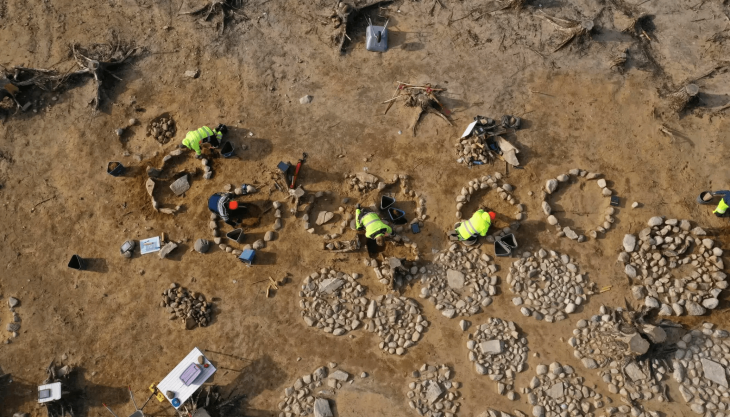
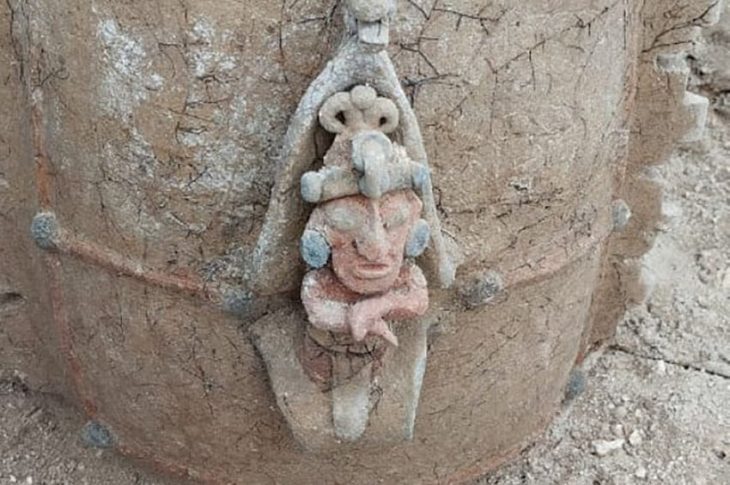
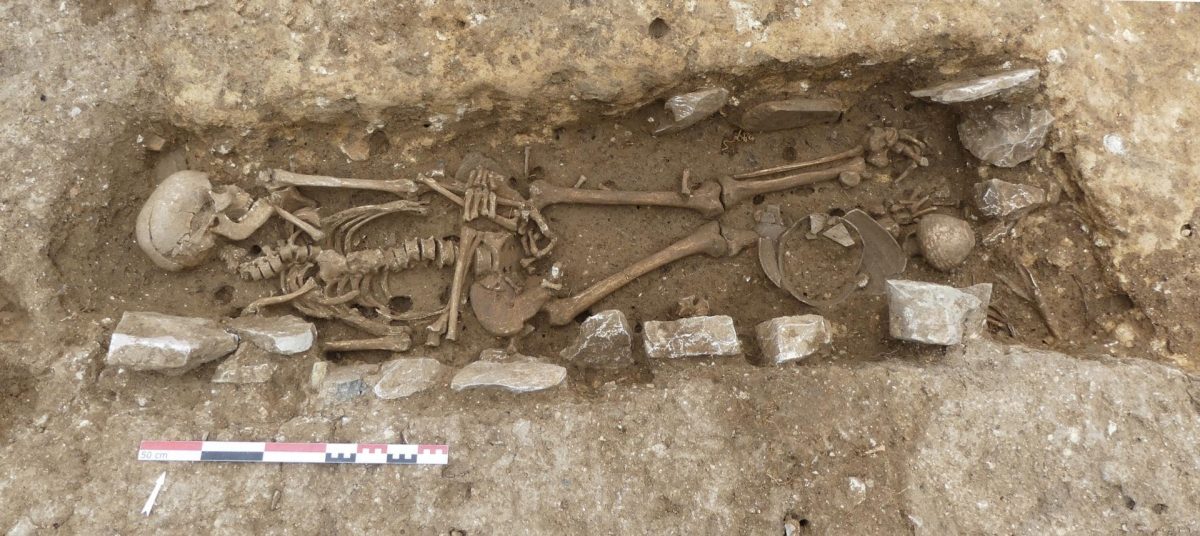
Inrap archaeologists excavating at Nîmes in southern France have uncovered a cemetery dating to the first to second centuries AD with an unusual variety of burial types.
