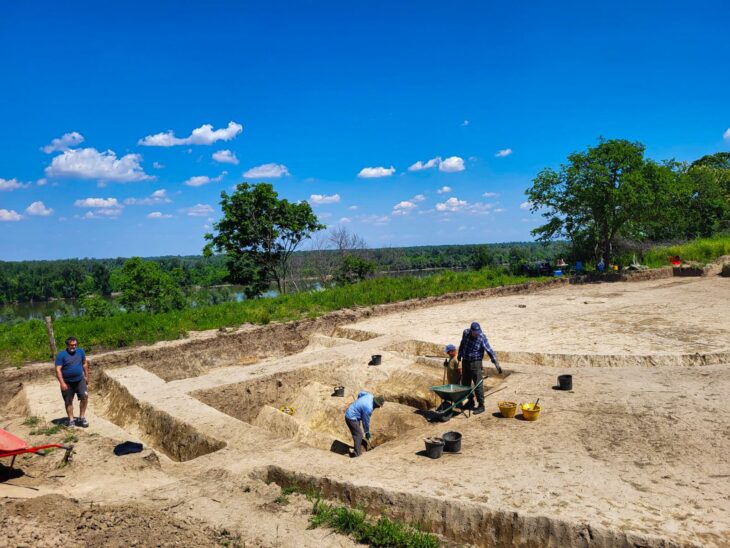
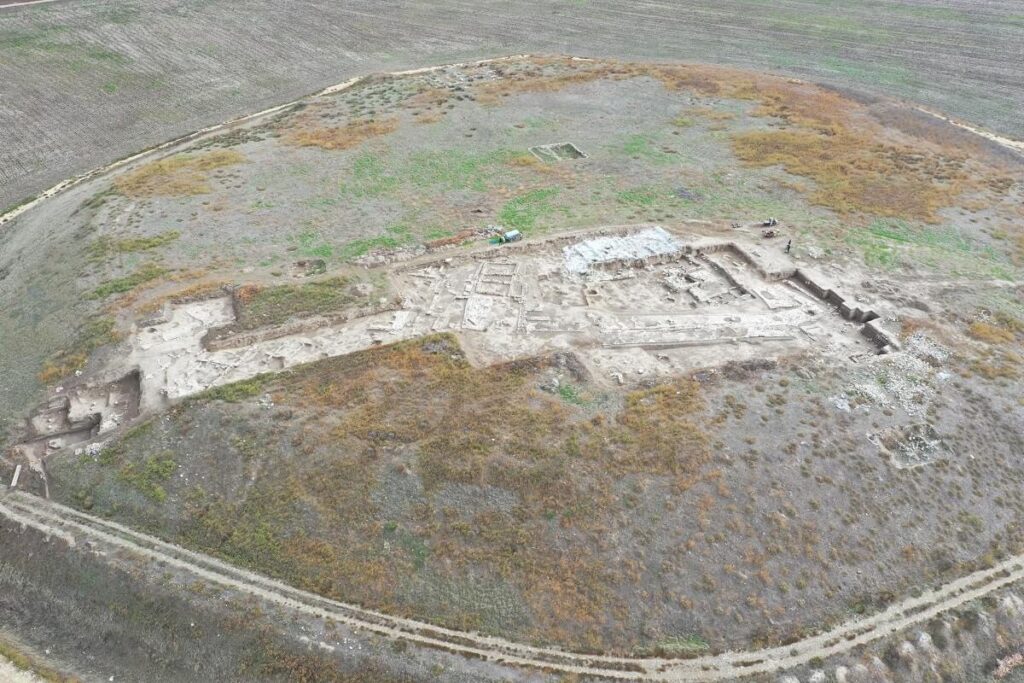
Oluz Höyük, located 25 kilometres west of Amasya, is an ancient city which has rich findings of religious structuring.
During the excavations that have been going on for 15 years, 10 settlement layers were encountered, each of them had a religious structure.
Prof. Dr. Dönmez In the article he wrote in Arkeotarih magazine, “In this belief system, whose basic practice is the Cult of Fire, there are fire houses (Ateşgede), places of worship, areas where sacred ashes are stored, bothros and sacrificial pits where sacred objects are buried; It shows the existence of “Archaic Monotheism” in which we catch the signs of monotheism, which has been observed to be institutionalized since 500 BC in Oluz Höyük.