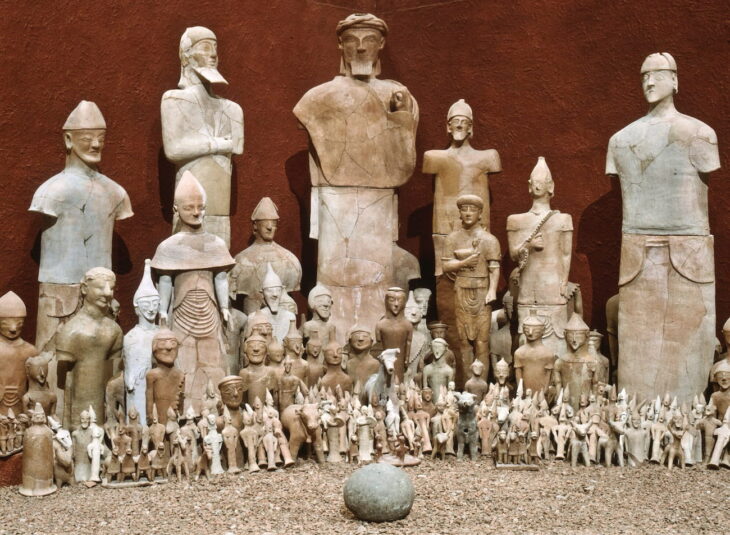
Excavations at 1bis rue de l’Abattoir on the corner of Jean-Jaurès street in Nîmes, so far the interred remains of fifty individuals have been recorded, laid to rest in inhumation burials, cremation urns, and funerary pyres. The graves contain a variety of well-preserved grave goods, primarily pottery.
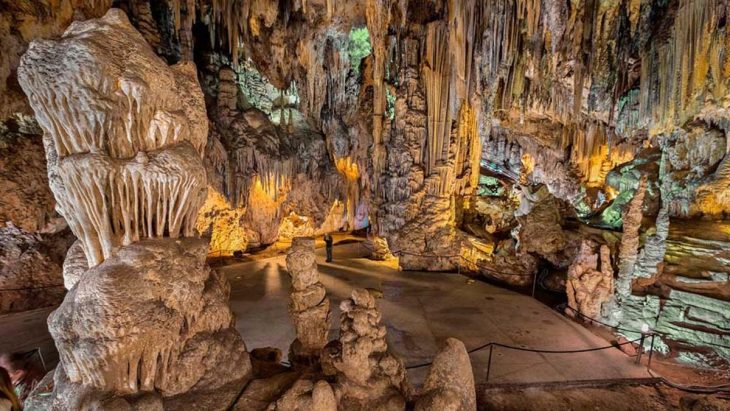
The area under excavation was just outside the southern perimeter of the ancient city when it was absorbed into the modern city of Nîmes in the 18th century. It was only about 165 feet from the Augustan-era city walls, and one of the main gates was only a few hundred feet west along the wall. Because the neighborhood had been archaeologically neglected until now, the excavation has revealed previously unknown details about the history of Roman towns’ peri-urban areas.

The first remains discovered in the dig were agricultural: furrows dug to plant vines. They have not been definitively dated, but they predate the 1st century A.D. funerary use of space. Although the majority of the fifty identified in the tomb were adults, at least two cases of child burials have been identified. The tombs are divided into groups, but only two are clearly defined on the western side. The eastern side, which contains the majority of the burials, is more ambiguously laid out, but one section has the remains of walls enclosing at least seven burials.

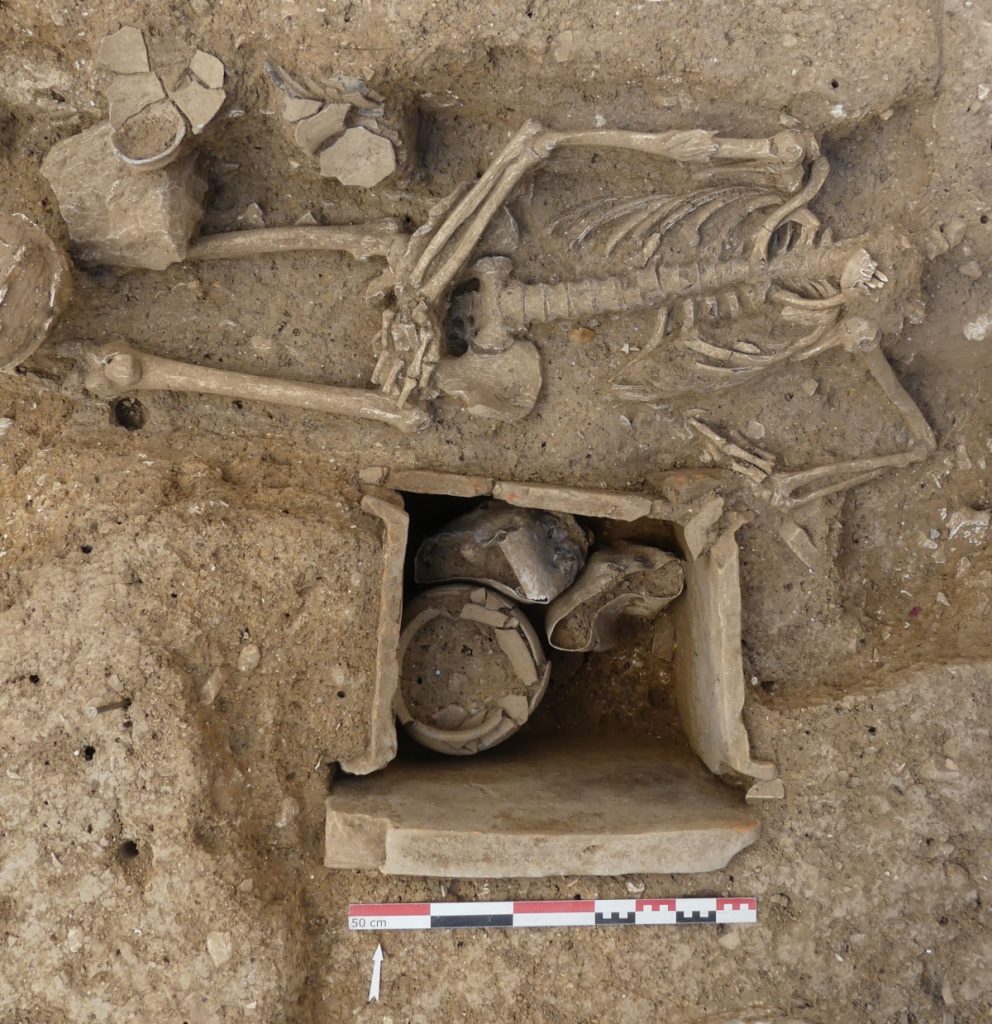
There have been several wooden coffin inhumations. The wood is gone, but the iron nails are still there. The coffins were then placed in cut graves. Outside the coffin, stone blocks were added, and some were used to line the grave walls. One coffin burial was buried in a stone-lined grave and covered with a slab. The deceased was unusually positioned in this grave on his side facing east as if reclining for his final funerary banquet. Another type of inhumation includes a secondary cremation deposit. A coffer lined with ceramic tiles to the deceased’s left (south) contains a cinerary urn and grave goods.