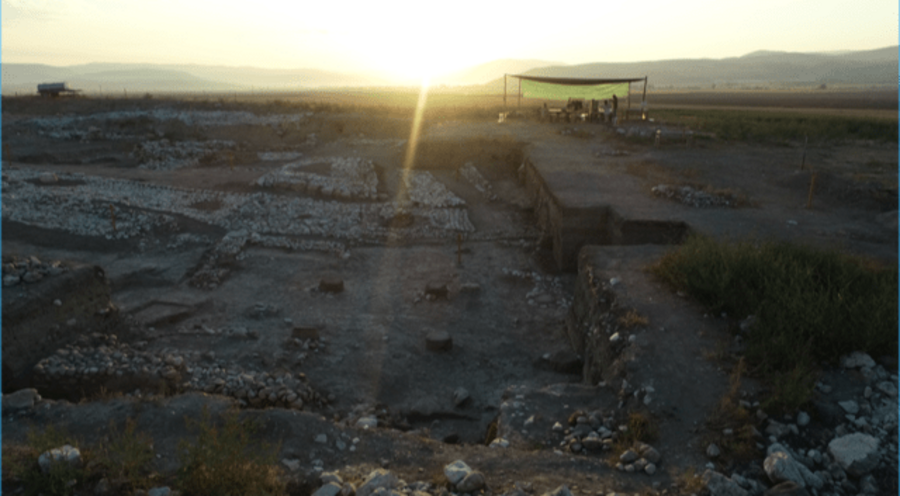
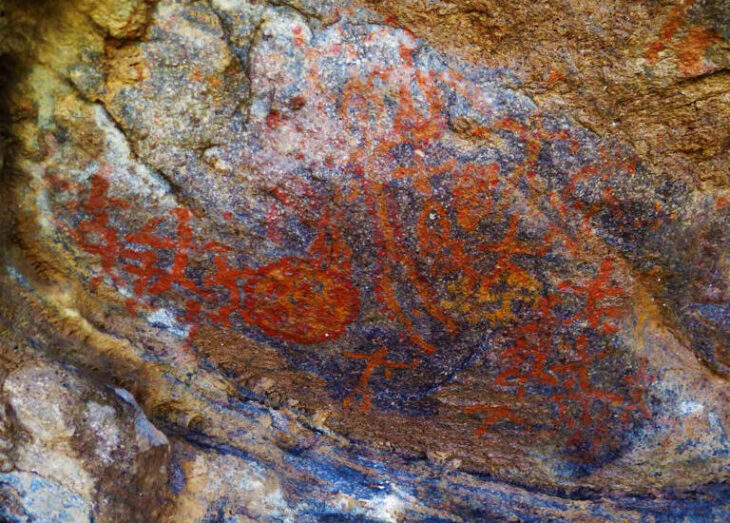
Built in 450 BC, the oldest fire house (Ateşgede) of Anatolia consists of a fire pit with a diameter of 1.60 meters placed on the ground and a small cella surrounding it. The remains of smoke residues in the row of stones forming the sacred fire pit and the ash and carbon in and around the pit prove that the burned fire here is defined as “eternal fire”, he said.

Dönmez stated that the findings of the Oluz Höyük excavations allowed us to understand that the temple and the place of worship were different structures.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Signs that the Havangah Prayer has been performed
Dönmez gave these information about temples and places of worship.
Fire house (Ateşgede) is a small building where the sacred fire is burned, and it is thought that it was not top covered so that the burning fire could be seen outside. Also, it was important that the top was uncovered so that the voice of the Magus (Mog), who prayed for hours every day next to the sacred fire, could be heard.

Oluz Höyük Fire Pit. Photo: Courtesy of Prof. Dr. Şevket Dönmez
Except for the south of the place of worship, it is understood that it was covered with a large roof supported by 6 columns. Although the excavation has not been completed yet, a total of 6 stone column bases, 3 of which are spaced in two rows in the north-south direction, were unearthed for the place of worship, whose current size is over 100 m2.
Stone bases are made of sandstone and have an average of 50 cm.
Members of the Zoroastrian religion pray five times a day, as in Islam. These times are called Havangah from sunrise to midday, Rabitvengah from midday to 3:00 PM, Uzeyrengah from 3:00 PM to sunset, Eyuhseritengah from sunset to midnight, and Ushehingah from midnight to sunrise.
The fact that the sacred fire and the sunrise could be watched from the place of worship at Oluz Höyük most likely indicate that the Havangah prayer was performed and, more importantly, the presence of prayer in the early Zoroastrian religion in the 5th century BC.
Cover Photo: ©Prof. Dr. Şevket Dönmez