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
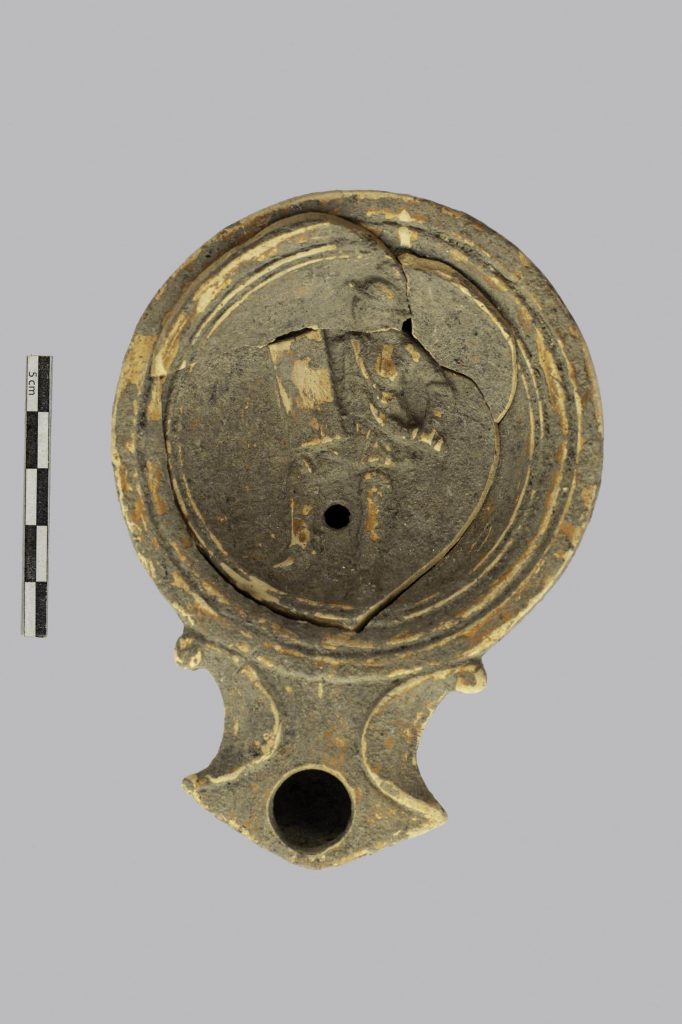

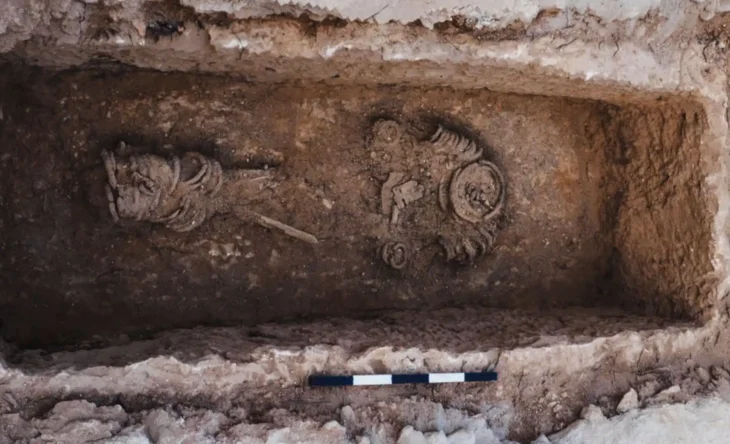
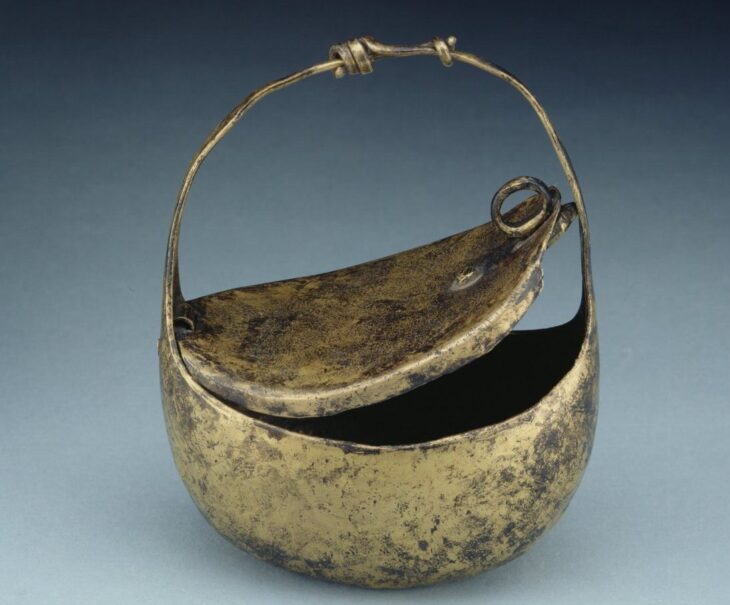
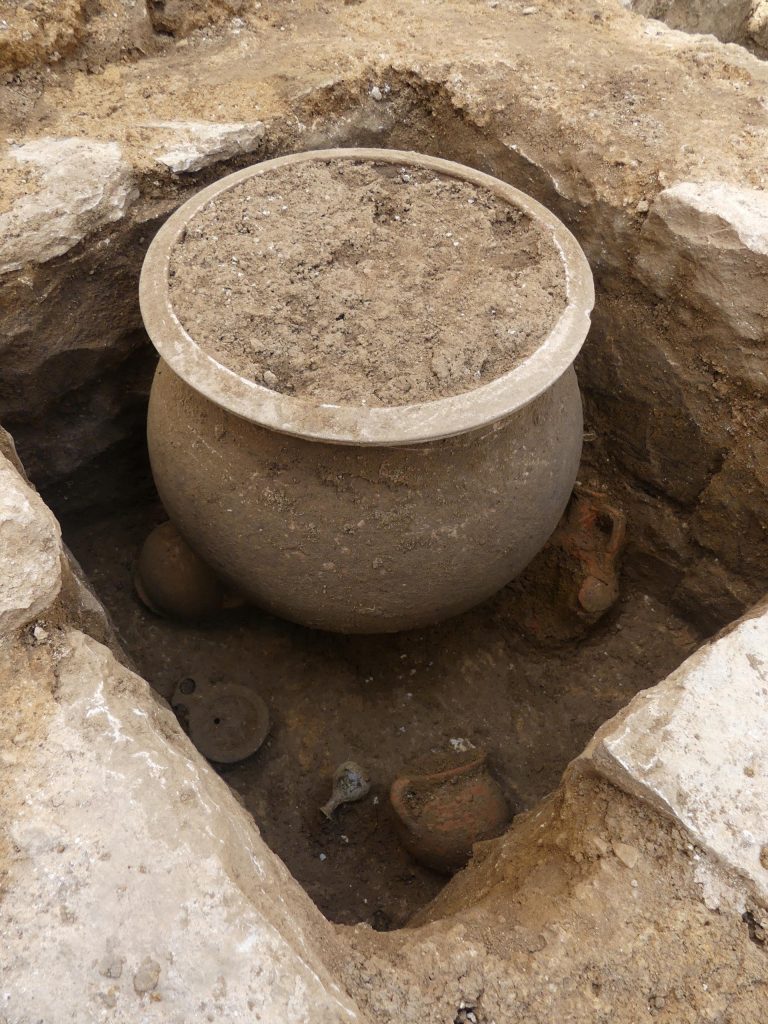
Inside a masonry loculus, a remarkable cinerary vase was discovered that is very large and in excellent condition (a niche made to contain funerary remains). A small ceramic vase was broken and used as the ossuary’s (a container or room in which the bones of dead people are placed) base before the large vessel was put inside the loculus. They were then positioned in front of and on either side of the ossuary, which towers over them, along with two jugs, a ceramic vase, a ceramic oil lamp, and a small glass balsamarium (unguent/perfume jar).
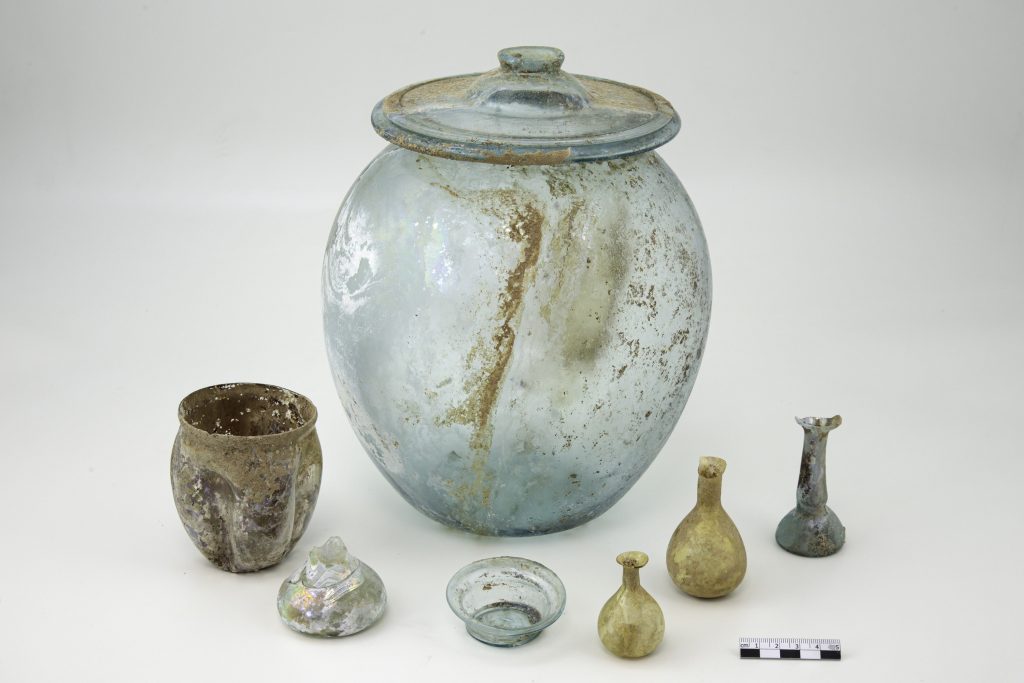

A coffer cut out of a single stone contains a precious glass cinerary vase topped by its glass lid, both intact, in another exceptional cremation burial. A ceramic jug, an oil lamp, a cup, a goblet, another glass balsamarium, three wooden styluses, a fragment of faunal bone, and two bronze mirrors are housed inside the coffer with the urn.
Cover Photo: © Claire Terrat, Inrap